The Anatomy and Physiology of Animals/Nervous System Worksheet/Worksheet Answers
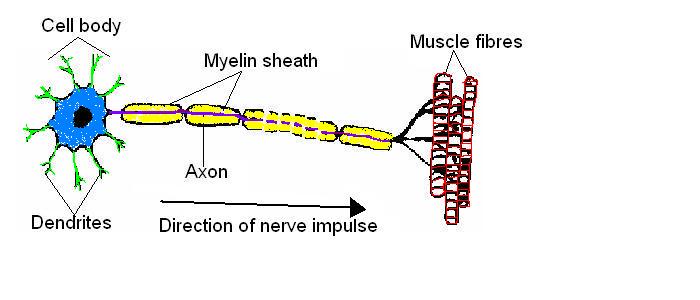
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neurone.
- i. Add the following labels to the diagram.
- Axon; Myelin sheath; Cell body; Dendrites; Muscle fibres;
- ii. If you like, colour in the diagram as suggested below.
- Axon - purple;
- Myelin sheath - yellow;
- Cell body - blue;
- Dendrites - green;
- Muscle fibres – red;
- iii. Now indicate the direction that the nerve impulse travels.
2. There are three different kinds of neurone or nerve cell. Match each kind with its function.
- A. Motor neuron; B. Sensory neuron; C. Relay neuron;
| Kind of neurone | Function |
|---|---|
| B. Sensory neuron | The nerve cell that carries impulses from a sense receptor
to the brain or spinal cord. |
| C. Relay neuron | The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons |
| A. Motor neuron | The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain
or spinal cord to a muscle or gland |
3. Match the descriptions in the table below with the terms in the list.
| Term | Function |
|---|---|
| B. Axon | 1. The long fibre that carries the nerve impulses. |
| J. Nerve | 2. A bundle of axons. |
| A. Synapse | 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. |
| K. Neurotransmitter | 4. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. |
| G.Reflex | 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. |
| C. Myelin sheath | 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up
the passage of nerve impulses. |
| L. Axon terminal | 7. The structure at the end of an axon that produces neurotransmitters
to transmit the nerve impulse across the synapse. |
| D. Nerve impulse | 8. The high speed signals that pass along the axons of nerve cells. |
| I. Dendrites | 9. The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. |
| E. Sense receptor | 10. The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from
within and outside the body. |
| F. Response | 11. The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. |
| H. Cell body | 12.The part of the nerve cell containing the nucleus. |
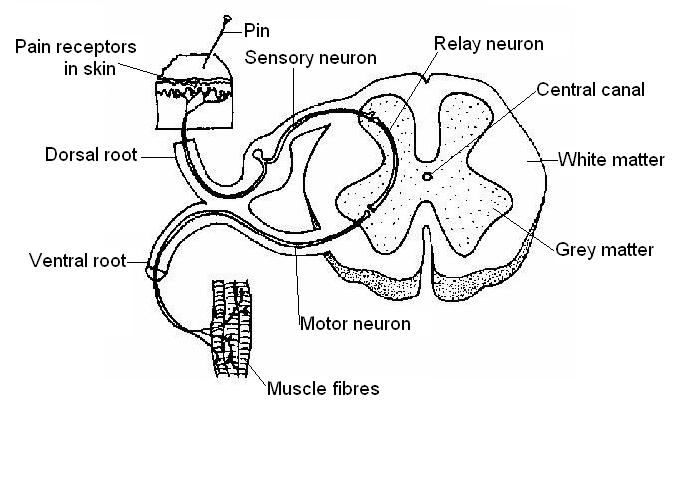
4. The diagram below shows a cross-section of the spinal cord. Add the following labels to the diagram.
- Central canal; White matter; Dorsal root; Grey matter; Ventral root; Skin;
- Muscle; Sensory neuron; Relay neuron; Motor neuron; Pain receptors in skin
5.
- a) List in order the 3 different neurons involved in a reflex arc from the stimulus to the response.
| Stimulus | sensory neuron | relay neuron | motor neuron | Response |
|---|
- b) Name 3 different reflexes found in animals.
Reflex 1. Blink reflex.
Reflex 2. Paw pinch reflex.
Reflex 3. Swallowing reflex, plus many others.
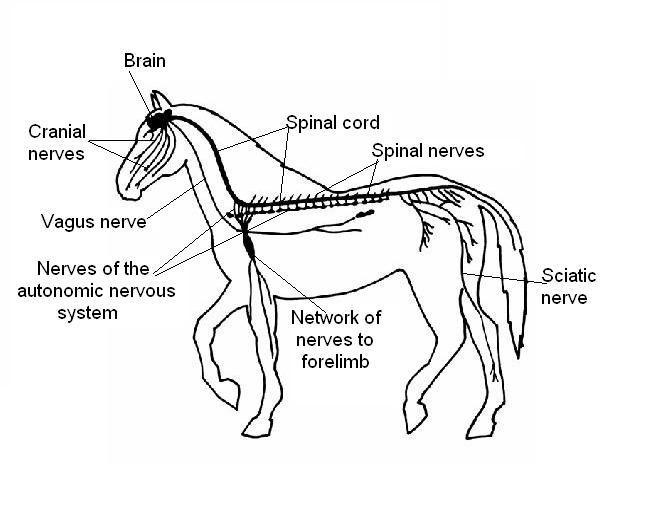
6. The diagram below shows the nervous system of a horse. Add the following labels.
- Brain; Spinal cord; Cranial nerves; Spinal nerves; Sciatic nerve; Nerves of the autonomic nervous system; Vagus nerve; Network of nerves to forelimb.
7. Indicate whether the following parts of the nervous system are part
of the Central Nervous System CNS) or the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
| Part of nervous system | CNS or PNS? |
|---|---|
| Brain | CNS |
| Autonomic nervous system | PNS |
| Spinal nerves | PNS |
| Spinal cord | CNS |
| Cranial nerves | PNS |
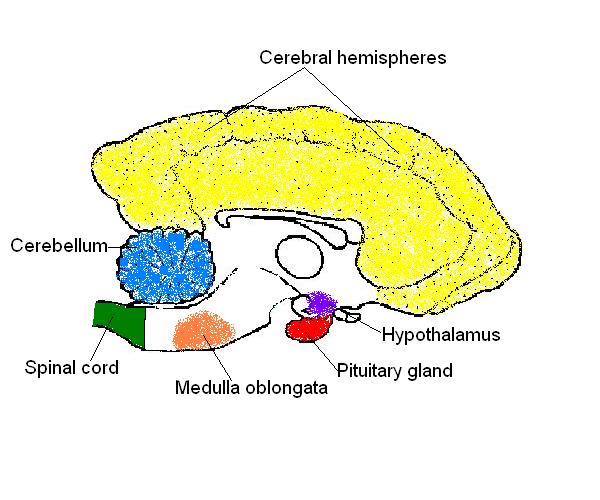
8. The diagram below shows a section of a dog’s brain. Add the labels
in the list below and, if you like, colour in the diagram as suggested.
- Cerebellum - blue;
- Spinal cord - green;
- Medulla oblongata - orange;
- Hypothalamus - purple;
- Pituitary gland - red;
- Cerebral hemispheres – yellow.
9. Match the descriptions below with the terms in the list. You may need to use some terms more than once.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| E. Hypothalamus | 1. Controls water balance and body temperature. |
| D.Medulla oblongata | 2. Where the respiratory rate is controlled. |
| C. Cerebellum | 3. Where posture, balance and voluntary muscle movements are controlled. |
| A. Cerebral hemispheres | 4. Contains centres governing mental activity, including intelligence,
memory, and learning. |
| H. Meninges | 5. The tough fibrous envelope enclosing the brain and spinal cord. |
| F. Pituitary | 6. The “master” gland of the endocrine system. |
| Cerebral hemispheres/cortex | 7. Responsible for instigating voluntary movements. |
| J. Cerebrospinal fluid | 8. The fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. |
| G. Grey matter | 9. Composed of cell bodies and nuclei. |
| B. White matter | 10. Composed of axons. |
| Cerebral hemispheres/cortex | 11. Where the sensations of sight, sound, taste etc. are interpreted. |
| I. Ventricles | 12. Spaces in the brain filled with cerebral spinal fluid. |
| K. Sulcus | 13. A fold in the cerebral cortex. |
| L. Carotid artery | 14. The artery that supplies the brain with oxygenated blood. |
10. Match the descriptions below with the parts of the nervous
system in the list. You may need to use some terms more than once.
| Description | Part of the nervous system |
|---|---|
| 1. Part of the nervous system that is composed of the
brain and the spinal cord. |
B. Central nervous system |
| 2. Part of the nervous system that is composed of the
cranial and spinal nerves. |
C. Peripheral nervous system |
| 3. The part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates
the activity of the heart and smooth muscle. |
A. Autonomic nervous system |
| 4. The part of the autonomic nervous system that increases heart and
respiratory rates, increases blood flow to the skeletal muscles and dilates the pupils of the eye. |
E. Sympathetic nervous system |
| 5. The part of the autonomic nervous system that increases gut activity
and decreases heart and respiratory rates. |
D. Parasympathetic nervous system |
11. Name the nerves described below using the choices in the list.
| Nerve | Description |
|---|---|
| Vestibular nerve | 1. The 8th cranial nerve that carries impulses from the organs of
balance and hearing to the brain. |
| Optic nerve | 2. The 2nd cranial nerve that carries nervous impulses from the
retina of the eye to the brain. |
| Sciatic nerve | 3. The largest nerve in the body serving the muscles of the leg. |
| Olfactory nerve | 4. The 1st cranial nerve that carries impulses from the organ of smell
in the nose to the brain. |
| Vagus nerve | 5. The 10th cranial nerve that supplies the pharynx, lungs, heart,
stomach and most of the abdominal organs. |