Human Population
| Environmental Science | |
|---|---|
| Topics | What is the Environment | Planetary Boundaries | Ecological Footprint and Sustainable Development | Food and Agriculture | Population | Ecology - Definitions and Outline | Energy Flow in Ecosystems | Population and Community Ecology | Material Cycles | Biodiversity | Energy | Atmosphere and Climate | Global Warming | Air Quality | Water Quantity | Water Quality | Solid Waste |
| To introduce the problems with human population growth
This section is in two parts:
|
Contents
Introduction
There are some who say that the population growth is the most serious of all environmental problems
The current world's population (2020) is about 8.1 billion[1]
- India 1.44 billion
- China 1.42 billion
- US 337 million
- Indonesia 282 million
- Thailand 72 million
Definitions
- Natality
- Number of people born over a specified time period
- Birth Rate
- Number of births per 1000 people per year
- Mortality
- Number of deaths over a specified time period
- Death Rate
- Number of deaths per 1000 people per year
- Population Growth Rate
- Birth rate minus death rate. Usually given as percent of population
Note that the birth and death rate is the number per thousand, whereas the population growth rate is in percent (per hundred). Therefore,
- [math]\textstyle Population Growth Rate = (\frac{Birth Rate}{1000}-\frac{Death Rate}{1000})X100[/math]
- or
- [math]\textstyle Population Growth Rate = \frac{Birth Rate - Death Rate}{10}[/math]
Examples - Population Growth Rate
- Hungary -0.4
- Spain 0.2
- Thailand 0.2
- Bangladesh 0.8
- Pakistan 1.9
- Uganda 3.2
- Population Density
- Population per unit area
Examples - Population density (per sq. km)
- Mongolia 2
- Spain 95
- Thailand 140
- Netherlands 524
- Bangladesh 1278
- Singapore 8229
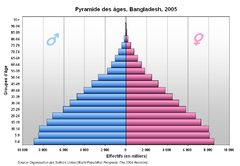
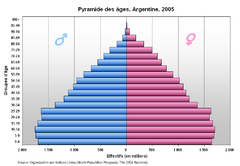
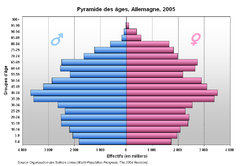
Age Distributions
- Age Distribution
- number of people of each age in a population
- Often given using age groups of five years
- Shown using a Population Pyramid
Migration
- Immigration
- movement of population into an area
- Emigration
- movement of population out of an area
Then the total population growth rate is then
- Population Growth Rate = Birth Rate + Immigration - Death Rate - Emigration
Migration is usually not a significant factor except where war or other conditions cause mass movement of people.
Health Care
The two best indicators of the quality of health care are infant mortality and life expectancy.
- Infant Mortality
- number of deaths of those under 1 year old per 1000 births
- Child Mortality
- number of deaths of those under 5 years old per 1000 births
Examples - infant mortality
- Sweden 3.7
- Thailand 15.8
- Brazil 23.9
- Myanmar 66.6
- Chad 126.5
- Life Expectancy
the average number of years a newborn can expect to survive
Examples - life expectancy
- Japan 84.85
- Thailand 76.56
- Russia 73.34
- Nigeria 54.63
Fertility
- Total Fertility Rate
number of children born per woman in her lifetime
- Replacement Fertility Rate
number of children born to parents to replace them
- = approx. 2.1
- more than 2.0 since some women die before bearing children or choose not to have children
Examples - total fertility rate
- Korea 0.73
- Thailand 1.20
- China 1.01
- India 1.96
- Cambodia 2.55
- Niger 5.94
If the total fertility rate exceeds the replacement rate, then the population growth rate will rise (and vice versa). Note there will be a delay between the two.
Population Growth
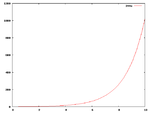
The number of members for each generation increases geometrically = 2x2x2x...
Therefore the total size of the population must increase exponentially = 2^n with n the number of generations
Population Growth Curve
A population growth curve begins with a lag phase. During the lag phase population grows very slowly.
After the lag phase we then get the exponential growth phase also called the log phase.
Finally the birth and death rates will begin to approach each other. This leads to a deceleration phase followed by a stable equilibrium stage.
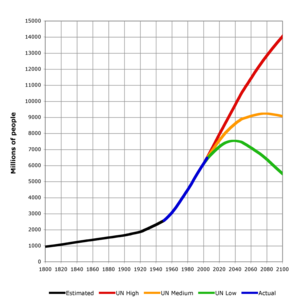
Human population curve
Humans have had a long lag period. It took until 1800 to reach 1 billion people. Then the second billion only took 130 years.
In the last eighty years population has increased from 2.0 to 7.8 billion.
- Doubling Time
- Time for the population to double in size
= 70 years/Growth Rate (in percent)
Urbanization
The percent of people living in urban areas has been rapidly increasing. Currently half of all people live in cities.
By 2030, UN-Habitat estimates 60% will live in cities.
In Latin America over 80% live in cities.
26 cities are megacities (> 10 million people), 9 have more than 20 million people
1 billion people live in urban slums
The problem is providing the necessary services to the cities inhabitants. For example, water, sanitation, police, and fire.
Most of the problems come from unplanned growth.
Smart Growth
Smart growth of cities tries to avoid the pitfalls of unplanned growth. It includes:
- Increase use of bicycles and mass transit systems
- Reduction in number of vehicles, especially in the city center
- Planning of services such as water, sewage, solid waste, flood prevention
- Greening of cities by adding greenspace (parks, wood areas, etc.) and possibly urban gardening areas
Effects versus Factors
In the discussion below what we call effects are the effects of increased population on the environment. Factors are what causes population growth rate to increase.
Factors → Population → Effects
Effects of population growth
- Food security
- Water, air, and land pollution; global warming
- Land availability
- Agricultural pressures
- water (70% of human water usage is from agriculture)
- land
- soil erosion, soil degradation
- desertification, soil salinity
- pollution from fertilizers and pesticides
- Pressures on natural resources
- energy resources
- mineral resources (metals, glass, stone, cement, gems, etc.)
- forest resources
- fisheries
- water
- Pressures on ecosystems
- deforestation
- habitat loss
- extinction of species
- poaching
- encroachment of people into wildlife areas
- Economic pressures
- jobs
- costs of material resources
- economic divide
- Health care
- spreading of disease from overcrowding
- shortage of doctors, nurses, etc.
- shortage of medicines, vaccines, and medical equipment
- Social
- shelter (housing)
- education (shortage of teachers)
- infrastructure (fire, police, utilities, transport, etc.)
- Political unrest/war due to scarce resources
Factors
Economic factors
The role of children in the economy is important in determining birth rate.
Many families feel they need children to help raise income. For example, farmers families are often large because the children can help on the farm.
Another important point is the cost of raising and educating children. Where the costs are higher, then couples will often delay having children until they are financially better off.
Cultural and Religious Factors
Culture and religion are important in determining number of children born. The role of women is especially important. In some cultures the role of women is to marry and have children. In other cultures women marry later and have fewer children.
Education
Fertility rates have a direct correlation to women's education. The education of women is the single most important factor in reducing the world's population growth.
Birth Control
Attitudes toward birth control vary widely around the world. The most important point is to give women choice in when to have a family and how large it will be.
Health style
As mentioned above the best indicators of public health are infant mortality and life expectancy.
Life expectancy has generally risen over the years. However, recently it has decreased in Africa due to the AIDS epidemic. In some African countries up to one-third of adult are infected with HIV.
Government Policy
The government's policy toward population growth can be very important. Some countries (for example, Thailand, China, and Bangladesh) have encourage family planning, etc. Other countries (such as Singapore) have encouraged people to have more children.
Solutions
- Family Planning
- Women's Education
- Respect for women's and children's rights
Case Study: Thailand
Thailand reduced its population growth rate from 3.2% to 1.6% in just 15 years.
It has a family planning program supported by the government, the Buddhist church, and nonprofit organizations. Program led by Meechai Viravidaiya aka Mr. Condom.
Thailand also has good educational and employment opportunities for women and a good health care system for mothers and children.
The following sites have statistics and reports on population:
|
Pick a country and go to the population statistics for the UN HERE. Then using the statistics, answer the following questions:
For more specific instructions on using the UN database see this page
|
References
- ↑ All population data except total world population and US population taken from the UN's World Population Prospects 2024. Total world population and US population taken from the US Census Bureau's Population Clock, viewed on 21 November 2024.