Smitashukla2

|
Introduction |
Economic efficiency of any firm operating in the market is determined by the ability of the firm to minimize cost and maximization the profits. Study of cost and its behavior as production pattern changes in the short run and the long run, gives useful insight into issues like: (I) How the cost pattern of a firm changes in case a firm is operating in the short run? (II) How the cost changes along with the change in the scale of production? (III) How the cost of operation can be minimized? (IV) What is the optimum level of operation of any firm (at optimum level the cost of the firm is generally reaches its minimum level)?
Cost is a function of Output. As the output of a firm changes the cost pattern of a firm also undergoes change. In this module various cost concepts are being explained in detail.
Learning Objectives
This model covers and explains various cost concepts which are critical and important in varied business operations and market situations. It is expected that after completion of the module the learner will be able to identify and relate to various cost aspects and concepts which any firm frequently has deal with, understand and control in the real life market situations.
Some Important Cost Concepts
- Opportunity Cost
- Money Cost and Real Cost
- Accounting Cost and Economic Cost
- Private Cost and Social Cost
- Fixed Cost, Variable Cost, Average Cost and Marginal Cost
Cost Concepts in Detail
Opportunity Cost
The resources of any firm operating in the market are limited and investment options are many. The firm therefore has to decide or select only those investment opportunities/options which provide the firm with the best return or best income on investment. This means that if a firm can invest money/ resources only in one investment option then the firm will select that investment option which promises best return on investment to the firm. In other words while doing so the firm gives up/rejects the next best option for investing the funds. The opportunity cost of a company is thus this income/ return which the firm could have earned on the next best investment alternative. Concept of opportunity cost is closely related to the concept of Economic profit. A firm earns or makes Economic profit only when besides covering various costs of operation, a firm is also able to earn more than its opportunity cost (or its possible earnings under the next best investment alternative). Opportunity Cost is also termed as Implicit Cost
Economic Profit is thus earned only when following is true for the Firm:
Income of a Firm > Various Costs of Operations + Opportunity Cost
Some simple examples of Opportunity cost are:
- Mr. Subodh has two job opportunities in hand. First job opportunity can help him to earn Rs. 20, 000 per month and the second opportunity can get him Rs. 15, 000 per month. Under normal circumstances Mr. Subodh will opt for the job opportunity which can help him to earn Rs. 20, 000 per month. In the process Subodh rejects the other job opportunity which can help him to earn Rs. 15, 000 per month. In this case Opportunity cost of Mr. Subodh is Rs. 17, 000 per month as this is the income which the can be earn from the next best alternative
- Miss. Kanta can invest her money under the following two investment options (a) Investment in Shares. Such Investment (investment made in the shares) is likely to provide Miss Kanta with return of 20% per annum. (b) Investment in Government Bonds which can provide Miss. Kanta with return of 10% per annum on the amount invested in the bonds. If it is assumed that risk involved in investing in the stocks/shares is very moderate then Miss. Kanta will most likely invest in shares (on account of higher return on investment in shares in comparison to the bonds. In this case the opportunity cost is the return of 10% per annum, which can be earned by Miss Kanta in the next best investment alternative
Money Cost and Real Cost
Money Cost of production is the actual monetary expenditure made by company in the production process. Money cost thus includes all the business expenses which involve outlay of money to support business operations. For example the monetary expenditure on purchase of raw material, payment of wages and salaries, payment of rent and other charges of business etc can be termed as Money Cost.
Real Cost of production or business operation on the other hand includes all such expenses/costs of business which may or may not involve actual monetary expenditure. For example if owner of a business venture uses his personal land and building for running the business venture and he/she does not charge any rent for the same then such head will not be considered/included while computing the Money Cost but this head will be part of Real Cost computation. Here the cost involved is the Opportunity Cost of the land and building. If the promoter of the company had not used the land and building for the business venture then they could have been used elsewhere and would have generated some income for the promoter. This income/rent which could have been earned under the next best alternative is the opportunity cost which is a part of the Real Cost expenses of the firm.
Accounting Cost and Economic Cost
Accounting Cost includes all such business expenses that are recorded in the book of accounts of a business firm as acceptable business expenses. Such expenses include expenses like Cost of Raw material, Wages and Salaries, Various direct and indirect business overheads, Depreciation, Taxes etc. Is from the Sales income of any firm the accounting expenses including the taxes are deducted then for a firm we get the data of its profit after tax. Such expenses or costs are also termed as Explicit Costs. Economic cost on the other hand includes all the accounting expenses and the Opportunity cost or Implicit cost of the business. Economic Cost and Economic Profit is thus calculated as follows:
Economic Cost = Accounting Cost (Explicit Costs) + Opportunity Cost Economic Profit = Total Revenues - (Accounting Cost + Opportunity Cost)
Private Cost and Social Cost
The actual expenses of individuals/ firms in the market can be termed as private cost. Thus for a business firm this may include expenses like Cost of raw material, salaries and Wages, Rent, Various overhead expenses etc. For an individual his/her private expenses can be expenses on food, rent of house, expenses on clothing, expenses on travel, expenses on entertainment etc can be considered as Private Costs. Social Cost on the other hand includes the private costs of individuals and firms and also the cost of damage/disutility caused by the operations of individuals and the business firms. For example is a Tannery releases its toxic wastes in the river flowing nearby then such act results in water pollution and environmental damage. Such damage/loss/cost is added to the private costs to get fair idea of Social cost.
Social Cost of an individual will include his private cost and the cost of damage on account of his actions (that has resulted in doing harm/damage to the environment/society at large).[1]
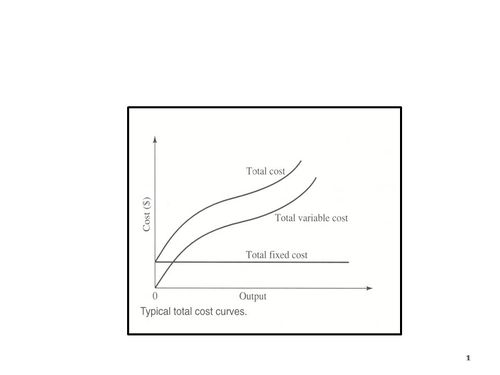
Fixed Cost, Variable Cost, Average Cost and Marginal Cost
Fixed Cost is that cost which does not change (that is either goes up or goes down) irrespective of whether the firm is operating or not. For example on account of Strike on account of Lockout in Maruti-Suzuki’s Manesar plant the production process stands still. Even when the plant is not operating the Firm still has to bear such expenses which are indirect in nature. For Example Rent of the factory premises, Wages of administrative employees etc. In other Fixed cost is not related direct production/manufacturing expenses.
Variable Cost on the Other hand is directly proportional to the production operations. As the size of production at any business grows, along with that grow the variable expenses. As the name suggests, the variable expenses vary with the business operations. When the firm is not operating on account of Strike/Lockout etc, then the variable cost of the firm is Zero
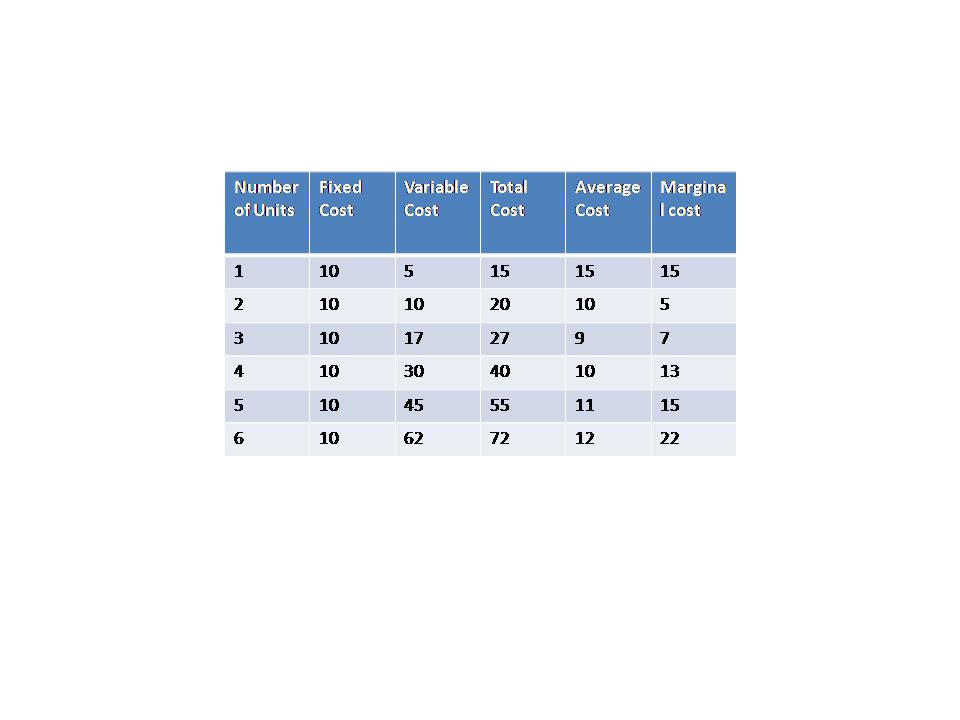
Average Cost is the cost that is obtained after dividing Total Cost with the number of units produced.
- Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost
- Average Cost = Total Cost / Units of Good produced
Marginal Cost is the change in the Total cost when an additional unit of good is produced. In other words Marginal Cost is difference between total Cost of producing ‘N + 1’ units of good and ‘N’ units of good
- Marginal Cost = TC (n+1) - TC(n)
Following table can help in understanding the cost concepts like Total Cost (TC), Average Cost (AC), Marginal Cost (MC) etc
Let us sum up
Various cost concepts help in understanding the business operations and cost involved in business operation of the firms better. For example opportunity cost is the return involved in the next best alternative. Social cost is the cost of damage caused by a business firm/individual to society at large. Private cost are the varied business expenses which a firm/individual has to bear on account of its business/personal operations pertaining to the business of the firm.
{{{4}}}==Points to Remember==
- The opportunity cost of a company is thus this income/ return which the firm can earn on the next best investment alternative.
- Money Cost of production is the actual monetary expenditure made by company in the production process. Money cost thus includes all the business expenses which involve outlay of money to support business operations.
- Real Cost of production or business operation includes all such expenses/costs of business which may or may not involve actual monetary expenditure. Economic cost includes all the accounting expenses and the Opportunity cost or implicit cost of the business.
- The actual expenses of individuals/ firms in the market can be termed as private cost. Thus for a business firm this may include expenses like Cost of raw material, salaries and Wages, Rent, Various overhead expenses etc. For an individual his/her private expenses can be expenses on food, rent of house, expenses on clothing, expenses on travel, expenses on entertainment etc can be considered as Private Costs.
- Social Cost on the other hand includes the private costs of individuals and firms and also the cost of damage/disutility caused by the operations of individuals and the business firms. For example is a Tannery releases its toxic wastes in the river flowing nearby then such act results in water pollution and environmental damage. Such damage/loss/cost is added to the private costs to get fair idea of Social cost.
- Fixed Cost: Fixed Cost is that cost which does not change (that is either goes up or goes down) irrespective of whether the firm is operating or not.
- Variable Cost on the Other hand is directly proportional to the production operations. As the size of production at any business grows, along with that grow the variable expenses. As the name suggests, the variable expenses vary with the business operations. When the firm is not operating on account of Strike/Lockout etc, then the variable cost of the firm is Zero
- Average Cost on the other hand is the cost that is obtained after dividing Total Cost with the number of units produced.
- Marginal Cost is the change in the Total cost when an additional unit of good is produced. In other words Marginal Cost is difference between total Cost of producing ‘N + 1’ units of good and ‘N’ units of good
For Practice Problems move to next Page {{{7}}}
Practice Test
- Identify Type of Cost
- Salary of the administrative staff of a firm which is going through lockout
- The income that can be earned under chance of investing in National Saving Certificates (Possible Return 10% per annum) and investing in shares (Possible Return 20%)
- Cost of Raw Material used in the Production Process
- The cost of producing 10th unit of good after producing 9 units of good
- Soda Ash released by power plant
- Explain following Cost Concepts
- Opportunity Cost
- Social Cost
- Private Cost
- Money Cost
- Real Cost
- State the difference between following Cost Concepts
- Social Cost and Private Cost
- Fixed Cost and Variable Cost
- Marginal Cost and Average Cost
- Money Cost and Real Cost
- The Profit and Loss Account Statement of M/S Singh and Sons gives us following details
- Sales = Rs. 10, 00, 000
- Direct Expenses = 4, 00, 000
- Indirect Expenses = 2, 00, 000
- Corporate Tax = 1, 00, 000
- It is also known to us that the shareholders who have invested their money in M/S Singh and Sons could have earned at least Rs. 1, 20, 000 per annum under second best investment alternative for them. In view of the details, calculate the following:
- Accounting Profit
- Economic Profit
- Opportunity Cost
Answer to 1
- Fixed Cost
- Opportunity Cost
- Variable Cost
- Marginal Cost
- Social Cost
Answer to 4
- Accounting Profit = 3, 00, 000
- Economic Profit = 1, 80, 000
- Opportunity Cost = 1, 20, 000

|
Further Readings |

|
References and Bibliography |
REFERENCES
- ↑ D.N. Divedi,Managerial Economics,Vikas Publication