Evaluation
| Learning and Teaching in Practice | |
|---|---|
| Module 9: Evaluation of Learning design | |
| Evaluation | Introduction | Reflective practice | Functions | Mixed methods | Summary |
How will you know if your design is effective? It is important to have a plan in place to gauge the success of your new or re-designed course or programme. The first thing to decide is when you will review your design. Will it be in the design phase, before you go live, during the pilot or once the course has finished? What criteria will you use to judge success? How will you gather your data? What will you do with the information obtained? These are all important things to consider.
The more phases you can evaluate the better, and it is best to start gathering feedback before the project is at the development stage. Otherwise it could turn out to be a very costly business. There are lots of different types of evaluation and how you evaluate depends on the reason for the evaluation. Several models of evaluation exist and it is a good idea to choose one and stick with it. More information on this later. There are a number of factors to consider when choosing how to evaluate.
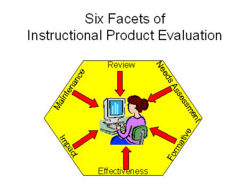
You may already be familiar with the terms: formative and summative, needs analysis, review, usability testing etc. Evaluation of learning design can include moderation but it is more. How much more is for you to find out.
- Listen to Evaluation and the ADDIE model- an explanation about how the ADDIE model fits with a range of evaluation methods, and how it may apply to your potential design and development project.
Emilia and Brett will help to guide you through the evaluation maze.
Emilia wants to gather feedback from a variety of different people to make sure her planned curriculum design for the Health Policy course is sound. She intends to ask several stakeholders to comment on the topics to be covered as well as the resources she is designing for the online classroom. For example:
|
| Brett wants to introduce a new learning strategy using smartphones so his students have more flexibility in how they create their ePortfolios. Presently, compiling evidence for assessment requires the use of Powerpoint for the portfolios which takes a lot of time. He decides to go ahead and trial three different mobile applications which can be used on smartphones as all his students have them. He plans to obtain feedback from students during the process.
Brett decides on an action research approach so that he can solve the problems associated with the current portfolio approach. He is hoping to find a more flexible way for his students to put together their assessment portfolios. He discusses different ways to collect data with a colleague who advises him to use three different methods. The word triangulation is mentioned so Brett investigates why this is important. |
|