VirtualMV/Flash12 (CS6)
From WikiEducator
| Flash12 (CS6) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Overview | What is Flash? | Resources | History | Quick reference | Upgrading | Design Examples | Journal | Troubleshooting | |
| Basics | Media Basics | Text | Graphics | Animation ( Timeline | Classic tween | Shape tween | Object tween | Motion guide | Movie clip ) | Audio | Video | |
| Text | Scrollbox | Stop Movie | Importing HTML | TLF Features | |
| Graphics | Spraybrush and Art Deco Tool | Fast Loading Photo Album | |
| Audio and Video | Audio ( Adding Sound to a button | Toggle Background Music | Toggle sound using buttons ) | Video ( Advanced Techniques | Alpha Channels | Video Resources ) | |
| Animation | Complex Animation | Mouth Animation | |
| Navigation | Introduction | Joke Book ( Adding Buttons ) | Journal Navigation | |
Overview
By the end of this page you will be able to:
|
What is Flash?
- Flash is an authoring tool that designers and developers use to create presentations, applications, and other content that enables user interaction. Flash projects can include simple animations, video content, complex presentations, and applications. In general, individual pieces of content made with Flash are called applications, even though they might only be a basic animation. Flash applications can include pictures, sound, video, and special effects.
- Flash, through the use of vector graphics is suited to creating content for delivery over the Internet because its files are very small. Vector graphics require significantly less memory and storage space than bitmap graphics as they are represented by mathematical formulas instead of large data sets. Bitmap (or raster) graphics are larger because each individual pixel in the image requires a separate piece of data to represent it.
- To build an application in Flash, you create graphics with the Flash drawing tools and import additional media elements into your Flash document. Next, you define how and when you want to use each of those elements to create your application.
- When you author content in Flash, you work in a Flash document file. Flash documents have the file extension .fla (FLA), and have four main parts:
- The Stage is where your graphics, videos, buttons, and so on appear during playback. The Stage is described further in Flash Basics.
- The Timeline is where you tell Flash when you want the graphics and other elements of your project to appear. You also use the Timeline to specify the layering order of graphics on the Stage. Graphics in higher layers appear on top of graphics in lower layers (this is the opposite of Director).
- The Library panel is where Flash displays a list of the media elements in your Flash document.
- ActionScript code allows you to add interactivity to the media elements in your document. For example, you can add code that causes a button to display a new image when the user clicks it. You can also use ActionScript to add logic to your applications. Logic enables your application to behave in different ways depending on the user's actions or other conditions.
- When you have finished authoring your Flash document, you publish it using the File > Publish command. Normally you would create an SWF file which is a compressed version of your fla file with the extension .swf,. The swf file can be played using a Flash Player, or a Flash player plug-in in a web browser. You can also publish the swf file to an executable allowing the application to be self contained as a stand-alone application.
(What is Flash, 2005)[1]
Flash examples
Also refer to Multimedia design examples
Why Use Flash?
- Availability – Flash is available as a plug-in for most web browsers, some PDAs and cell phones.
- Download Speed - Flash creates a small application that can include many media types.
- Visual Control – Flash gives you complete control over position, colour, fonts, etc. regardless of the platform or browser from which it is displayed.
- Interactivity – Flash give you the ability to create interactivity using ActionScript.
- Combine Vectors & Bitmaps – Flash allows both. Vector based graphics can be resized without loss of clarity.
- Streaming Content – Flash files can be downloaded in small chunks, allowing background downloading.
How does Flash work on multiple platforms
- Flash unfortunately is not supported on all Apple devices particularly mobile devices (like the iPhone). This can cause issues when users are using a mobile browser and encounter a flash based web site.
- Flash allows you to create run-able versions (e.g. Packaged with an exe file for Windows) and you can use the Adobe Integrated Runtime (AIR) environment to create versions for specific hardware. (AIR, AIR for Android, AIR for iOS). Sneer-Well has a collection of "50+Enormously Useful Adobe AIR Apps" and gives you some idea of the scope of AIR applications.
Adobe Integrated Runtime (AIR)
- According to Adobe Integrated Runtime. (2012, July 18)[4] AIR provides a runtime-environment that
- allows existing Flash, ActionScript, or HTML and JavaScript code to be used to construct Internet-based applications that have many of the characteristics of more traditional desktop-like programs.
- Adobe positions it as a browser-less runtime for Rich Internet Applications (RIAs) that can be deployed onto the desktop, rather than as a full-fledged application framework. An application deployed in a browser does not require installation, while one deployed with AIR requires the application be packaged, digitally signed, and installed on the user's local file system. This provides access to local storage and file systems, while browser-deployed applications are more limited in where and how data can be accessed and stored. Interestingly in Contains the WebKit Browser engine used by Google Chrome and Apple Safari)
- Adobe AIR internally uses Adobe Flash Player as the runtime environment, and ActionScript 3 as the sole programming language.
- Flash applications must specifically be built for the Adobe AIR runtime in order to utilize additional features provided, such as file system integration, native client extensions, native window/screen integration, taskbar/dock integration, and hardware integration with connected Accelerometer and GPS devices.
- AIR enables applications to work with data in multiple different ways, including local files, local SQLite databases for which AIR has inbuilt support, a database server via web services, or the encrypted local store included with AIR.
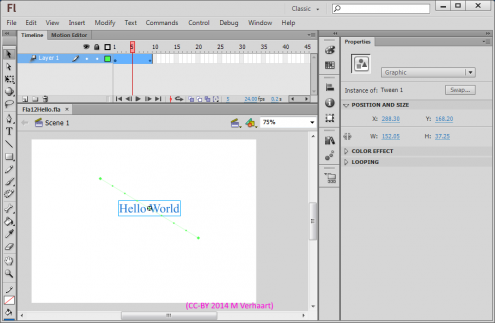
Hello World in Flash
Notes:
- A fla file (in this case 2014vmv_Fla12_HelloWorld.fla) containing the animation instructions.
- In Flash 12 Text (Hello World) is added to the stage.
- Using the Selection tool > Right click on the text object and select Create motion tween. Frames are added to the timeline to allow the text to move.
- A Tween path is added by dragging the text object to its end point (make sure the timeline bar is in the last frame)right clicking on the text).
Then..
- Use File > Publish to create an html and an swf (shockwave flash) file
|
 References
References
- ↑ What is Flash (2005) Online help files, Macromedia.
- ↑ Deutsche Bank (n.d.) Test your Agile Mind. Retrieved March 9, 2011 from http://www.db.com/careers/content/en/test_your_agile_mind.htm
- ↑ McCann Erickson Japan, Inc. (2006). Ecodaidobutsuen. Retrieved 16 March, 2011, from: http://ecodazoo.com/
- ↑ Adobe Integrated Runtime. (2012, July 18). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 23:21, July 22, 2012, from http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Adobe_Integrated_Runtime&oldid=502892257
|
virtualMV | Superquick wiki guide | Please give me some feedback |
VirtualMV/Flash12 (CS6). (2024). In WikiEducator/VirtualMV wiki. Retrieved December 21, 2024, from http:https://wikieducator.org/VirtualMV/Flash12_(CS6) (zotero)
|