Ipyet/Creating an Enabling Environment - Youth Policy and Advocacy
| Work in progress, expect frequent changes. Help and feedback is welcome. See discussion page. |
Module 1.2: Creating an Enabling Environment: Youth Policy and Advocacy
A discussion paper by
Nellie Munala
Welcome to the ‘creating an Enabling Environment: Youth Policy and Advocacy’ session. It is my hopes that the discussions and engagements in this forum will assist us deepen our understanding on how we can utilize this information to promote youth entrepreneurship in our respective communities. I anticipate that the interactions will carry on long after the completion of this session for on-going peer support. I look forward to our active participation.
|
Contents
Introduction
The session will attempt to elaborate/define the major working definitions utilised in the discussions, that is: ‘enabling environment’ in regard to youth entrepreneurship, ‘youth policy’ and ‘youth enterprise’. The session will discuss key indicators that can facilitate an enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship to effectively occur. The discussions will then narrow down to one of the major indicators that support youth entrepreneurship – policy framework – this will lead to identifying good practices in policy formulation on youth entrepreneurship. A question is posed ‘Can youth entrepreneurship occur/flourish in the absence of an enabling framework in place’?
The discussions will lead to identifying opportunities as well as challenges in youth policy development and practice in regard to youth entrepreneurship. From participant’s experiences and contributions, the session will be able to collate good practices in youth policy development and practice/implementation. This will facilitate development of a ‘reference guide’ in policy development for use by youth development practitioners.
Through experiential knowledge participants will contribute towards identifying other policy and structural frameworks that support youth entrepreneurship and key actors that can assist in establishing/strengthening policy and structural frameworks depending on the environment. Roles that key actors can play in promoting an enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship and youth development in general. The discussion will lead to a second reflective question: ‘what role can I, as a facilitator, play to help increase young people’s contribution to employment creation’? After completion of the session it is hoped that the interaction will continue which will lead to an e-peer group to support on-going discussions on good practices facilitating creation of enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship.
Definitions
For purposes of the session discussions the following are working definitions in regard to youth entrepreneurship that will frequently be used in the discussions;
1. Enabling environment (for youth entrepreneurship)
Supportive policy and structural framework(s) that allow for (a) easy start-up of businesses by young people, and (b) businesses owned by young people to flourish and contribute to wider community/national development
2. Youth policy
It’s the end result of a process during which Governments and other institutions recognize that a particular youth development need or problem exists and then their intention to do something about it. These expressions of general concern and the guidelines for action that follow are the essence of the policy.
3. Youth enterprise
An enterprise/business venture (generally a Small Medium Enterprise) run by young people.
Issues in ‘enabling environment’: Youth policy
Creating an enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship is essential for effective youth and national development.
a) Holistic approach to creating an enabling environment
An enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship consists of a number of variables which include policy frameworks, resources (both funds and human), access to raw materials and markets, lending institutions (structures), training opportunities etc. An increasing number of young people enter into self-employment to gain a livelihood – often with limited skills and barely any knowledge of the prevailing entrepreneurship environment to help sustain these livelihoods.
b) Dis-integrated youth policies
While a majority of youth policies globally and locally identify that youth unemployment is on the rise therefore requiring actions to address the situation, there is often a lack of integrated approach to policy in this area. Lack of integration contributes to absence of regular and robust evaluation. An effective policy framework has to have a set of programmes that directly address a number of interrelated themes.
At this juncture I request us to do some ‘baseline survey’ on youth enterprise policy frameworks that exist in our countries and their operationalisation. Use these prompts to carry out your survey, you may also need to contact offices responsible for youth affairs development or entrepreneurship nearest you.
- Does your country have a national youth policy? If so does it identify youth entrepreneurship as a key element towards national economic development?
- What other national policy frameworks are in place to compliment the national youth policy or employment/entrepreneurship policy? Are the policies working in tandem?
Prepare to share the results of your survey with other participants during our next online discussions.
Key elements in youth entrepreneurship policy
A comprehensive policy can provide solid basis for effective action to address many entrepreneurship needs of young people. Policies have to address the ‘real’ needs of that particular concern. Some examples of key elements that address the concerns of youth entrepreneurship are; gender differences, marginalized groups, segment youth population needs e.g. 15 – 19, 20 – 24 as well as level of involvement of youth. This is not an exhaustive list of key elements to look out for in a youth entrepreneurship policy however I wish to draw us back to our discussions on ‘dis-integrated youth policies’ above and the emphasis that policies have to be complimented by programmes on the ground that address the needs identified.
If you have a copy of your youth policy or entrepreneurship policy it will help you prepare for the next assignment;
Question: what improvements would you suggest?
Prepare to share your thoughts in our next online discussions.
This brings us to work on policy advocacy …
Advocacy for Youth Policy Development
Definition:
Advocacy is speaking, acting or writing on behalf of the perceived interests of a disadvantaged group or person to promote, protect and defend their welfare and social justice.
Advocacy Cycle
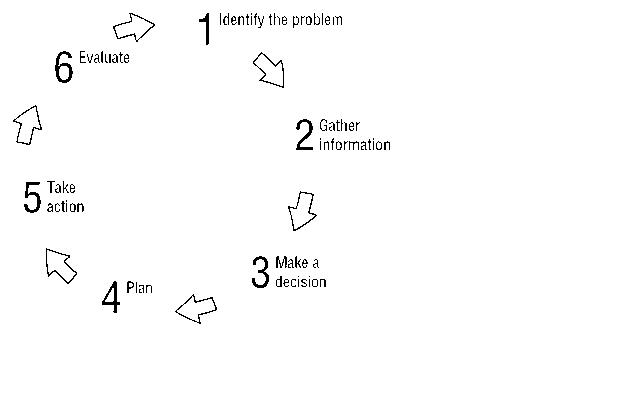
Below is a simplified advocacy cycle. It portrays the key elements needed in advocacy work.
Key Elements in Advocacy
- Identify the problem: what is the real cause of the situation? Why do you and others want to try to change things? Could the situation be changed through advocacy
- Gather information: find out all the information possible about the situation e.g. the problem, possible solutions, targets, opportunities, supporters and opponents, risks and advantages
- Make a decision: a decision whether or not to take action has to be made.
- Plan: once decision is made, work out a clear plan of action to include; the problem, objectives of advocacy work, important people to the cause, methods, time schedule, possible risks, responsibilities, measures of success
- ACT
Policy framework: a Tool for Development
Inclusive policy frameworks and functional youth development structures are necessary tools to support the implementation of youth entrepreneurship. In the absence of the above tools it is important that strategies on establishing and developing policy and structural frameworks are in place. Governments, young people and cooperating partners therefore have different roles to play in efforts towards developing or strengthening policy and structural frameworks for effective youth entrepreneurship.
Different advocacy strategies have worked for different circumstances. In the case of policy development, in many instances, providing evidence based information on the matter and linking it to a specific priority area in a community/national development framework assists in getting policy development work done.
You may have been part of an advocacy campaign that led to the development of a particular policy:
- how did the process unfold
- what role did you or your organization play?
Read the following literature on successful advocacy strategies.
Summary and Assignments
Try your hands on the following questions ...
Assignment
The Namibian Youth Policy calls for all young people in Namibia to participate in socio-economic development of the country thereby contributing to the country's policies, the vision 2030 and the development millennium goals. The country has policy and programms on Small and Medium Enterprises development and has a youth credit scheme policy and programms which runs for a period of five years.
Though Namibia is still very young, a number of policies have been put in place for the country to run to its industrial development. A number young people are participating in economic development activities through a number of initiatives by the government to mention a few, NYCS, Skills development programme and many others.
|
Keep up mobilization of youth to participate in economic development and to become entrepreneurs of Namibia. Encourage young people to contribute to community development thereby contributing to poverty eradication and employment creation, and also encourage community product development. The production of food in the community through rural youth programme with the assistance of experts searched though the government and the programme of one village one product campaign.
Conclusions
Thank you for participating in the ‘creating an enabling environment: youth policy and advocacy’ session. We have discussed several issues and points related to ensuring an enabling environment for youth entrepreneurship. Let us consider some of the Key Points we touched on...
|
Throughout the session we have looked at;
|
It is my hope that you will be able to apply the learning’s from the discussions, interactions and readings to your respective situation. I trust that the process has stimulated your thinking and practical actions towards understanding and facilitating creation of enabling environments for youth entrepreneurship through policy frameworks.