Decision Making
Contents
Decision Making
Decision making involves exploring plausible alternatives to a problem and choosing the one that will work best.Six simple steps in decision making are:
1. Creating a constructive environment(Do this by deciding your objective clearly, involving the right people, deciding on the way the decision will be taken)
2. Generating good alternatives..(brainstorm using different techniques, invite suggestions from team)
3. Exploring these alternatives.(Consider the workability, plausibility, risk involved, Cost benefit analysis, expected results).
4.Choosing the best alternative.
5.Considering the decision.
6. Pursuing action.
Some Models in Decision Making
Grid Analysis
A certain school has to buy some technological devices for their Audio Visual Aids Room.Four tenders from different dealers are put forth before the school committee. The school has to decide who to place an order with. The grid is made by putiing the four names as heads of rows and various factors to be considered as the heads of columns. Each is rated as 0 for very poor to 5 for very good.Each score is multiplied by the weight accorded to each factor. The weighted scores are added to make a decision.
| Dealer | Quality of material | Cost effectiveness | After sale service |
|---|---|---|---|
| Educare Technologies | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| ABC Tech | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Vision Enterprises | 3 | 4 | 4 |
Assuming that quality of material is of high priority, after sale service is next in importance and cost factor is of least importance, the weighted scores are calculated.This is what the table looks like after the weighted scores are calculated.
| Dealer | Quality of material | Cost effectiveness | After sale service | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| score X 4 | score X 2 | score X 3 | ||
| Educare Technologies | 4 X4 =16 | 3 X 2 = 6 | 4 X 3 =12 | 34 |
| ABC Tech | 5 X 4 =20 | 3 X 2 =6 | 3 X 3 =9 | 35 |
| Vision Enterprises | 3 X 4 = 12 | 4 X 2 = 8 | 4 X 3 = 12 | 32 |
The above grid makes it obvious that ABC tech ought to get the contract.
PMI Technique to weigh pros and cons
PMI stands for Plus , Minus , Interesting. Under Plus , note down all advantages of taking a decision, under Minus note all the disadvantages and under Interesting note down possible implications of the action. Assign scores to each point noted. Scores could be positive or negative. Add the scores. A high positive score means the action needs to be take.A negative score indicates the action is best avoided. Look at the example provided.
Example:
A certain school has to decide whether to hire a curriculum consultant or not. The consultant is expected to help the school formulate a curriculum, implement it, train teachers to apply the curriculum.
| Plus | Minus | Interesting |
| More effective curriculum (+10) | Expensive affair (-8) | Better prospects for students passing(+4) |
| Inservice training of teachers (+5) | More work for teachers(-2) | Updated curriculum(+4) |
| Interesting activites added(+4) | Opposition from teachers(-4) | Expensive for students?(-4) |
| School effectiveness is enhanced(+5) | Time consuming(-5) | |
| (+ 24) | (-19) | (+4) |
The total score is +9 . Hence hiring a consultant will be a wise decision.
Force Field Analysis
Force Field analysis involves finding out all forces that favour and do not favour a particular decision. By identifying forces one can strenghten favourable forces and reduce the impact of the non favourable forces.
Method:
The plan or proposal is put in the middle. Favourable forces are listed on one side and non favourable forces on the other. Assign scores for each factor starting with 1 for weak and 5 for strong.
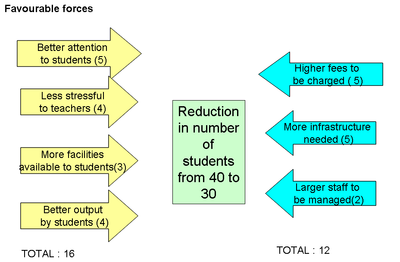
Example: A certain educational institution is planning reduce the strength in each class from 40 to 30. Is the decision worth taking?
( forces in favour indicated by yellow arrows and those not in favour indicated by blue arrows)
As seen from the above Force Field Analysis, factors not in favour total to 12 whereas factors in favour of change total to 16. Hence the decision is good enough to be accepted.