The Anatomy and Physiology of Animals/Digestive System Worksheet
Chapter 11 The Gut and Digestion
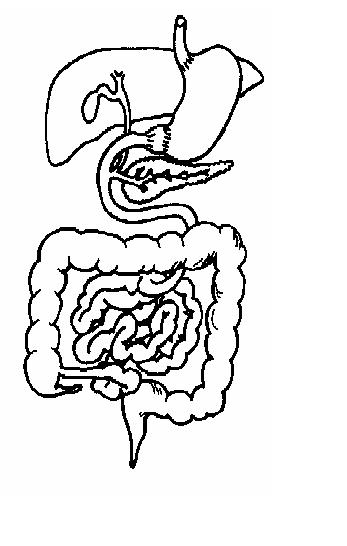
1. Add the following labels to the diagram of a mammal’s gut below.
- pancreas; caecum; stomach; rectum; gall bladder
- pyloric sphincter; small intestine; colon; liver; oesophagus; bile duct
2. Match the region of the digestive system in the list below with the correct function.
- A. Rectum, B. Pancreas, C. Functional caecum, D. Pharynx, E. Stomach, F. Gall bladder
- G. Colon, H. Tongue, I. Liver, J. Small intestine, K. Oesophagus, L. Salivary glands
- M. Pyloric sphincter, N. Rumen
| Region/organ | Function |
|---|---|
| .......................... | Produces the enzymes to digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the small intestine.
Also produces the hormone insulin |
| ......................... | Organ that mixes food in the mouth and makes swallowing happen |
| ......................... | Micro-organisms digest cellulose in this modified part of the stomach |
| ......................... | Produce saliva containing salivary amylase |
| .......................... | Carries the food from the mouth to the stomach |
| ......................... | Stores bile |
| .......................... | This muscle controls the passage of food out of the stomach |
| .......................... | Both food and air pass along this |
| .......................... | Indigestible matter held here before defecation |
| ........................ | Produces bile |
| ........................ | A bag made of muscle where food is held. Gastric juice and
hydrochloric acid are added here. |
| ........................ | Where food is mixed with bile and digestion of proteins, fats and
carbohydrates takes place |
| ........................... | Water and salt are absorbed here |
| ........................... | Where micro-organisms digest fibre in rabbits and horses |
3. True or False?
- a) Carnivores eat meat, herbivores eat plants and omnivores eat both. T / F
- b) These are all herbivores: cows, horses, goats, giraffes, rabbits and guinea pigs. T / F
- c) Plant material has high food value and animals need to eat only a little to get all the nutrients they need. T / F
- d) Herbivores have well developed teeth for crushing and grinding plant cell walls. T / F
- e) Herbivores have glands that produce enzymes to digest plant material. T / F
- f) The rumen holds micro-organisms that digest cellulose. T / F
- g) Animals with a rumen also have a functional caecum to help digest cellulose. T / F
- h) Carnivores need to eat most of the day to get enough nutrients. T / F
- i) Carnassial teeth are modified canines for shearing flesh and bone. T / F
- j) Open rooted teeth are found in rats and rabbits and grow throughout the animal’s life T / F
- k) The numbers in a dental formula indicate the numbers of different kinds of teeth in one side only of the mouth of an animal. T / F
- l) Dentine is the hardest substance in a tooth. T / F
4. Match the terms in the list below with the descriptions in the table
- Canines, Diastema, Dentine, Incisors, Open rooted, Enamel, Molars, Premolars, Carnassial teeth, Dental formula
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| ..................... | Hardest substance in the body; covers the tooth |
| .................... | Found under the enamel of the tooth |
| ..................... | Chisel-shaped teeth at the front of the mouth |
| ..................... | The way in which the number of the different kinds of teeth of mammals can be expressed |
| .................... | A space in the mouth of rodents and herbivores where the canines would normally be. |
| .................... | These teeth keep growing through the life of the animal. (E.g. in rodents). |
| .................... | These teeth are used for grinding food. |
| ..................... | These teeth are also used for grinding food. |
| .................... | Long cone shaped teeth, well developed in carnivores, form tusks in male pigs (boars). |
| ....................... | These teeth are found in carnivores. They are formed from premolars and molars and are used for shearing flesh |
5. Circle the odd one out.
- a) Rabbit, guinea pig, horse, goat, rat, zebra
- b) Sheep, cow, goat, antelope, giraffe, pig, camel
- c) Incisors, canines, carnassials, molars, premolars
- d) Stomach, oesophagus, liver, small intestine, rectum, caecum.
- e) Saliva, bile, pancreatic juice, chyme, gastric juice
- f) Pancreas, salivary glands, liver; gall bladder; intestinal glands
- g) Pepsin, amylase, lipase, bile, protease
- h) Reticulum, functional caecum, omassum, abomassum, rumen,
6. The dental formula below is of a rabbit.
- 2 0 3 3
- 1 0 2 3
This formula indicates that the rabbit:
- a) has a total of 3 incisors, 5 premolars and 6 molars
- b) has a diastema
- c) has open rooted teeth
- d) eats plant material
7. Peristalsis is:
- a) the rhythmic contraction of the smooth muscle in the gut wall to push food along
- b) the secretion of bile into the small intestine when a fatty meal is eaten
- c) the churning movement of the stomach to mix its contents
- d) the rhythmic contractions of the diaphragm to produce hiccups
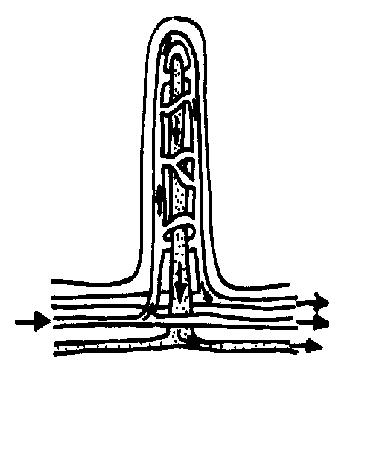
8. Colour in (and label) the diagram of a villus in the small intestine using the colours suggested below.
- Outer layer of columnar epithelium - Yellow
- Artery - Red
- Vein - Blue
- Lymphatic vessel - Green
- Capillaries - Red turning to blue
- Label the lacteal; lumen of the gut; artery; vein; lymphatic vessel
9. Arrange the following parts of the digestive system in the order in which food passes through on the way from the mouth to the anus.
- A. pharynx, B. pyloric sphincter, C. rectum, D. stomach
- E.caecum, F. small intestine, G. colon, H. oesophagus
| mouth | .................. | .................. | .................. | .................. | ................. | ................. | ................. | ................. | anus |
|---|
10. The digestive enzymes in the gut break down the large food molecules into smaller ones that can be absorbed through the walls of the villi.
Complete the table below showing the large food molecules, the enzymes that digest them and the product of that breakdown.
| Large molecule | Digestive enzyme | Small molecule after digestion |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates e.g. Starch | ........................ | ........................ |
| ........................ | ........................ | Fatty acids and glycerol |
| ........................ | Pepsin, protease | ........................ |
11. Some of these are functions of the liver: (Circle seven)
- Making bile
- Producing heat
- Storing bile
- Making digestive enzymes
- Storing vitamin A
- Making insulin
- Storing glycogen
- Storing copper
- Storing iron
- Removing toxic molecules like alcohol from the blood
- Making blood proteins
12. Just for fun!
There are a number of errors in the description of digestion below. Correct as many as you can find.
- Food egested by the animal is bitten off by the canine teeth and chewed by the incisors.
- Saliva, an acid solution secreted by the tonsil glands, contains the enzyme pepsin which begins the digestion of fats.
- In the stomach pyloric juice is secreted which contains enzymes to digest starch. In all herbivore animals the small intestine is modified into a two chambered organ called the gizzard. Here the grass etc. is mixed with micro-organisms that break down the protein plant walls.
- A ring of muscle called a rictus controls the passage of food from the stomach into the caecum, where gall and pancreatic juice are secreted. Hydrochloric acid is also secreted here to make the chyle acidic.
- In the small intestine villas increase the surface area for absorption of the digested material. Food then passes into the colon on its way to the caecum.
- In horses and sheep the facultative colon holds micro-organisms which break down animal cell walls. In the reticulum gas is absorbed and the waste material passes out of the digestive system via the urethra.