User:Vtaylor/CIS2/Spring 2009/Mobile learning
CIS 2 Computers and the Internet in Society :: FALL 2008
Contents
Introduction
Mobile Learning(or mLearning) is focus on learning through a mobile medium with mobile devices (such as Cell Phones, PDA’s, portable gaming systems, portable music players, etc.)
With the immense penetration rate of mobile devices and a new wave of mobile laptops (as characterized by recent ASUS WEE), the opportunity to use this medium as a educational tool so that people can learn anytime and anywhere is being developed and taken advantage of. Mobile Learning and E-learning are often mentioned in the same context, however mobile learning is differentiated by it being untethered. That is, it involves learning anywhere with no need to be physically connected to an outlet. There is also a focus with the latest technology of e-learning being delivered with “just-in-time”, “just enough” and “just-for-me” concepts.
Definition
What is mobile learning?
Mobile learning (or m-learning): learning that is enhanced with mobile tools and mobile communication. M-learning is the exciting art of using mobile technologies to enhance the learning experience. Mobile phones, PDAs, Pocket PCs and the Internet can be blended to engage and motivate learners, any time and anywhere. A wide definition of mobile learning (commonly referred to as m-learning) is the ability to learn independently of place and time, facilitated by a range of mobile devices. It as a follow-up of e-learning.
How it works
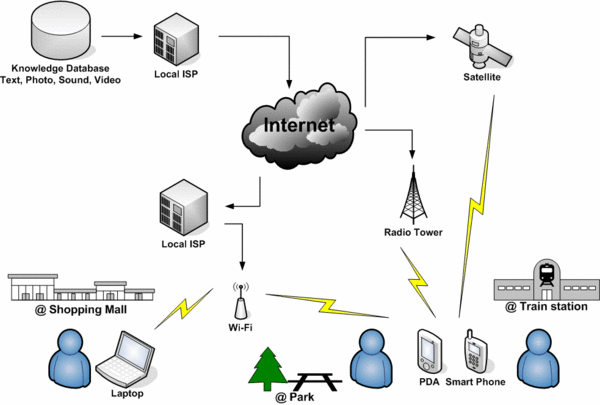
Model
This is a model of how information is distributed, and how mobile learning works.
Mobile Device
Mobile devices fall into a series of categories: Laptop PCs, PDAs/Smart phones, and non-telephony devices including MP3 players.
There are three main forms of PDAs/Smart mobile technologies:
1. PDAs/Smart phones:
- Palm operating system (running on 65% of the PDA market).
- Pocket PC or mobile device runs by Windows Mobile from Microsoft.
- Mobile device runs by linux kernal software, such as Android and Google Phone.
- Apple iPhone.
2. Digital phones:
- Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Samsung and equivalent – including third generation (3G) phones with larger screens and audio/video/flash/java capabilities
Non-telephony mobile devices:
- These include: MP3 players, the dominant being Apple’s iPod.
History
| Timeline | Product | Programming language | Networking technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1970s | Dynabook idea | Smalltalk | Arpanet |
| Alto | Ethernet | ||
| 1980s | Xerox Star | ||
| Apple Lisa | C++ | TCP/IP | |
| Apple Macintosh | Analog cellualr radio | ||
| 1990s | Windows PCs | Java | Worldwide web |
| Laptop PCs | Digital cellular radio | ||
| PDAs | Wireless LAN | ||
| 2000s | Wireless PDAs | CORBA | Bluetooth |
The European Commission funds the major multi-national MOBIlearn and M-learning projects. There are three core areas of mobile learning.
- Authoring and publishing
- Delivery and Tracking
- Content Development
Many trade shows and conferences were created to deal with mobile learning and hand held education. The trade shows that were included are: mLearn, WMUTE, and IADIS Mobile Learning international conference series, ICML in Jordan, Mobile Learning in Malaysia, Handheld Learning in London, SALT Mobile in USA.
Mobile Learning Today
K-12
Technology revolution in 21st century draws big impact to traditional grade school education. In United States, Internet technologies and mobile devices play an important role in primary and secondary school (K-12) education. Many major industry corporations offer relevant solution of mobile learning to K-12 education. Nokia partners with some educational institutions delivering students’ contemporary curriculum through mobile communication devices; students are able to use personal communication devices, such as smart phone, instead textbooks to study or prepare school exam on the bus or subway. Apple offer a solution called “Apple Mobile Learning Labs”, it provides a way to share educational information among classrooms. In 2004, the Alvin Intermediate School District in Taxas passed a multimillion- dollar bond that called for the purchase of handheld computers for all students. The Alvin district tapped GoKnow!, a company that develops K12 resources for mobile computing devices, to provide the educational software and professional development. GoKnow!'s Handheld Learning Environment turned the Axim, a business-oriented device, into a mobile learning environment by providing software that enabled teachers to create lessons and that supported students.
College/University
Higher level educational institution, such as college or university, takes mobile learning even further. In America, most of community colleges and universities offer online class; students are able to study and earn course credits without attending in formal classroom. Using Tablet PCs, laptops, PDAs, cell phones, digital wireless cameras and printers, and mobile wireless access points, students and faculty are engaged in exciting initiatives that re-define the classroom, creating new opportunities for inquiry-based curriculum. Through online learning activities in and out of the classroom, instructors can engage their students and assist them in constructing their own knowledge. In 1995, computer science faculty member Michael Loceff, who offered the first online class at Foothill College of California, developed a course management system known as Easy to Use Distance Education Software (ETUDES). ETUDES enabled Foothill College to revolutionize instructional delivery via the Internet. In January 2005, Ohio State University approved a 5-year funding proposal to build and support a centrally managed wireless network for Ohio State University converting 190 - 200 existing wireless hotspots in over 60 buildings and key student gathering areas on campus. In UK, sponsored by Microsoft, Toshiba, and Viglen, students at the University of Birmingham’s School of Engineering are being equipped with Tablet PCs to support their learning, and in order to carry out research in higher education. The students are free to use the Tablet PCs in class, at home or anywhere they choose. Their department and much of the University campus have wireless network coverage, allowing mobile access to learning materials and communication with peers and faculty.
Continuing Education and Corporate Training
The faster and cheaper high speed Internet access provides an environment of mobile learning for continuing education and corporate training. Many corporate employees have long history of using mobile devices at work; and mobile learning delivers just-in-time on job training and support at whenever/wherever they need. According to market research conducted by Ambient Insight, LLC, it is estimated that “corporate and business expenditures for mobile learning products and services in the US alone will reach over $246.9 million by 2011.” Merrill Lynch offers three mandated courses in a seven-week period to over 2,100 investment banker and select support staff via MLU (Merrill Lynch University) and via the BlackBerry. The outcomes exceeded the goals. Higher scores were obtained in half the time. Bankers who completed the training did so in 54 less minutes and tested higher on the final assessment tests than the remainder of the firm. Mobile users also completed their training twenty days earlier than those who trained via MLU. Financial giant Capital One even goes as far as handing out iPods to employees enrolled in training sessions. This change from classroom to personal education arose from the lack of time during the workweek to physically attend training. This audio equivalent, which allows employees to use it when and where they desire, seems like the logical answer to this dilemma. In the summer of 2006 National Semiconductor Corporation gave each of their 8,500 employees a 30-gigabyte video iPod. These iPods were for employees to download National training podcasts and other employee communications.
Future Outlook/Trends in Mobile Learning
Currently E-Learning is still just being starting to be adapted with many studies being conducted in elementary schools, such as in the bay area by Berkeley (http://best.me.berkeley.edu/~aagogino/papers/datta_masters_final.pdf) to understand the limitations and best applications of e-learning. However there’s still social stigma in accepting mobile devices such as cell phones in a classroom environment and as a tool for learning (as opposed to gaming and socializing). (http://eprints.usq.edu.au/2042/1/MoLTA2007conferenceproceedingspaperAHafeezBaigPADanaher.pdf)
There is also a convergence of mobile devices (PDA, Cell Phone, GPS, Computer) that will make applications more standard. Also with the recent proliferation of a new wave of smart phones (such as the IPhone and Blackberry Storm), there will be larger screens and more intuitive user interfaces that are more readily accepted (http://www.xplanazine.com/2008/03/mobile-learning-developments-aiu-incorporates-lms-features-with-iphone-itouch). According to the research done, the touch screen and interface more readily aligns the mobile learning experience with the user.
Other emerging improvements include increased mobile connectivity globally (web 2.0), new technological devices such as Origami (http://origamiproject.com/default.aspx), increased bandwidth to transfer rich media, and improved user interfaces.
Globally, there will be expansion of technology to third world countries, with mobile learning being a cornerstone in bridging the educational gap. (http://www.checkpoint-elearning.com/article/5475.html)
In the far future, we may be looking at brain cells being fused with computer chips to create living computers that allow cybernetics and learning as easy as downloading a program (http://www.livescience.com/health/060327_neuro_chips.html ).
Advantages and Disadvantage
Advantages
The greatest advantage is the ability for teachable moments, when the willingness and attentiveness is at its greatest levels. Other advantages include:
- Flexibility in where, when, and how learning is conducted
- Learning in environments more comfortable and secure for users
- Offers cost saving benefits to users
Disadvantages
The greatest disadvantage as seen is the need for a higher self-discipline. Other disadvantages include:
- Familiarization with medium
- Impersonal Learning
- Difficult verification of the learning success
- High level of technological know-how
Also experts often criticize the small displays often characteristic of mobile devices such as PDA’s and Cellular Phones.
References
[1] Mobile technologies and learning by Laura Naismith, Peter Lonsdale, Giasemi Vavoula and Mike Sharples.
[2]Mobile Learning versus E-Learning - Is There a Difference? by Thomas
[3] Getting Mobile by Cathleen Norris and Elliot Soloway
[4] Mobile Learning Update by Judy Brown and David Metcalf.Ph.D
Project Role
Cynthia: Recorder/Content manager/Writer
Yadong: Style Coordinator or Tech wiz /Writer
Plamen: Editor/Writer
Michael: Style Coordinator or Tech wiz /Writer
William: Project Manager/Team coordinator/Writer
Desiree: Editor/Writer
| Students @ Work - a student collaborative writing project. Help us by providing feedback on the Discussion page. |