User:Fordn/Books/Podcasting
Contents
Podcasting for learning
Welcome
to this short course on podcasting. Participating in these learning modules will provide you with:
the skills to create and publish a podcast.
an understanding of how you can use this web 2.0 technology in the classroom to: develop your students’ literacy skills, provide an authentic context for learning, utilize a wide audience for students to engage with
There are five modules in the course. You can see them listed down the left hand side of your screen.
Module 1: What is a podcast?
- Topic 1: How do I listen?
- Topic 2: How do I subscribe?
Module 2: Why podcast?
- Topic 1: How can podcasting support students' learning?
Module 3: What do I need to make a podcast?
- Topic 1: Software and equipment
- Topic 2: Exploring other software options
- Topic 3: Downloading the software
- Topic 4: Setting up a Podcasting host site
- Topic 5: Uploading an MP3
- Topic 6: Publishing your podcast
- Topic 7: Publishing more widely
Module 4: Planning for podcasting in the classroom
- Topic 1: Podcasting in the classroom
- Topic 2: Possible learning experiences
- Topic 3: Selecting a podcasting learning experience
- Topic 4: Planning for learning in your classroom
Module 5: Podcasting with your students
- Topic 1: Introducing the topic - What makes a good podcast?
- Topic 2: Planning your podcasts
- Topic 3: Recording your podcast
- Topic 4: Copyright and digital citizenship
- Topic 5: Producing your podcast
- Topic 6: Publishing your podcast
- Topic 7: Going further with podcasting – enhanced podcasts
Work through them at your own pace.
Each module is broken up into short topics, with small tasks. Each module should take about an hour to complete, but you may wish to spend more time:
developing an understanding of the podcasting freeware available
selecting and becoming familiar with the tools you will use
planning how to use it with your students.
There are four activities that run through the course where you'll apply what you've learned with your students:
- storyboarding your podcast
- producing your podcast
- podcast post-production
- publishing your postcast
Your course is available for ten weeks.
What is a podcast?
Podcasting is a method of communication that allows you to create audio files and publish these to the Internet for others to download and listen to at any time. These audio files can be downloaded to a personal computer or handheld device such as an iPod or MP3 player.
What is a podcast?
Podcasting is a method of communication that allows you to create audio files and post them to the Internet for others to download and listen to at any time. These audio files can be downloaded to a personal computer or handheld device such as an iPod or MP3 player.
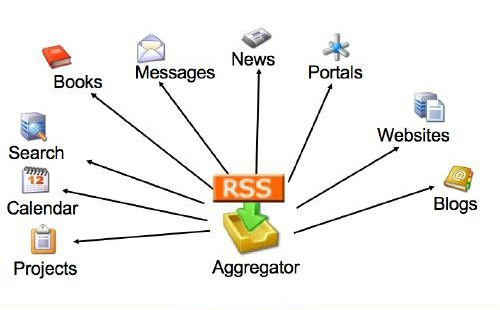
A Podcast consists of two parts; the episodes and the RSS feed. Each episode in a Podcast is the audio file you create, and the feed is the way the podcast is distributed to subscribers.
A pod cast can be purely audio or be enhanced to include images and video.
Watch this video clip (Podcasting in plain english) explaining how podcasting works.
How do I listen?
You can listen to podcasts directly from the websites of the people who make them. Or, you can "subscribe" to podcasts using aggregator software like Google Reader. These programs will automatically download the latest shows, and you can then listen to them on your computer, iPod or MP3 player.
How do I subscribe?
Subscribing to a podcast means that your computer downloads the latest episode and periodically checks for new episodes.
To subscribe to a podcast, you need to use the RSS feed - this information is on the podcaster's website. For example, iTunes has its own directory, where you can subscribe to a show, simply by clicking the "Subscribe" button.
Task: Listen to some of the podcasts from the Teaching with Technology Podcast website. To do this:
- Click on the play button.
- Try subscribing to the site.
- Click on the Subscribe link on the top right of the page

- Select the tool (aggregator) you use to subscribe. This maybe Google, netvibes, pageflakes, iTunes or something else on the list.
If you don’t have an aggregator I suggest you create a Google account and use that.
Why podcast?
Podcasting provides students with the opportunity to:
- present and share their learning with a wide audience
- participate in media creation
- develop personal understandings
- communicate effectively
Shamburg (2009), suggests the benefits of podcasting go beyond technological proficiency and academic content knowledge.
Students who podcast become active participants in society. They can create original content or ethically remix the work of others. This hands-on approach to copyright, fair use, and digital media is a tool for students to understand their responsibilities as digital citizens. Podcasting provides an authentic context for this learning.
How can podcasting support students' learning?
Your students are publishing with a purpose in an authentic context to a potentially vast audience. The process facilitates:
- Improved student learning outcomes
- ICT literacy development
- The development of key competencies
Building links with the community. Podcasting is a push technology - once people have subscribed via the RSS feed podcasts are automatically sent to them. Parents and the wider community can engage with the work that is happening in the classroom. They can be invited to send their comments, giving valuable feedback to students about their work
Podcasting is not a one-off - it's a series of episodes and there's a great incentive to carry on.
Read: Jane Nicholls blog post, 'Now this is interesting', comparing students and teachers perceptions of the learning taking place while podcasting.
Task: list the ways you think podcasting could improve your students learning.
What do I need to make a podcast?
Podcasting requires very little equipment and the software you can use is free. There are many different types of software available which give you a lot of choice in the way you want to host and publish your podcasts. The process and software selected for this module have been chosen because they are free and easy to use.
Software and equipment
Choose the tools that fit your purpose.
You need:
- A computer with some kind of recording ability (an internal or external microphone) OR a portable microphone that records such as an Easi-Speak recording microphone.
- Audio recording & editing software - For this module we are using Audacity. Audacity is freeware that can be downloaded from the web for both Windows and Mac users. It allows you to record, edit and export your recording as an mp3 file.
- A site to host your podcasts. For this module we are using PodOmatic. PodOmatic is free of charge, and supplies an ample amount of bandwidth and storage space. It automatically generates an RSS feed which your followers can subscribe to. You do need to be aware that on PodOmatic although there is a content filtering option, the 'censoring' is done by the podcast creator not a moderator. We recommend teachers setup their own account and restrict student use to this as a safety precaution. Further information on PodOmatic is found on the Software for Learning website.
- A site to publish your podcasts. This could be your class blog, wiki, or school website.
Exploring other software options
These other tools are suggestions you can explore if you wish:
Recording tools
- If you have a Mac, your computer will have come with Garageband and you may wish to use that.
- Myna Audio Editor is a free online audio editor that is easy to use and contains a sound library.
- Software for Learning provides information on different audio recording software.
Hosting sites
- MyPodcast is a free site that does everything for you from recording to publishing for free.
- Podbean – this free site provides you with a blog that your podcast is automatically embedded into. You can also use the embed code provided to publish your podcast elsewhere. The embedded player has an RSS feed subscription with it.
- Another free option if you use Blogger is using Feedburner to create your RSS feed. The Learning in Hand website has clear instructions for this process.
- Podcaster – has special education pricing. For more information see the Software for Learning website review.
Watch the video 'How to create a podcast' that shows you a variety of different software packages you can use to create and distribute your podcasts.
Downloading the software
Before starting to podcast with your students you need to setup the software and become familiar with how to use it.
Task: Download Audacity and the LAME encoder. Follow these instructions for downloading and installing the LAME MP3 encoder.
Practice recording using Audacity
Create a simple voice recording with a music track that fades in and out at the beginning and end using Audacity. Save your recording as an MP3. The sound files need to be saved in MP3 format to upload to your podcasting host site. You will need this for this course
Use these resources to help you:
- Using Audacity – the basics [PDF]
- Audacity tips and tricks for podcasters [PDF]
- Creating a simple voice and music Podcast with Audacity tutorial.
Setting up a Podcasting host site
Using a podcasting hosting site is a simple way to both store your podcasts and generate an RSS feed. For this module we are usingPodOmatic.
Your podcasts will sit on the PodOmatic website. Your audience can subscribe to this via the RSS feed on your page or you can embed your podcasts into your class wiki or blog.
Have a look at the podcasts for this course in my PodOmatic account.
Task: Setup your PodOmatic site account. You will need to supply your email address and create a password.
You can upload a photo at this stage or select “skip for now” and do that later. The photo you upload will travel with your podcast to any podcatchers that you send your RSS feed to.
Uploading an MP3
Now that your PodOmatic site is setup you need to practise uploading an MP3 to create a podcast.
Task: Use one of the MP3 files you made when experimenting with Audacity in Topic 2.
Follow the instructions or watch the video below to help you.
- Login to the PodOmatic website.
- Click on “Post your first episode”. This is in the upper right section of the screen.
- This link will take you to the next page where you will click on “Upload media from your computer.”
- Browse for the MP3 file you have saved.
- Fill out the information about the episode. This information will also travel with the podcast on the RSS feed you send to podcatchers.
- Once completed click on “Next step” and upload picture for the episode, add in any keywords for search engines.
- Click on “Next step” and confirm all the information by clicking on “Post episode”.
Each time you create an MP3 you upload it to Podomatic. Each episode will sit on your Podomatic homepage.
Watch this video explaining how to upload an mp3 file to PodOmatic
Publishing your podcast
Now that you have created your podcast you can publish it for the world. To do this, copy the embed code and paste it into your blog, wiki or school website.
Follow these intructions, or watch the video clip on how to find the code:
- Click on the “Publish” tab, click on “Podcast” in the dropdown menu, then click on “Manage” in the expanded dropdown. Under the heading “Promotional Tools” click on the “Embedded player” link.
- Choose whether you want to publish an individual podcast (single-track player) or all of your podcasts on your playlist (multi-track player).
- Select the colour, size and whether you want the player to start automatically or not.
- Copy the code and paste it into your blog, wiki or school website. This embeds your podcast and future episodes into your blog or wiki. People can then click on the “Follow” link and follow your podcasts.
Watch this video on publishing your podcast.
Publishing more widely
You may wish to promote your podcasts more widely than just through your blog, wiki, or school website.
- PodOmatic allows you to “Share”, “Email” or post on Facebook.
- Submit your podcast to iTunes. You can either:
Go to the iTunes store, if you have an account, and click on “Submit a podcast”, then paste in the RSS feed url and complete the form.
OR
From the PodOmatic homepage, click on the “Publish” tab, click on “Podcast” in the dropdown menu, then click on “Settings” in the expanded dropdown. Complete the basic info section.
Click on the “iTunes” tab and click on the link for “iTunes settings and information” complete the form and submit.
Watch the video on how to submit your RSS feed to iTunes.
Planning for podcasting in the classroom
In this module you will plan a student-produced podcast that fits into your classroom programme.
Podcasting in the classroom
Watch this video in which Simon Shaw, from St Albans Meadows School in Melbourne outlines the ways his school uses podcasts to engage, motivate and encourage deep thinking. Simon describes the process that takes place before a teacher presses record - the building of associated language, key ideas and understanding of the topic.
Task: Answer the questions; How Simon uses podcasting to develop literacy skills andconnect with a wider audience and what are the learning benefits of podcasting identified by Simon?
Possible learning experiences
Task: Listen to some of the student podcasts below. As you explore, consider:
- How does podcasting support learners to engage with the curriculum?
- Where are there examples of collaboration?
- List the different learning experiences can you identify
A selection of school podcasts
- KPE – Korero Pt England - Students at Point England School podcasting book reviews and news.
- Room 10's Podcasts - Podcasts from Room 10, Paremata School.
- The Downs FM - At the top of this link is an explanation of The Downs FM project. Scroll down the page to hear the podcasts.
- Radio Sandaig - This team of primary children in Scotland produce a radio style podcast with news, jokes, stories and competitions.
- Toko Talk - Toko School, Central Taranaki, students podcast book reviews, music, current events, and Kids Talk.
- Central Otago - Students from eight schools share what’s cool about this part of New Zealand.
- Paparoa School - Podcasts with students taking on the role of a character involved in a NZ historical disaster.
- South New Brighton School - Interviews and reports from students in South New Brighton School, Christchurch.
Selecting a podcasting learning experience
Task: Think about the learning experiences that you have planned for later this year that will be enhanced by podcasting.
Record these, use the list below and your own list from Topic 2: Possbile learning experiences to help you.
Possible learning experiences
Instructions - students explain some new learning e.g. explaining a strategy to solve a maths problem, how to construct or create something.
Reporting:
- Local classroom, school or sporting events - a great way of telling children and parents what is going on at your school.
- Try an outside broadcast - Use an mp3 player with recording facilities e.g. Easi-Speak recording microphone to record a feature "on location" around the school, or on a school field trip. You can then download this to your computer and edit it.
- Weekly reminders - homework, sports or trip reminders, school notices.
- Interviews - with members of staff, children, members of the community, and visitors to school.
- Plays.
- Book Reviews.
- Read a story or poem – either a school reader or a story they have written.
- School or class songs.
- Look at the list of ideas you have jotted down.
Choose one learning experience to work with a group of students to create a podcast that will support their learning.
Planning for learning in your classroom
Now that you have identified a learning experience or context for learning....
Task: create a plan focused on the learning outcomes your students will develop through podcasting.
Identify the learning outcomes
These may include developing:
- The technical skills needed to record a high-quality podcast.
- Oral language skills through – clear organised presentation with expression, adjusting language to suit the audience
- Written language skills through – planning, organising, editing, vocabulary development, questioning, summarizing, expressing opinions
- Key competencies
- thinking – able to be creative, plan and reflect on the process of scripting, recording and producing
- using language, symbols, and texts – selection of appropriate content, vocabulary for audience
- managing self – project management, time management, making decisions
- relating to others – ability to take on different roles within the production, work as a team, connect with the audience
- participation and contributing – representing the school, connecting with the community appropriately
Organisation
Decide on:
- The group of students you will work with.
- How you will introduce the topic and process with your students.
- Where students will work to record.
Assessment
How will you and your students assess their learning?
Look at these podcast rubrics and identify some of the key skills that are appropriate for the level you are teaching.
Create your own draft rubric.
Time Allocation
Podcasts usually take 3-4 weeks to produce, so you should aim to make one Podcast a month initially. Once students are more familiar with the process, the number of Podcasts produced can increase as desired.
Throughout the rest of this course we will work towards producing a podcast in the classroom.
Podcasting with your students
In this module you will create a podcast in the classroom with your students.
When beginning this process with your students it is easiest to begin with a group of students recording. These students then become the experts and are able to support the next group of students that you will work with.
What makes a good podcast?
Part of the process of creating a podcast is ensuring it is appealing to an audience. When working with your students it is important for both yourself as a teacher and the students to have a clear idea of what makes a good podcast. This criteria is best co-constructed with your students.
Check - Prior to beginning with your students have you ….
- Got the hardware you need?
- Got the software needed for production process and do you know how to use it?
- Selected a learning context and defined the purpose of the Podcast?
- Identified the learning outcomes?
- Found a quiet space where students can record?
Task: listen to a selection of podcasts from the list 'A selection of school podcasts with your students'.
Invite your students to:
- List the podcasts they like
- Identify a list of features that make these podcasts appealing
- Compare the list of features with your draft rubric from Module 4: Topic 4 Planning for learning
- Create your own version of a podcast rubric together
- Evaluate two podcasts in terms of content and production
Planning your podcasts
Your students need to develop an understanding of: what makes a good podcast, and the skills they need to develop.
Podcasts have to be organised and structured.
Task: work with your group of students to:
- Decide on what their podcasts are to be about.
- Identify the target audience.
- Discuss the content, language, and tone.
- Decide how long should the episode be? Shorter is better.
- Create a rubric with them to so they can assess their work.
- Create a script.
- Decide who is going to moderate the content and approve the podcast? This is very important to avoid the possibility of unsuitable materials being made public.
Organisation
- Students work in pairs for content/script production.
- Use the rubric to evaluate them and make any necessary changes.
- Share and peer review them.
Recording your podcast
Find a quiet space for students to record their podcast so that background noise is eliminated.
Work through the recording process with your students. They will need to:
- Practice recording the content a few times (like a dress rehearsal).
- Record the Podcast content and save as a project in Audacity ready for editing later.
Copyright and digital citizenship
You can integrate teaching about digital citizenship as your students develop their podcasts.
Task: use these resources to help you consider the following scenarios. For each one note your ideas about how you would help the students in each situation.
Resources
- Netsafe’s learn guide protect website
- Creative commons Aotearoa New Zealand
- Creative Commons copyright – Podcasting legal guide
Scenarios
- A student has found a picture from the Google images and wants to put it up with the podcast.
- A student wants to use part of a song from one of their own CD’s on the podcast sound track.
- When introducing themselves the students were using their full names.
- Someone posted a negative comment on the class blog about the latest podcast.
- Your students want to record an interview with someone for their podcast. What do they need to consider before publishing it?
Producing your podcast
This is the stage editing takes place. The age of your students will factor into the decision of how you will set this up. You can either train some experts or if your students are very young do this part yourself.
It is at this stage you can add in sound effects, background music, and insert the introduction or "jingle" to your podcast.
Producing a podcast provides an authentic context for looking at copyright and our responsibilities as digital citizens when adding music to a podcast. You can find "podsafe" music in special directories. Some examples to try are:
Task: review the Audacity editing tools in Module 3: Topic 2 - Recording an MP3. Make sure you save your file as an MP3 so it is ready for publishing.
Publishing your podcast
You are now going to publish the MP3 file saved as a podcast via your PodOmatic account.
Task: follow the steps you practised in Module 3: Topic 5 Uploading an MP3.
- Each time you create an MP3 you upload it to PodOmatic. Each episode will sit on your homepage in PodOmatic. Followers can subscribe to your podcast from here.
- To bring your podcast to the audience you have already build up on your class blog, wiki, or website copy the embed code and paste it into your blog, wiki or school website. Follow the steps you practised in Module 3: Topic 6 Publishing your podcast.
- If you want to publish more widely than your school website, follow the steps you practised in Module 3: Topic 7 Publishing more widely.
Writing on blogs
Because many podcasters post their work in a blog, this is an ideal time to introduce blogging practices. Emphasising the importance of including links show students how to "connect" the information that they are discovering.
The skills necessary for effective participation in threaded conversations can be taught while commenting on blogs/podcasts. This is an ideal situation to develop appropriate rules and responsibilities with them. Find out more about blogging considerations for schools on the Netsafe Learn-Guide-Protect web site
Going further with podcasting
As you gain confidence in the podcasting process you will become ready to go further, and you can.....
Enhanced podcasts
Enhanced podcasts may contain chapters, images and hyperlinks.
Any digital image can be included, such as a photograph from a digital camera, special graphics such as titles and logos as well as diagrams and drawings. Selecting the right image to convey extra information to enhance the audio is what you should be aiming for.
Watch this enhanced podcast from KPE – talking to Dick Hubbard
PodOmatic enables the creation of Minicasts which are Mashup of photos and audio to create a video slideshow.
Try making a minicast.