User:Phaello/sandbox/Chemistry/SCI 3204P-B/Bonding
From WikiEducator
< User:Phaello | sandbox | Chemistry | SCI 3204P-B
Contents
Chemical Bonding
|
|
Ionic Bonding
|
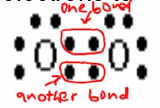
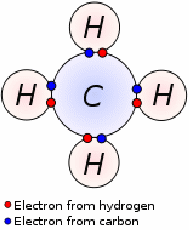
Covalent Bonding
|
|
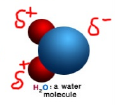
Polar and Non-polar Covalent Bonds
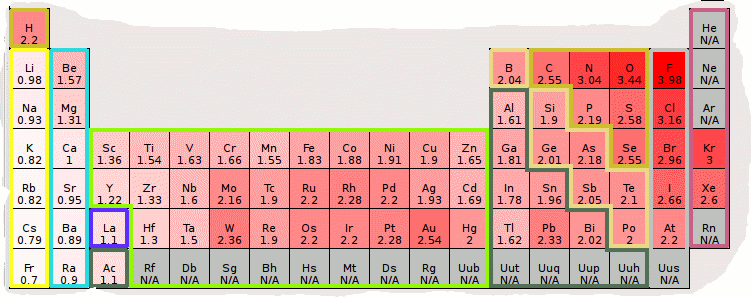
Electronegativity
Periodic Table Showing Electronegativity values of elements
|
|
Refer to the following websites for more information