Logic model
Overview
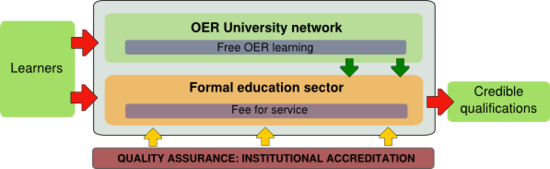
The OER universitas (OERu) concept aims to create a parallel learning universe based solely on OER to augment and add value to the formal education sector. Learners may choose to enrol at formal education institutions in the traditional way or participate in free learning provided through the OERu network. Assessment and credential services will be provided by participating institutions on a cost-recovery basis or may be funded through scholarships or grants from the respective Ministries of Education.The OERu network will facilitate pathways for OER learners to gain credible credentials from participating institutions who will be formally accredited institutions in their national jurisdictions. Quality assurance and institutional accreditation is the foundation stone on which this parallel learning universe is based. The OERu concept must ensure equivalence and parity of esteem for qualifications gained through the OERu network. OER resources and systems used to support the OERu are free for reuse and re-purposing in the formal sector thus contributing to improved efficiencies and greater return on investment for participating institutions.
Contents
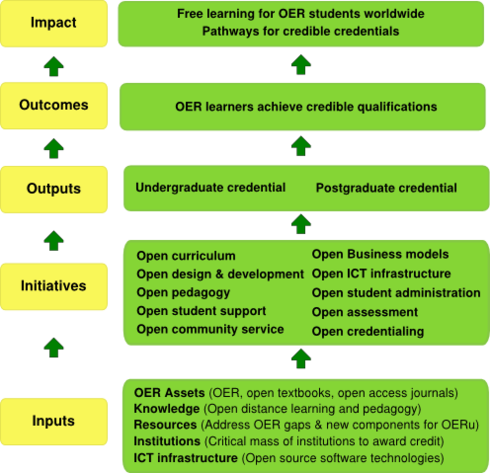
A logic model for planning OERu results
The logic model is directed by the intended impact of the OER universitas concept (OERu), namely to provide free learning opportunities for all students worldwide using OER. The OERu is designed primarily to provide affordable access to post-secondary education for the estimated 100 million learners in the world who are qualified for a seat in tertiary education today, but due to funding issues or lack of tertiary education provision will not be able to gain credible qualifications. The outputs of the OER university concept will also add value to existing tertiary education systems worldwide.
The overall aim of the OERu intervention is to:
|
In order to achieve the overall impact of the OERu, the logic model is structured according to the required inputs for key initiatives aimed at achieving a number of project outputs on the pathway to achieving the stated outcomes. These components of the logic model are summarised below.
Inputs
A number of important building blocks exist for input into the OERu:
- OER assets: There is a rapidly growing inventory of existing international educational resources which can be integrated into the open pedagogy model envisaged by the OERu. These include: open access content, open access journals, open textbooks, and OER.
- Existing expertise: There is a wealth of transferable experience from distance education and open distance learning to support the design and development of the OERu. In addition, the team at the OER Foundation has extensive experience in open models and approaches to building sustainable open systems. The project's commitment to transparent and open planning facilitates participation by OER thought leaders from around the world.
- Financial resources: Financial resources including contributions in time from participating institutions and external donor funding for strategic elements will be required to address gaps in available OERs and the design of new components of the OERu system.
- Participating institutions: To launch the project, the OERu aims to achieve a critical mass of anchor partners who agree to the core principles of engagement for providing formal academic credit for OERu courses. Initially, the project aims to recruit one institution from each of the major regions of the world. As an open project, all post-secondary that care about sharing knowledge as a core value of education are free to join the OERu in planning and implementing sustainable education futures.
- ICT infrastructure: Reliable and scalable open source software systems exist for implementing the OERu collaboration.
Initiatives
To facilitate planning and coordination across national boundaries, the project is sub-divided into a number of initiatives. Each initiative may include a number of activities (with corresponding inputs, outputs and outcomes) ultimately contributing to the implementation of an OER universitas.
The logic model aims to be sufficiently robust to accommodate the requirements for credible certification within the formal education sector so learners and society will have confidence in the qualifications, but also be flexible enough to leverage the potential OER offers for re-use and re-purposing for local learning contexts. Conceptually, the key initiatives of the logic model are grouped into three main categories with distinctive strategies for achieving financial sustainability of the OERu system which aims to provide free learning for all students worldwide.
| Initiative category | Description |
|---|---|
| OER universitas open collaboration | The grouping of initiatives necessary to enable the provision of free learning opportunities.
|
| Educational institution services |
The grouping of initiatives which are provided by registered education institutions in the formal education sector.
|
| OER support infrastructure |
Refers to the support infrastructure including open source software ICT infrastructure and sustainable business models.
|
The initiatives for each category are summarised in the following table:
| | |
| Open curriculum[1] |
|
| |
| |
| |
| | |
| |
| |
| |
| | |
| |
| |
| |
Activities for each initiative
Each of the initiatives will require a number of activities to achieve the envisaged outputs within the logic model. So for example, the Open design and development initiative will require staff who have the skills for the collaborative development of OER with knowledge of Creative Commons licensing. The Learning4Content project and the Open Content Licensing for Educators courses are examples of existing activities of the OER Foundation that contribute to the achievement of the outputs of a particular initiative. Determining and selecting the first qualifications for the OERu is an example of an activity required for the 'Open Curriculum initiative.
The detailed planning of the activities for each initiative will be linked from their respective initiative page or accessed via the planning portal for the OERu. Activities will specify detailed output targets, milestones and key performance indicators.
This logic model approach is designed to provide a framework for international collaboration where different institutions and individuals can take responsibility for leading the successful completion of the range of activities necessary for building the OERu.
Outputs
During the foundation phase of the OERu, we aim to develop two credentials. One undergraduate and one postgraduate credential. Depending on available resources and contributions from participating institutions, the project may develop more credentials. More detailed output statements will be specified as the project progresses.
Outcomes
Students who enrol for free learning opportunities provided by the OERu must achieve credible qualifications. More detailed metrics relating to targeted enrolment numbers and throughput will be specified as the project progresses.
Footnotes
- ↑ Critical path priority. OERu selects the first credential(s) to be offered.
- ↑ Solid experiential base on the team approach for design of ODL. However, new design approaches needed for cross-institutional collaboration and the dynamic web.
- ↑ Solid scholarship on digital literacies and early prototypes leveraging the pedagogy of discovery and social media.
- ↑ Prior experience of volunteer services in other domains are transferable. Scalable design for "Academic Volunteers International" needed plus integration of community service learning credits for student support.
- ↑ Solid experiential base for scalable assessment in ODL. Opportunities for networked open assessment exist.
- ↑ Protocols for prior learning assessment can be refined. Build on ground-breaking work of Transnational Qualifications Framework for VUSSC pioneered by COL. Map course articulation within existing organisational frameworks.
- ↑ New ground. Requires reallocation of existing resources -- not new money to achieve greater ROI of community service budget.
- ↑ Strategic priority to ensure institutions can cover the cost of engagement in OERu. Will also research of new national funding models based on funding academic services.
- ↑ Well advanced. Open source software solutions exist to cover the spectrum of ICT infrastructure required. Seamless OER content interoperability requires attention.
- ↑ Can piggyback existing institutional systems, but significant opportunities to streamline and enhance capabilities through collaboration.