INCOME EFFECT/Next
| Negative Income Effect |
The negative income effect measures changes in consumer's optimal consumption combination caused by changes in her/his income. Prices of goods X (PX)and Y (PY)remaining unchanged, where good X is an inferior good (including Giffen goods) and good Y is a normal good.
Assumptions:
1. Consumer's preference for combinations of goods X and Y is given as represented by the indifference map.
2. Goods X is an inferior (including Giffen Goods) good and good Y is a normal good.
3. Price of goods X (Px) and Y (Py) are given and constant.
4. Initial income is given.
Figure.2 starts with the initial optimal consumption combination attained at point e at which OX units of good X and OY units of good Y are purchased.
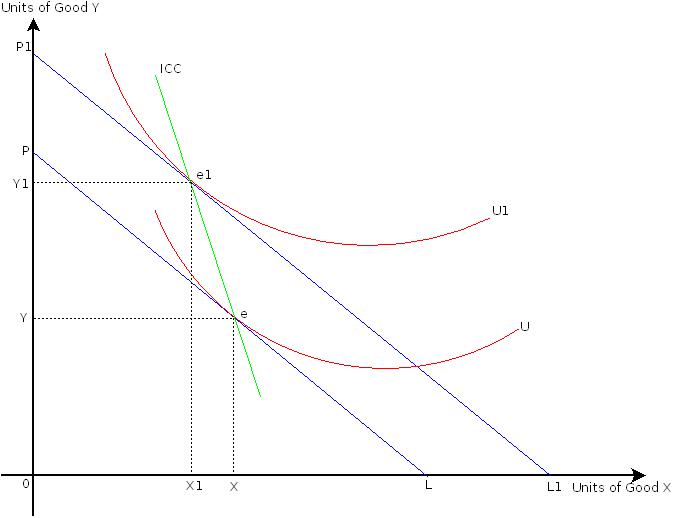
When income of the consumer increases, then entire budget constraint shifts outwards and it is a parallel shift. This is shown by budget constraint P1L1. The optimal consumption is now located at point e1, at which the consumer now buys OX1 units of good X and OY1 units of good Y.
Understand that consumer’s total utility has increased as the optimal consumption point is now located on a higher indifference curve. The consumer is better-off in terms of total utility. However, she/he reduces consumption of good X to OX1 units as good X is an inferior good. As mentioned in chart.1 we observe inverse relationship between income and quantity demanded of good X.The consumer increases quantity demanded of good Y to OY1 as good Y is a normal good. Here income effect is negative for good X.
The ICC obtained by joining optimal consumption combinations such as e, and e1, in Figure.2 rises upwards but bending backwards. It shows that the consumer successively moves on a higher indifference curve and becomes better off, with increase in her/his income. however, she/he also reduces purchase of good X as it is an inferior good. Chart.3 presents a summary of Figure.2.
| Zero Income Effect |
The zero income effect measures changes in consumer's optimal consumption combination caused by changes in her/his income. Prices of goods X (PX)and Y PY)remaining unchanged, where good X is a neutral good and good Y is a normal good.
Assumptions:
1. Consumer's preference for combinations of goods X and Y is given as represented by the indifference map.
2. Goods X is a neutral good and good Y is a normal good.
3. Price of goods X (Px) and Y (Py) are given and constant.
4. Initial income is given.
Figure.3 starts with the initial optimal consumption combination attained at point e at which OX units of good X and OY units of good Y are purchased.
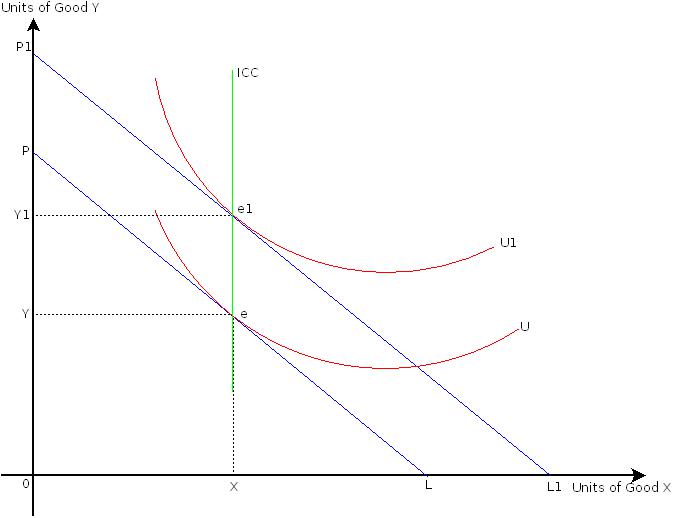
When consumer's income increases, then entire budget constraint shifts outwards and it is a parallel shift. This is shown by budget constraint P1L1. The optimal consumption is now located at point e1, at which the consumer now buys same OX units of good X and OY1 units of good Y.
Understand that consumer’s total utility has increased as the optimal consumption point is now located on a higher indifference curve U1. The consumer is better-off in terms of total utility. However, she/he keeps consumption of good X fixed at OX units as good X is a neutral good. As mentioned in chart.1 we observe no change in quantity demanded of good X.The consumer increases quantity demanded of good Y as good Y is a normal good. Here income effect is zero for good X.
The ICC obtained by joining optimal consumption combinations such as e, and e1, in Figure.3 is a vertical straight line. It shows that the consumer successively moves on a higher indifference curve and becomes better off, with increase in her/his income. However, she/he is keeping purchase of good X fixed as it is a neutral good. The consumer increases quantity demanded of good Y as it is a normal good.
Chart.4 presents a summary of Figure.3.
| Forms of Income Consumption Curve |
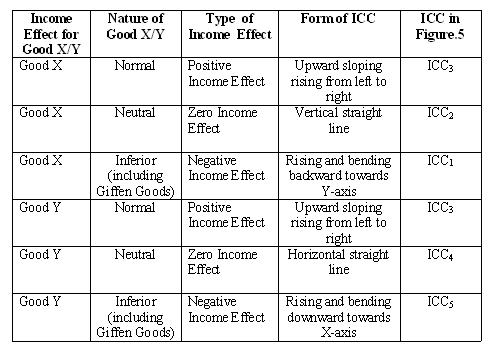
In the above discussion on positive, negative and zero income effects we have considered good X to be normal good, inferior good and neutral good respectively. Similarly, we can explain income effect for different types of good Y. Figure.4 shows different forms of ICC for different natures of good X or good Y.
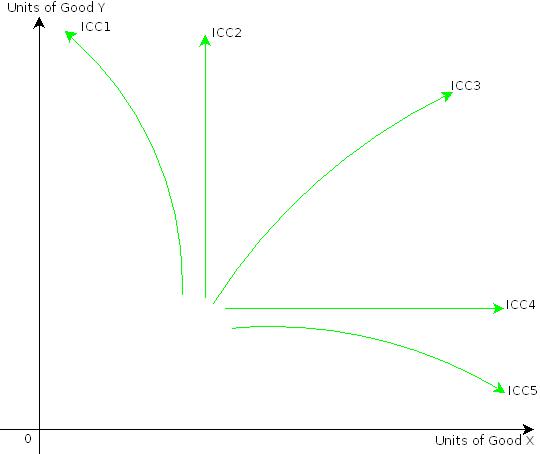
ICC1 is rising upwards and bending towards Y-axis. This form of ICC is obtained when good X is an inferior good (including Giffen goods). The ICC is a vertical straight line as shown by ICC2 when good X is a neutral good. It is a rising curve from left to right as shown by ICC3 when goods X and Y are normal goods.The ICC is a horizontal straight line as shown by ICC4 when good Y is a neutral good. Finally, ICC5 is rising upwards bending towards X-axis. This form of ICC is obtained when good Y is an inferior good (including Giffen goods). Chart.5 presents a summary of Figure.4.