Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project; A Teacher Collaboration on WikiEducator
Openly shared content, practices, and developing resources from Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project. Join this collaboration and make a difference!
 Bartlett Brook |
|---|
|
| Stream code: | LCD_BrtltBrk_139 |
| Basin: | Lake Champlain Direct |
| State or Province: | Vermont |
| Country: | USA |
| Latitude: | 44.42602563 |
| Longitude: | -73.21359202 |
| School: | Rice Memorial High School |
The following are the most common invertebrates collected from this stream site.
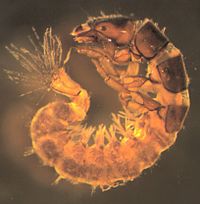
Chironomidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Chironomidae
- Common name
- Nonbiting midge
- Tied fly
- Griffith's Gnat
Midge larvae tend to be the most common macroinvertebrate at our sites. As with other Diptera, there are no true jointed legs. Chironomidae do have a pair of prolegs at each end and preserved individuals tend to curl into a 'C'. Identification past family requires slide-mounted heads. We have seen philopotamid caddisflies misidentified with the chironomids and we suspect that that happens when samples are being sorted from trays. Under a microscope, six prominent legs can be seen on members of the caddisfly family Philopotamidae.
More information on Philopotamidae.
Stenelmis
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Elmidae
- Genus
- Stenelmis
The larvae of
Stenelmis, as in
Ordobrevia, have a sternum on the ventral side of the pronotum. The main difference between the two genera is in the antennae the second segment is less than twice as long as the first in
Stenelmis.
The adult Stenelmis has a clear separation between the thorax and abdomen as well as a more distinctly separate head as compared to other genera.
Click here to see pictures of the sternum and
antennae-
Hydropsychidae
- Order
- Trichoptera (caddisfly)
- Family
- Hydropsychidae
- Common name
- net spinning caddisfly
- Tied fly
- Emergent Sparkle Pupa, Vermont Hare's Ear
This family of net-spinning caddisflies is very abundant at several sites. They are important filtering collectors and are quite common at urban and agricultural sites where particles of organic material can be important food resources. Genus-level identification is possible for mature specimens and we will include the genera we found at your site if possible.
When using the key, some features that are challenging to see are the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites in the folds between segments. Other, more easily seen key features include filamentous gills on the abdominal segments and the sclerotization of the dorsal surfaces of all three thoracic segments. Keep in mind that with smaller or more immature specimens, genus-level ID may not be possible.
Commonly found genera include Cheumatopsyche, Ceratopsyche, and Hydropsyche. Less commonly, we have found Arctopsyche and Potamyia.
Images of the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites.
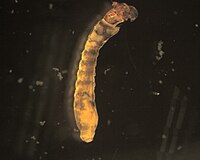
Antocha
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Tipulidae
- Genus
- Antocha
This small dipteran in the cranefly family is quite common. It is distinguished from most other dipterans we found by the 'creeping welts' that appear as prominent dark stripes along the abdomen. The dark head is usually partly exposed; however, it can be pulled back into the thoracic cavity during preservation.
Gammaridae
- Order
- Amphipoda
- Family
- Gammaridae
The body of this scud is flattened side-to-side. It has seven pairs of walking legs and two pairs of antennae. On third third antennal segment, there is a segmented flagellum.
Images of the body flattened side-to-side, and the segmented flagellum.
Cheumatopsyche
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Hydropsychidae
- Genus
- Cheumatopsyche
Cheumatopsyche has a
forked foretrochantin (as does
Ceratopsyche). The foretrochantin is the projection at the uppermost portion of the front leg closest to the head. The leg may need to be pulled away from the body to expose this feature.
Cheumatopsyche have a small or inconspicuous
pair of sclerites under the prosternal plate that are difficult to see. Contrast that with the
larger pair of sclerites found on Ceratopsyche. To access sclerites, it's best to gently pull the pronotum and mesonotum in opposite directions. Note: the large single sclerite is the prosternal plate.
Cheumatopsyche have only 2 types of
hair on the abdomen: long thin plain hairs and thicker club hairs, which are narrow close to the body and widen out at the distal end. Paired sclerites on the ninth abdominal segment are notched.
Hydropsyche
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Hydropsychidae
- Genus
- Hydropsyche
- Common name
- spotted caddis
- Tied fly
- dark cahill
Hydropsyche are net-spinning caddisflies and share most characteristics with other members of the Hydropsychidae, including the
Ceratopsyche.
Hydropsyche are distinguished from
Ceratopsyche by the presence of scale hairs and minute spines on the three most posterior abdominal segments.
More information on the Ceratopsyche can be found here.
Image of the sclerites in the intersegmental folds.
Optioservus
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Elmidae
- Genus
- Optioservus
The larvae of
Optioservus have open coxae, as determined by the straight definition between segments on the ventral side of the pronotum.
The adult Optioservus have a compact appearance, especially the head and thorax. There are also dorsal ridges and a characteristic diamond-shaped sutellum observable in the dorsal view.
Images of the straight definition between segments, the dorsal ridgesand the diamond-shaped scutellum.
Simuliidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Simuliidae
Simuliidae appear rather like bowling pins with heads. Relatively speaking, we collect few members of this family and have we have not identified them past family at this point.
Click here for a close up image of the heads.
Asellidae
- Order
- Isopoda
- Family
- Asellidae
- Common name
- sow bugs
These aquatic sow-bugs have seven pairs of legs and a dorso-ventrally flattened body. They have two pairs of antennae; one pair is much longer than the other pair.
Images of the body and the two pairs of antennae.