Energy Flow in Ecosystems
| Environmental Science | |
|---|---|
| Topics | What is the Environment | Planetary Boundaries | Ecological Footprint and Sustainable Development | Food and Agriculture | Population | Ecology - Definitions and Outline | Energy Flow in Ecosystems | Population and Community Ecology | Material Cycles | Biodiversity | Energy | Atmosphere and Climate | Global Warming | Air Quality | Water Quantity | Water Quality | Solid Waste |
|
Contents
Energy Flow
All of nature is driven by energy. How this energy flows through the environment is important for understanding ecolgy.
It is governed by three laws:
- Conservation of Mass
- Conservation of Energy (First Law of Thermodynamics)
- Second Law of Thermodynamics
Conservation of Mass
Conservation of Mass
All mass is conserved - it is neither created nor destroyed.
Definitions
- Work
- force acting through a distance
- Energy
- the capacity (ability) to do work
- Heat
- energy transferred due to a temperature difference
Conservation of Energy
Conservation of Energy
All energy is conserved - it is neither created nor destroyed.
(or There is no free lunch)
For historical reasons this is also known as the First_Law_of_Thermodynamics
Examples:
- you need fuel to keep your car running
- you need food to keep yourself running
An alternative way to define the Conservation of Energy is
The change in energy (U) is equal to work (W) plus heat (Q)
- ΔU = W + Q
This implies that energy can only be transferred two ways: work and heat.
It also implies that heat and work should behave the same way, but they do not.
Second Law
Questions:
- How do we uncook rice?
- How do we unpeel an orange?
- A book easily falls to the floor, but takes much effort to get back up. Why?
First law says cooking and uncooking are exactly the same.
These questions lead to the second law of thermodynamics.
Second law of thermodynamics
No system can completely convert heat to work
or
All systems tend toward disorder
The measure of disorder is called the Entropy
The second law therefore says that the total entropy will always increase.
Important notes about the Second Law:
- We can convert work entirely into heat.
- Since heat cannot be entirely converted to work, we say heat is lower quality than work.
- Whenever energy is converted from one form to another, some is lost as heat.
Life
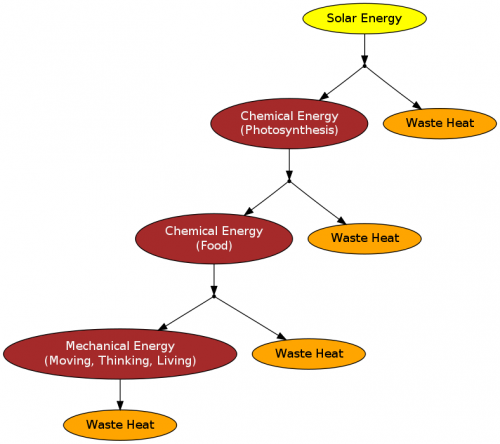
The ultimate source of energy for life processes is the SUN.
↓
Plants convert the sun's energy (light) into food (energy reserve) by photosynthesis
↓
Plants and animals then use respiration and other processes to breakdown the food releasing energy
↓
This energy is then used to move, think, and other actions.
- Each step above involves changing the form of energy. Therefore, by the second law of thermodynamics each step losses waste heat and the resulting energy is of lower quality.
|
Thermodynamics - A wikieducator project on this topic |