Talk:Life Skills Development/Module Four/entrepreneurship/Archive
{{Introduction|
In everyone is the potential to be an entrepreneur. The qustion is, are you ready to become an entrepreneur or do you wish to work for someone, for the rest of your life? In this unit, we will open the world of your own business to you.
|
|
What is an Entrepreneur?
What is meant by Entrepreneurship?
Economic analysts have realised that small firms contribute considerably to economic growth and vitality.
Entrepreneurship, can be defined as, the practice of starting new organizations, particularly new businesses generally in response to identified opportunities.
Generally, the new organisations started by entrepreneurs are small businesses.
B. How do we define Small Business?
A small business is "one that is independently owned and operated and which is not dominant in its field of operation."
Small Businesses are defined using size standards. Different countries have different standards which are used to determine the size of a business. These standards include:
- Number of Employees
- Amount of money used to start – Start up investment
- Rate of turnover - average annual receipts of the business
For example:
- St. Vincent & the Grenadines: A small business is one that employs ten persons or less and has an initial investment of Twenty five ($EC25,000.00)or less.
- Belize: A small retail business is one which has annual sales receipts under $ 2 million.
- European Union: A Small Business has less than 50 employees and a turnover of less than 10 million Euro. The EU also defines a medium sized enterprise as one which employs less than 250 people and has a turnover of of less than 50 million Euros and a micro enterprise as one with less than 10 employees and a turnover of less than 2 million Euro
Typical examples of small businesses include: small shops, hairdressers, tradesmen, solicitors, lawyers, accountants, restaurants, guest houses, photographers, small-scale manufacturing etc.
Have you been thinking of your business idea? Focus on your talents, skills, your hobbies, your pleasure and also on the needs of your community.
You may want to be an Entrepreneur or you may just want to try on the idea. Let's proceed.
Running a business in not easy. In order to succeed, you need to do these four things:
4.1 Seeing me as an Entrepreneur?
An Entrepreneur is a person who owns and operates a business enterprise. He/she takes all the risks involved in the operation of this enterprise.
Entrepreneurs are innovative; and as a result, are always able to see possibilities which would not be normally seen by ordinary persons. They have a strong desire to succeed; and so, it is often quite common for entrepreneurs to fail at several initial enterprises before finally making it big. Also, entrepreneurs have the capacity to work long hours, ensuring that their business ideas are fully developed rather than, take holidays and time off from their businesses.
The table below gives some qualities that help people to better understand themselves. Try the activity.
Characteristics of an Entrepreneur
- The entrepreneur has an enthusiastic vision, the driving force of an entreprise.
- The entreprenuer's vision is usually supported by an interlocked collection of specific ideas not available to the marketplace.
- The overall blueprint to realise the vision is clear, however details may be incomplete, flexible, and evolving.
- The entrepreneur promotes the vision with enthusiastic passion.
- With persistence and determination, the entrepreneur develops strategies to change the vision into reality.
- The entrepreneur takes the initial responsibility to cause a vision to become a success.
- Entrepreneurs take prudent risks. They assess costs, market/customer needs and persuade others to join and help.
- An entrepreneur is usually a positive thinker and a decision maker.
4.2 What is an Enterprise?
Almost any business or organisation can be called an enterprise, possibly led by an entrepreneur
An enterprise is any activity which provides customers with a product (goods/services) with a view to making a profit.
Building Your Business Plan
For a Business Plan you need a Business Idea. What is your Idea? What Business do you want to start?
Write this down and as we move along we will build a business plan for that Idea.
How to write your Business Plan | Business Plan Template | Business Plan Sample
| No idea yet? Here are some links to view to help you get started: |
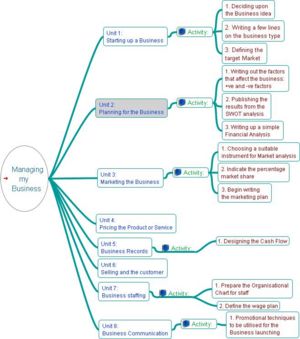
Introduction | Objectives | What is Business Management? | What is meant by Entrepreneurship? | What are the different business types? | How is a business idea developed? | What Factors Influence the Business? | The importance of a business in a country | Summary
6. How is a business idea developed?
Think about your talents, your passion, your hobbies: which can be developed into a micro business? New opportunities occur from changes in industry, social, or economic environments. New ventures arise in the following ways:
A. External Causes
- Changes in industry stimulated by advancing technology and new knowledge spur new products and services ; A good example of this are the changes in the ICT - tele-communication etc, and the IT - the computer, internet and the e-learning technologies.
- Accidental discovery ; Sometimes a person stumbles upon an idea instead of deliberately trying to invent a new product, as was the case of the Post-It product of the 3M company.
- Changing perceptions ; There are times when the social environment is an element of new venture creation. For example, the emphasis on health activities in the 1980's created full-service health clubs.
- Economic changes ; often involve opportunities that arise out of the necessity such as the energy crises leading to new ideas
| Share your thoughts about the following with a friend. Then write them in your portfolio.
Identify one of each of these four kinds of ideas(listed above)in a business in your country/ region.
|
B. Voluntary Self-Employment
1. Prior work experience is the most common origin of new ventures:
a) Frequently a person, perceiving ways to modify a product or improve a service will start a new venture from the knowledge acquired from a former workplace;
b) A person can also obtain the right to manufacture a product based on a patent;
c) An individual observing scant competition afforded to a particular business can go out and duplicate that same business, as long as there is a market.
2. Follow family traditions especially if they have been serving the needs of that community for so long.
3. Being your own boss can give self satisfaction and can also achieve leadership and recognition.
C. Hobbies
1. A love of horses or animals can lead someone to an opportunity of running a riding school or a animal farm.
D. Advantages of starting your own business
1. The entrepreneur can select his/her own location, employees, and avoid any undesirable precedents set by a previous owner.
2. A start up business can start fresh without having to follow old practices.
5. Competition (SWOT Analysis)
How much of a risk is your business idea? How much is it an opportunity not to be missed?
Can you manage competition?
Competition may be defined as a business relation in which two or more parties compete to gain customers.
Goods and services will be bought from those who, in the view of buyers, provide ‘the most for the money'and/or from those who offer greater buying convenience. Hence, competition tend to drive the entrepreneurs to find ways and means of ensuring that the customers make their goods and services their first choice.
Therefore, all business persons must consider competition when deciding to start a business regardless of the size of business. Special efforts must be made in assessing existing competition; as well as, planning to deal with competition which may come after the business has started.
As an entrepreneur, you must define competition correctly; select the appropriate competitors to analyze; plan how you will deal with new competitors and explain your competitive advantages. This information will be important when developing the competition section of your business plan.
In identifying competitors, entrepreneurs often find themselves in a difficult position. On one hand, they want to show that they are unique (even under the investors' broad definition) and list no or few competitors. However, this has a negative connotation. If no or few businesses are in a market space, it implies that there may not be a large enough customer need to support the new business' products and/or services.
After identifying your competitors, your business plan must describe them. In doing so, the plan must also objectively analyze each competitor's strengths and weaknesses and the key drivers of competitive differentiation in the marketplace.
In analysing your competitors'strengths and weaknesses you will begin to use a rather common tool used by many business persons. It is called a SWOT Analysis.
What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a tool for auditing a business and its environment. It is the first stage of planning and you as a new entrepreneurs to focus on key issues. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- S - Strengths
- W - Weaknesses
- O - Opportunities
- T - Threats
Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors. Opportunities and threats are external factors. For example:
A strength could be:
- Specialist marketing expertise
- New, innovative products or services
- Location of business
- Any other aspect of their businesses that add value to their products or services
A weakness could be:
- Lack of marketing expertise
- Undifferentiated products or services (i.e. in relation to your business)
- Location of their businesses
- Poor quality goods or services
- Damaged reputations
In SWOT, opportunities and threats are external factors. For example:
An opportunity could be:
- A developing market such as the Internet
- Mergers, joint ventures or strategic alliances
- Moving into new market segments that offer improved profits
- A new international market
- A market vacated by an ineffective competitor
A threat could be:
- A new competitor in your home market
- Price wars among competitors
- A competitor has a new, innovative product or service
- Competitors have superior access to channels of distribution
- Taxation (such as VAT)is introduced on your product or service
Now try to do a SWOT on one of your competitors.
Follow these steps: My SWOT Analysis of...
What is Entrepreneurship?
Entrepreneurship is the practice of starting new organizations, particularly new businesses generally in response to identified opportunities. Entrepreneurship is often a difficult undertaking, as a majority of new businesses fail. Entrepreneurial activities are substantially different depending on the type of organization that is being started. Entrepreneurship ranges in scale from solo projects (even involving the entrepreneur only part-time) to major undertakings creating many job opportunities.
Many "high-profile" entrepreneurial ventures seek venture capital or angel funding in order to raise capital to build the business. Many kinds of organizations now exist to support would-be entrepreneurs, including specialized government ministries, business incubators, corporate banks, and small independent loan offices.
|
ENTREPRENEUR SELF-TEST This assessment is designed to help an individual identify and understand his/her entrepreneurial potential. This test can be used at the community level with residents engaged in or considering involvement with a business. The Entrepreneur Self-Test consists of three sections: motivation, capacity, and support. Motivation Evaluate your overall motivation to start and operate your own business. Score on a I to 10 scale, where 10 indicates strong agreement with the statement and I indicates little or no agreement with the statement.
Flexible - I am flexible and I am able to adapt to changes and surprises quickly and successfully.
Capacity Evaluate your capacity related to the following business skills. Consider not only your own capacities, but also the capacities of the other members of your management team. Rate yourself on a scale of 1 to 10 with 1 being no capacity and 10 being high capacity.
Capacity for Networking Evaluate your ability to network and partner with other organizations and individuals. Score on a I to 10 scale where 10 indicates strong agreement with the statement and I indicates little or no agreement with the statement.
Support Evaluate the level of support you feel from your family and community as you pursue your business opportunities. Score it on a 1 to 10 scale, where 10 indicate strong agreement with the statement and I indicate little or no agreement with the statement.
SCORING OF TEST Not all questions carry the same value and weight. The following scoring approach is used:
|
A Business Plan
<flash>file=Magnifier.swf|width=475|height=438|scale=noscale|salign=lt|flashvars=?glassSize=2&initialZoomSize=150&borderWidth=12&file=../../../../../images/b/b1/Business_palns.jpg&width=475&height=438</flash>
A business plan is a summary of how a business or entrepreneur intends to organize an entrepreneurial endeavor and implement activities necessary for the venture to succeed. It is a written explanation of the company's business model for the venture in question. Business plans are developed for ventures in both business and government.
Business plans are used internally for management and planning and are also used to convince outsiders such as banks or venture capitalists to invest money into a venture.
A business plan is prepared for customers for they need to know whether the product serves the purpose or not and the utility of the product, for government because it is necessary to know for government whether the legal economical and subsidy concerns are met or the like.
8 Steps to Creating a Simple Business Plan
© Herman Drost
Your business plan is like a road map to long-term success. Have you ever been in a situation where you didn't have a map to find your destination and got lost wasting precious time and money? Well, the same can happen to your business if you don't plan out your business strategies.
Why you need a business plan.
It gives you a clear direction where your business is heading. Many business owners just jump into creating a business without researching and making a concrete plan. Inevitably, they soon find that they are out of money and have no time or clear strategies how to market their business.
Here are 8 simple steps to creating your own business plan (this is by no means a comprehensive plan but a primer to get you started):
1. Name of your business - create a name or re-evaluate the name of your business. Does it integrate well with what you are selling? Is it easy to spell and remember? Is it a name that can be well branded over time?
2. Vision - what will your business look like 5 years from now? Think of how you may want to expand it to include other branches or extra employees.
3. Mission statement - this defines what your business really does, what activities it performs and what is unique about it that stands out from your competitors.
4. Goals and objectives - clearly define what you want to achieve with your business. Make sure they are quantifiable and set to specific time lines. Set specific goals for each of your products or services.
5. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats (SWOT) – by analyzing these characteristics in your business, you will get a clearer idea of what it will take for you to not only to survive but also prosper.
This could include such factors as:
- your companies own changing industry
- The marketplace which may change due to social and economic conditions.
- Competition which may create new threats and/or opportunities.
- New technologies which may cause you to change products or the process in how you do things.
Evaluating your SWOT will help you to:
- build on your strengths
- resolve your weaknesses
- exploit opportunities
- avoid threat
6. Strategic action plan - this is the most critical step of your business plan, because without it, your business will not get off the ground. This should include your sales and marketing.
7. Financial plan - a business can operate without budgets, but it is clearly good business practice to include it. With budgets, you will be more likely to achieve your business objectives, you will make more-reasoned decisions and you will have better control of your cash flow.
For any period, a cash flow statement would include:
- The cash and credit sales (or accounts receivable) expected to be received during the period.
- The anticipated cash payments (for example, expenses for purchases, salaries, utility charges, taxes, office expenses etc.)
- A description of other incoming and outgoing cash, with a calculation of the overall cash balance.
This will assess how much money is on hand to meet your financial obligations - what cash has been received and what has been paid out. Knowledge of this cash flow cycle will help you predict when you will receive funds and when you will be required to make a payment.
8. Measuring and evaluation - you wrote your business plan and set the goals with the intent of achieving them. So now break them down into measurable pieces and monitor the results regularly. A plan that cannot be measured is almost always destined for failure. Celebrate your wins and recharge yourself to accomplish your next goal.
Decide beforehand what constitutes a real serious loss and what loss will be acceptable.
If you find your goals are unrealistic and unattainable, adjust them, but realize that it takes hard work to achieve them, so don't give up easily.
Conclusion: Now that you have a business plan, make it a part of you by knowing and understanding it clearly. Build upon it continuously and refer to it often, so you remain on track to building a profitable business.
Open the following attachments with Open Office:
More information on Business Plans
Please click on the link above to get more information on How to write a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Microsoft Word, thus, you will require this software or one similar to it that would enable document to be opened properly.
An example of a Business Plan for an Internet Cafe
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be openend properly.
An example of a Business Plan for a Events Planner
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be openend properly.
An example of a Business Plan for a Hair Studio
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be openend properly
|
Now that you are well equipped with more that sufficient information on Business Plans, create a simple Business Plan Outline that would outline the basic infomration for your portfolio. Please ensure that you provide the following:
|
Unit summary
In this unit you learned what it takes to be an entrepreneur that it takes hard work and research to start a business. You know that to start a business in a new or existing trade requires high risk and heavy investing to be able to gain sustainable profits. You have learned the there are entrepreneurships that exist from small ventures to large businesses.
Checklists of Performance Task
| RUBRIC of performance criteria | V. Well Done | Well Done | OK | Not Ok- Will redo by …. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | I have completed the list of qualities of a successful entrepreneur that I will emulate |
| RUBRIC of performance criteria | V. Well Done | Well Done | OK | Not Ok- Will redo by …. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | I have written my reflections on the qualities of an entrepreneur and on my considering becoming an entrepreneur. | ||||
| 2. | I have demonstrated understanding of a Business Plan by beginning to use one for my business idea |
| RUBRIC of performance criteria | V. Well Done | Well Done | OK | Not Ok- Will redo by …. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | I have completed my plans for developing my product and my niche market. |
| RUBRIC of performance criteria | V. Well Done | Well Done | OK | Not Ok- Will redo by …. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | I have developed the outline of my business plan |
| RUBRIC of performance criteria | V. Well Done | Well Done | OK | Not Ok- Will redo by …. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | I have completed a slogan, and market promotion plan for my company |
Deciding on a Business
Provided by My Own Business, Content Partner for the SME Toolkit
Characteristics of a Successful Entrepreneur Step-by-Step Approach Decide if you really want to be in business Decide what business and where Decide whether to start full-time or moonlight Selection Strategy Things to Watch Out For Required Activities Comparative Evaluation How to Evaluate a Specific Business you have in Mind "For" and "Against" List Get Completely Qualified Decision Time SESSION 1 Quiz
[Back to top]
Characteristics of a Successful Entrepreneur
Testimonial Collette Paul STM Media Inc. Publisher of Trade Magazines "Be able to sustain a financial commitment to whatever business you start."
Transcription - html
Guts: Guts means you must have an entrepreneurial instinct, which is an overwhelming desire to have your own business. You must have the guts and dedication to be completely devoted to your goal. Incidentally, devotion to your goal is much more likely if you have a love for your intended business. Life is too short to start a business that doesn't give you satisfaction and joy. And, through good times and bad times, you will stick with something you love. Brains: While appropriate educational credentials are important, entrepreneurial "brains" means more than scholastic achievements. To become a successful entrepreneur, you must have a working knowledge about the business you plan to start before you start it. Common sense combined with appropriate experience is the necessary brainpower. Prudence, follow through and attention to detail are very important.
Capital: You will need seed money of your own plus sufficient cash to maintain a positive cash flow for at least the first year. In a future session you will learn how to forecast future cash requirements through cash flow control. Many businesses can be started on a very small scale with a small investment. Then, as the business grows and you gain experience, cash flow from your business can be used for growth. In some cases you don't need starting capital to hire other people because you might start by doing everything yourself. The "do it yourself" start is a good way to learn everything about your business and also makes you better qualified to delegate work to others later on. You can control your risk by placing a limit on how much you invest in your business.
[Back to top]
Step-by-Step Approach
Testimonial Elaine Mitchell Specialized Veterinarian "Hiring good staff members who also share the same philosophy has been very important."
Transcription - html
Decide if you really want to be in business:
You will be putting some (not all, hopefully) of your net worth at risk. You will run the risk of becoming eccentric, meaning creating a life that is out of balance, with working hours taking away from other family or pleasurable activities. There may be levels of stress you have not experienced as an employee.
Decide what business and where:
Once you have decided you have the characteristics of a successful entrepreneur and that you definitely want to be in business, then you must decide which business is best for you and where to locate that business. Selection strategy is covered later on in this Session.
Decide whether to start full-time or moonlight:
There are some interesting advantages and some pitfalls in starting as a moonlight business. (That is, a business you start in your off hours while still working at your current job.) More often than not, the advantages of starting as a moonlighter outweigh the risks:
You avoid burning your bridges of earnings, including retirement, health and fringe benefits and vacations. Your full-time job won't suffer if you maintain certain conflict of interest disciplines, including compartmentalizing your job and business into completely separate worlds. You can avoid conflict of interest with your job by choosing a business that is appropriate for moonlighting, such as: single products, real estate, specialized food, e-commerce, direct marketing or family-run operations. There are great advantages for operating a family business. The family can run the business while you are at work. You have a built-in organizational structure. You can teach your kids the benefits of being in business. But there are also some pitfalls to consider in starting a moonlight business:
There is a temptation to spend time at your job working on your moonlight business. That is unfair to your employer and should not be done under any circumstances. (You may need a family member or some trusted person to cover emergencies when you are at your job.) Another problem may be competing with your employer, which, again, is not right. Think of how you would feel or handle this employee if you were the boss. Any kind of conflict with your regular work can jeopardize your job and your moonlight business. Overwork and mental and physical exhaustion can also become a very real problem for moonlight entrepreneurs. [Back to top]
Selection Strategy
Testimonial Millard MacAdam Pro Active Leadership "As the saying goes, fail to plan and you are planning to fail."
Transcription - html
Selecting the wrong business is the most frequent mistake that start-up entrepreneurs make. Here is a checklist to help you select a successful one:
Take your time and wait for the business that is just right for you. You will not be penalized for missing opportunities. The selection process takes a lot of planning and your experience and complete knowledge is vital for your success. Don't tackle businesses that may be too challenging. It is better to identify a one-foot hurdle than try to jump a seven-footer. Try to identify a business that has long-term economic potential. Follow Wayne Gretzky's advice, "Go to where the puck is going, not to where it is." A big mistake can be an error of omission. This means you may fail to see an opportunity that is right in front of you. Look for a business that will grow in today's and tomorrow's markets. Many small retail stores are no longer in business because huge stores such as Wal-Mart and Home Depot provide more choices to the customer and often at a cheaper price. Follow the advice of Warren Buffett, Chairman of Berkshire-Hathaway Inc. and the most successful business picker in American history: Mr. Buffett looks for businesses that focus on a "consumer monopoly" with pricing power and long-term predictable growth prospects. Examples include: See's Candy's, Coca-Cola and Gillette Razors. Can you copycat this philosophy in a small way? Businesses to avoid are "commodity" businesses where you must compete entirely on price and in which you must have the lowest cost to survive. As Mr. Buffett has said, "In a commodity type business you're only as smart as your dumbest competitor." Most service businesses have pricing power. Should you bet on a business you don't know when you can bet on a business you do know? If you intend to manufacture a product, consider the pros and cons of contracting out production to a low-cost supplier. In other words, operate a "hollow corporation." A "hollow corporation" is a company that subcontracts manufacturing and packaging. [Back to top]
Things to Watch Out For:
Testimonial Sophia Garcia A-Z Glass Company "To get ahead in this business you do everything to get the job."
Transcription - html
Impatience Do not let overconfidence short-circuit you from analyzing your selection of businesses carefully. You must not fear of hearing the negative aspects; it is much better to be aware of them and face them early on. Be realistic. Do not become lured by high rewards. They will come if you choose the right business and if you understand every aspect of the business before you open its doors.
[Back to top]
Required Activities
It is worth repeating again: The most common mistake and the most costly one is not picking the right business to begin with. This is the time for soul searching.
IF YOU HAVE NOT DECIDED ON A BUSINESS, DO THIS:
On the top of a blank sheet of paper, write an activity you like to do (make this the heading). Do a separate page for each activity or interest you have.
On those same sheets list as many businesses you can think of that are related to that activity.
On the same sheets list all the products or services you can think of that are related to that activity. Use your imagination and think of every possible product or service you could do.
Make a list of businesses that do better in bad times (one may be appropriate for you). Some examples might be pawnshops, auto repairs and fabric stores.
EXAMPLE
Let's assume you end up with three potential businesses: towing service, selling used cars and auto repairs. You can now make a comparative evaluation using the following check-list (or better still your own checklist) with a 1-10 scoring system:
Objective Towing Service Selling Used Cars Auto Repair
Can I do what I love to do? 6 3 10 Will I fill an expanding need? 8 5 10 Can I specialize? 7 8 10 Can I learn it and test it first? 9 8 9
This kind of analysis can help you gain objectivity in selecting your business.
How to Evaluate a Specific Business you have in mind.
Here are some questions to help clarify your thoughts:
Is it something I will enjoy doing? My favorite activities are: __________________________ I like to serve people by: ________________________________ Will it serve an expanding need for which there is no close substitute? Can I be so good at a specialized, targeted need that customers will think there is no close substitute? Can I handle the capital requirements? Can I learn the business by working for someone else first? Could I operate as a hollow corporation, without a factory and with a minimum number of employees? ("Hollow corporation" refers to a business where everything is "outsourced," meaning you would subcontract manufacturing and packaging to outside sources. ) Is this a product or service that I can test first? Should I consider a partner who has complementary skills to mine or who could help finance the business? Once you have decided what business you want to start, do this:
Make a "for" and "against" list regarding characteristics of the business. On a blank piece of paper, draw a vertical line down the middle of the page and list on one side all the "for's" and on the other all the "against's." Sometimes this will help clarify your thinking.
Write down the names of at least five successful businesses in your chosen field. Analyze what these five businesses have in common and make a list of reasons that make them successful.
Talk to several people in your intended business. Don't be afraid of the negative aspects of your intended business. Instead, seek out the pitfalls: better now than after you open your doors. Take notes if possible. Write down the information as soon as you can.
Analyze the competition that are not doing well and write down the reasons.
Get Completely Qualified
Before you start, get completely qualified:
The best way to become qualified is to go to work for someone in the same business. Attend all classes you can on the subjects you need, for example: accounting, computer and selling. Read all the appropriate "how-to" books you can. Don't be afraid to ask questions or seek help from the most successful people in your intended business. [Back to top]
Decision Time: What could you sell or what services could you perform that would make money and you would enjoy?
To complete this session you should have decided on a business or at least selected a business you think would be best for you. To get the most benefit out of the next eleven sessions you should have a definite plan in mind. Session Two will show you how to prepare your business plan.
[Back to top]
SESSION 1 Quiz: DECIDE ON A BUSINESS
Which of the following actions must always be taken to become a successful entrepreneur?
You should be prepared to risk all of your family assets. Plan to quit your job before starting. Choose a business that is in a field you enjoy. Be prepared to put down a lot of money.
The most common and biggest mistake made by entrepreneurs is in not having sufficient money.
True False
Which one of the following is NOT a good reason to consider starting a moonlight business?
You won't burn your bridges of income and benefits while you're getting your business started. Family members can become involved in your business. You have the time and equipment available on your regular job to conduct your own business. New tools including the Internet, pagers and fax machines are available to conduct home-based businesses including e-commerce, direct marketing and single products. If a part-time business proves out and becomes successful, you can decide at that time whether to quit your job and become a full-time entrepreneur.
Let's say that you are looking for some overall guidelines for picking a business. Which one of the following answers would be a good decision?
You have the choice between taking on a business that would be a huge challenge to make successful and one that would be a no-brainer for you to accomplish. You would go for the challenging one. Realizing that you're not getting any younger and this is going to be a big step, it would be better to jump right in and get something started and see what happens. If you had the choice between getting into a business in which you already have experience and one that would be a fresh start in an entirely new field, you would go for the fresh start. You'd take your sweet time to seek out that one great opportunity. If your heart is really set on opening a toy store in a strip shopping center, you would go for it no matter what.
Realizing that there are no hard and fast rules, generally speaking, which of the following businesses would be easier to start and command better pricing power?
Operate your own gasoline service station. Sell your grandma's special candies.
In most cases, the very best way to become qualified in a business you intend to open is to:
Talk to everyone you can who is in that business. Do a "for" and "against" analysis. Do a twelve-month pro forma balance sheet, income statement and cash flow projection. Work for someone in the same business. Objectively weigh the collective opinions of your accountant, banker, lawyer and insurance agent.
Starting a "hollow corporation" means:
Starting a company with no assets. Starting a company with negative net worth. Acquiring a shell corporation. Creating a company where all activities are outsourced (manufacturing and packaging).
You have always dreamed of opening a hardware store but now that you're ready to start you realize that the Home Depots of the world would be too hard to challenge. You should:
Find a niche segment in the hardware business that you can specialize in. Find another business. Go to work for one of the "big box" hardware chains and see if any needs exist that you could uniquely fill. All of the above
What is the single most frequently made mistake that leads to failure?
Lack of experience in the business chosen. Undercapitalization. Not picking the right business to begin with. Lack of knowledge of accounting. Lack of familiarity with the competition.
You don't need to worry about the dumbest competitor in a business that is service oriented.
True False
- [View source↑]
- [History↑]