CCNC/CCNC Module 5/The database application/Database Concepts/Normalization
| Database Concepts |
What is a Database | How a Database is Organized | Data Types | Normalization | Self Assessment | Summary & FAQs |
Database Normalization
Upon completion of this tutorial the learner will:
|
Entity relationships
An understanding of a subject domain increases as entities and their attributes are identified. The relationships among the entities becomes an essential part of your database design. When identifying entities and their relationships, think in terms of nouns and verbs. The entities are nouns and relationships are verbs. In the previous example of the Students and their Addresses; "Students" and "Addresses" are the entities (nouns) and "live at" and "contain" are the relationships (verbs).
| Wikipedia has a number of entity relationship and normalization based entries, here are a few of the most relevant;
A review of object role modeling can also provide a good method for identifying entities and relationships. |
Exploring first and second normal form
A solid understanding of normalization and normals forms is essential for database design. During database normalization you analyze entities and attributes through a series of rules known as normal forms. There are five basic normal forms, and each builds upon the rules of the previous. In other words, you cannot have a database design in third normal form without also meeting all the rules of first and second normal form. Consider the process of normalization as the process of simplification and the removal of redundancy. For our first review of normalization we are only going to look at the first and second normal forms. What you learn from these two normal forms will provide enough foundation to begin normalizing a database design.
First Normal Form
A database is said to be in first normal form when the tables;
- are guaranteed to not have any duplicate records (i.e. have a way to identify uniqueness within each record)
- do not have any repeating groups (i.e. {grade-id, course1, course2, course3} where course is the repeating group)
Second Normal Form
A database is said to be in second normal form when the tables;
- are in first normal form
- have fields (or attributes) that create a logical entity. And the fields relate back to the unique identifier of the record. (i.e. Students consist of first-name, last-name, gender, and birth-date. A phone number field would NOT be a part of the Student)
Normalize this
Normalize the following table into second normal form.
| person_id | first_name | last_name | birth_date | gender | phone_numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M | home: (604) 555-1234; fax : (604) 555-2345 |
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M | cell: (778) 555-2345 |
| 005 | Fiona | Jones | 26/10/1961 | F | home: (604) 555-1234; pager (605) 555-9988 |
| 006 | John | Morrison | 14/07/1951 | M | home: (604) 555-0987; fax: (604) 555-2345; cell: (877) 555-7654 |
| 012 | Lisa | Ballard | 11/03/1965 | F | home: (604) 555-1234 |
Using these 5 steps modify the above table into first, then second normal form;
|
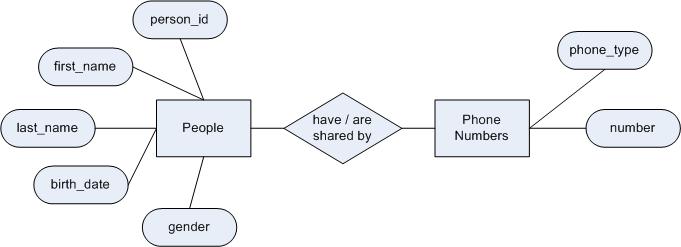
Step 1 (entity relationship diagram)
Step 2 (first normal form)
| person_id | first_name | last_name | birth_date | gender | phone_type | phone_number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M | home | (604) 555-1234 |
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M | fax | (604) 555-2345 |
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M | cell | (778) 555-2333 |
| 005 | Fiona | Jones | 26/10/1961 | F | home | (604) 555-4455 |
| 005 | Fiona | Jones | 26/10/1961 | F | pager | (604) 555-9988 |
| 006 | John | Morrison | 14/07/1951 | M | home | (604) 555-0987 |
| 006 | John | Morrison | 14/07/1951 | M | fax | (604) 555-0096 |
| 006 | John | Morrison | 14/07/1951 | M | cell | (877) 555-7654 |
| 012 | Lisa | Ballard | 11/03/1965 | F | home | (604) 555-6543 |
Step 5 (second normal form)
| person_id | first_name | last_name | birth_date | gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | Bill | Smith | 28/12/1963 | M |
| 005 | Fiona | Jones | 26/10/1961 | F |
| 006 | John | Morrison | 14/07/1951 | M |
| 012 | Lisa | Ballard | 11/03/1965 | F |
| phone_type | phone_number | person_id |
|---|---|---|
| home | (604) 555-1234 | 001 |
| fax | (604) 555-2345 | 001 |
| cell | (778) 555-2333 | 001 |
| home | (604) 555-4455 | 005 |
| pager | (604) 555-9988 | 005 |
| home | (604) 555-0987 | 006 |
| fax | (604) 555-0096 | 006 |
| cell | (877) 555-7654 | 006 |
| home | (604) 555-6543 | 012 |
- You will notice that the person_id is present in both the People and PhoneNumbers tables. This allows you to join the phone numbers to their people 'owners'. More on keys in the next section.
If your getting bored with all this theory
Well we've covered enough material where you could jump into actually building a database. So go to tutorial 5.2 (Designing and creating tables) and get your hands dirty. I would strongly recommend you come back to this section as we are going to get deeper into normalization and how to build a database in third normal form.
Test your knowledge