User:Joannabarclay/Mobilizing Energy
Contents
The Facilitative Way to Mobilize Energy
By Joanna Barclay, Senior Consultant and Facilitator, Intersol Group
Striving for 100% engagement
The Gallup Organization regularly surveys the workforce to measure the levels of employee engagement. The latest figures show that only 30% of the workforce consists of engaged employees ( loyal and productive). Over half – 54%- are not engaged (just putting in time), while 16% are actively disengaged (unhappy and spreading their discontent).
Why is such a high percentage of the workforce not engaged? Is it because old forms of security and certainty have disappeared and we haven’t figured out how to operate standing on a bowl of Jell-O? Regardless, we all may be in need of new tools and processes to increase active engagement.
We have moved out of the industrial age and into the information age where people have become isolated as they relate to the world and each other through technology. People have lost the appreciation that collective participation leads to better solutions, and commitment to those solutions.
A town hall meeting that engages and mobilizes the community is not the same as a chat room or an email exchange. The communal results of thinking and taking action together to find new solutions are vastly different. The facilitative approach is one that engages people, directly, not by technology proxy.
Facilitative leaders are engaged in:
- asking questions to enrich engagement
- sharing knowledge and information
- linking minds
- learning and unlearning
The Facilitative way means shifting from “keeping control” to new ways of asking questions and relating to people so they can assume more responsibility. Helping a group face its challenges lets them build a clear picture of the situation so they move on actions.
A Transformation
Using a facilitative style that helps the way people think and take action together is sweeping the workforce. Being a facilitative leader means working together in a way that thinking and action are tied to the organization’s strategy, mission and vision and the capacity for people to carry it out.
When working strategically, a group’s thinking and planning stays connected to:
- The historic –- what has happened in the past in the organization?
- What was the original passion/plan?
- The present –- what is going on now?
- What is the current mission/message?
- What are current accomplishments?
- The future –- what is needed and what are the priorities for the future?
Use Leverage to Mobilize Strategic Action
Focus on Nine (9) Points of Leverage
Using leverage mean placing the most emphasis and energy to get maximum strategic advantage for your actions.
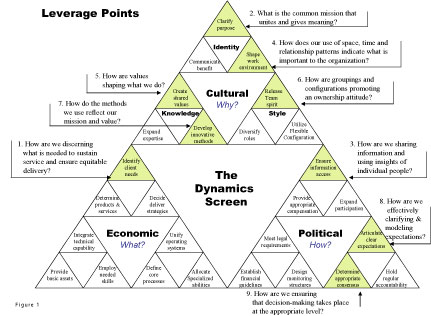
Experience with client organizations has shown that certain dynamics in an organization provide more leverage than others. The nine points where leverage is most likely are shaded in the Dynamics Screen in Figure 1. The leverage dynamics are numbered in order of importance.
Figure 1: The Dynamics Screen
(![]() : Hi Joanna, it would be great to see Figure 1 on this page, thanks. --Gurmit 17:43, 1 November 2009 (UTC))
: Hi Joanna, it would be great to see Figure 1 on this page, thanks. --Gurmit 17:43, 1 November 2009 (UTC))
The leverage point in the Economic Dynamic, identifying client needs, drives everything in today’s organization. The five leverage points in the Cultural Dynamic are clarifying purpose, shaping the work environment, creating shared values, releasing team spirit and developing innovative methods. These dynamics are critical in creating an atmosphere of buy-in, synchronizing time and space with the purpose and ensuring the importance of people as a guiding principle for the organization. In today’s workplace, team spirit is essential. Finally, the three leverage points in the Political Dynamic are ensuring information access, articulating clear expectations and determining appropriate consensus.
Since the greatest emphasis during the last three or four decades has been in the Economic Dynamic, it is not surprising that the greatest leverage today is in the Cultural Dynamic in order to rebalance thinking in a organization.
You get the most results from your efforts when you:
- Identify client needs to understand the demands of today’s marketplace.
- Clarify common purpose to understand who you are and why you are involved in the organization. When the purpose changes, all the other dynamics must be re-aligned with the new purpose.
- Make certain there is meaningful information access so people can be involved and engaged – significant engagement. The key is learning how to quickly extract meaning from data and information.
- Reshape the work environment so the use of time, space and relationship support the common purpose.
- Create shared values that highlight what is important in the operating values. Operating values are changing:
- Release a team spirit that mobilizes energy and commitment with an entrepreneurial attitude.
- Develop innovative methods to grow knowledge. Encourage and train people in leading facilitative conversations that solve problems, clarify issues, change work patterns and create new ideas.
- Articulate clear expectations to empower people to act like owners and get things done. Model expectations consistently.
- Provide support for appropriate consensus decision-making