PRICE EFFECT
MICROECONOMICS

|
PRICE EFFECT |

|
Introduction |
At the market place a consumer faces market conditions that change constantly. Some times there is increase in the price of a good or there is decrease in the price. As a policy change new taxes are imposed on goods or the goods are subsidized. These situations lead the consumer to change her/his consumption, in order to maximize the utility of spendable income. The analysis of price changes on consumption, therefore, is an important part of the theory of consumer's behavior.
In term of indifference curves analysis,as explained in the section on CONSUMER'S EQUILIBRIUM, we have seen how the optimal consumption combination, the one that maximizes the utility of consumer's spendable income, is determined at a point where budget constraint is tangent to an indifference curve. The price effect on the other hand measures consumer's movement from one optimal consumption combination to another, on her/his indifference map, as a result of change in the price of a good. Hick's price effect, discussed in this section, explains the logic and process of decision making by the consumer to arrive at optimal decision, as a response to price changes.
| Price Effect |
The price effect represents change in consumer’s optimal consumption combination on account of change in the price of a good and thereby changes in quantity purchased, price of another good and consumer’s income remaining unchanged. The consumer is better-off when optimal consumption combination is located on a higher indifference curve and vice versa. In the words of Lipsey," The price effect shows how much satisfaction of the consumer varies due to the change in the consumption of two goods, as the price of one changes, the price of the other and money income remains constant." []
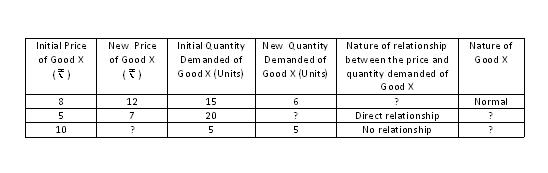
Understand that a consumer's responses to a price change differ depending upon the nature of a good, viz. a normal good, inferior good or a neutral good. Accordingly we have different types of price effects such as positive, negative and zero price effects. These types of price effect corresponding to consumer's responses for different nature of goods are summarized in chart.1:
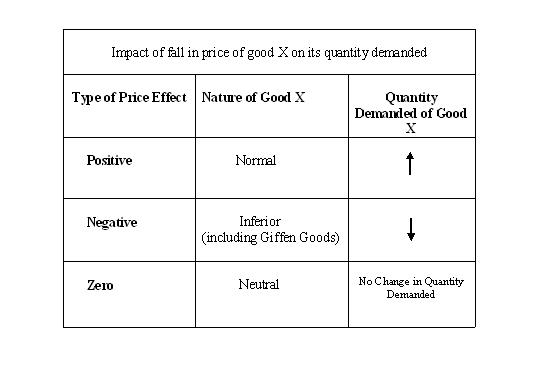
Thus, a price effect is positive in case of normal goods. There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. It is negative in case of inferior goods (including Giffen goods) where we find a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. Finally, price effect is zero in case of neutral goods where consumer's quantity demanded is fixed.
Solve the following activity. We then move on to understand positive, negative and zero price effects with the help of indifference curves.
In the following subsections we discuss positive, negative and zero price effects with the help of indifference curves.