CCNC/CCNC Module 5/The database application/Database Concepts/How a Database is Organized
| Database Concepts |
What is a Database | How a Database is Organized | Data Types | Normalization | Self Assessment | Summary & FAQs |
Contents
[hide]How a Database is Organized
Outcomes
Upon completion of this tutorial the learner will:
|
Tables Records and Fields
A database is a collection or tables. The tables contain records that are organized into fields. Or using database terminology; A database is a collection of entities. The tables contain data that are organized into attributes. The use of these two terminologies is frequent when working with databases; become familiar with the terms table and entity, data and record and field and attribute being used interchangeably. Another important concept is the idea of a design view and a query view. Consider the two tables below, one being design view the second being query view;
A design view is a look at the structure of a table as it is being designed.
| field name | data type | length | allow nulls |
|---|---|---|---|
| first_name | Text | 32 | No |
| last_name | Text | 64 | No |
| birth_date | Date | 10 | No |
| gender | Char | 1 | Yes |
- field name is the name given to the field as it will be stored in the database.
- data type is the type of data stored in the database. Usually; Numeric, Text, Date or Char.
- length is the number of characters long the field will be.
- allow nulls indicates if the field can be left blank or empty
A query view is a look at the data in rows and columns. Notice the field names from design view are the column headers in query view.
| first_name | last_name | birth_date | gender |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peter | Rawsthorne | 28/12/1963 | M |
| David | Rawsthorne | 26/10/1961 | |
| Lisa | Rawsthorne | 11/03/1965 | F |
| Malcolm | Rawsthorne | 03/05/1987 | M |
| Hannah | Rawsthorne | 23/09/1989 | F |
Note: it is common for field names to not contain spaces. There are a number of different conventions for naming fields which can change depending on the standards defined by the organization you are working. The convention used in this course is to be clear with your field names and use underscores for spaces. (i.e. 'first name' becomes first_name)
Design an address entity;
|
Identifying entities and attributes
This is where we start to use the small school scenario introduced at the beginning of this module. From now on all the analysis and design we do will be based upon this scenario.
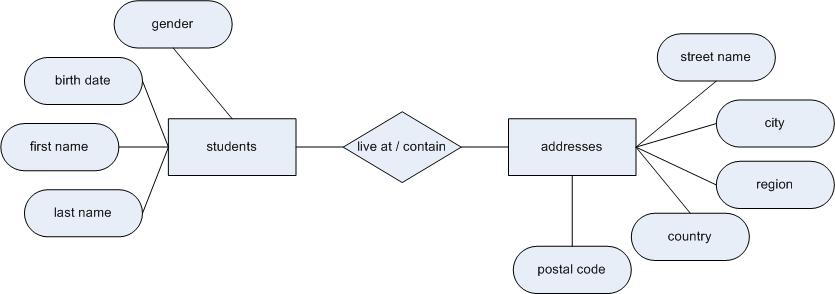
Identifying entities and attributes could be considered both and art and a science. It is an art for you need to bring together and analyze information from many different sources. The ability to understand a subject domain and identify the entities with their attributes challenges you to see something virtual from many perspectives and groupings, this can be a very creative process. It is also a science for we use proven analysis processes based upon relational algebra, this process refines how our database is structured into entities and attributes. Analyzing a subject domain for the purpose of designing a database means you identify three things; the entities, which are objects you seek information, the attributes, which are the data collected for an entity and the relationships among entities.
This simple diagram shows the relationship between the students and addresses entities.
And once we begin to add attributes to the entities, the diagram will look like this;
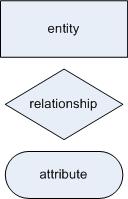
Entity diagram symbols
The symbols used to create these entity relationship diagrams are as follows;
Read over the small school scenario and using a paper and pencil identify all the entities described.
|
Test your knowledge