The Anatomy and Physiology of Animals/Endocrine System Worksheet
From WikiEducator
1. Fill in the gaps in the sentences below using the words in the list.
- target; blood system; ducts; hormones
- a. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the blood. In other words they have no ...................
- b. Endocrine glands secrete chemicals called ....................
- c. Hormones are transported from the endocrine glands to all parts of the body by the ..............................
- d. Although hormones are carried throughout the body they only affect specific ......................... organs and tissues
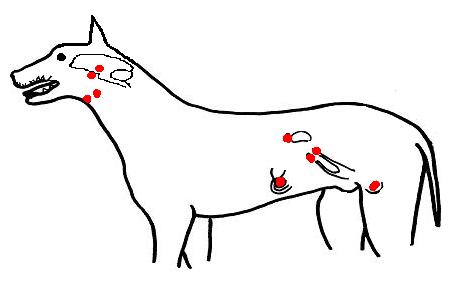
2. The position of endocrine organs have been indicated in red on the diagram of a composite male and female dog shown below. Add the labels in the list to the diagram.
- Ovary; Pancreas; Thyroid gland; Pituitary gland; Testis; Adrenal gland; Pineal gland; Parathyroid gland
3. On the diagram of the brain below indicate the position of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland.
4. In the table below list 3 hormones produced by the pituitary gland and state the function of each.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| 1............................ | ..................................................... |
| 2............................ | ..................................................... |
| 3............................ | ..................................................... |
5. Fill in the following table with the endocrine organ the hormones are produced by.
| Hormone | Produced by: |
|---|---|
| Insulin | ......................... |
| Progesterone | ......................... |
| Oestrogen | ......................... |
| Growth hormone | .......................... |
| Adrenaline | ........................... |
| Antidiuretic hormone | ........................... |
| Testosterone | ........................... |
| Aldosterone | ........................... |
| Melatonin | ............................ |
| Oxytocin | ............................ |
| Thyroxine | ........................... |
6. Match the hormones in the list below with their functions.
- Oxytocin; Insulin; Oestrogen; Growth hormone; Antidiuretic hormone; Testosterone; Adrenaline; Cortisone; Melatonin; Progesterone; Thyroxine; Luteinising hormone; Follicle stimulating hormone
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| ................................. | 1. Stimulates development of the ovarian follicle. |
| ............................... | 2. Stimulates milk “let down”. |
| ................................ | 3. Controls blood glucose levels. |
| ................................. | 4. Influences the rate of growth and development of young animals. |
| ............................... | 5. Stimulates the growth of long bones. |
| ............................... | 6. Stimulates absorption of water from the kidney tubule. |
| ............................... | 7. Influences the development of sexual maturity. |
| ................................ | 8. Stimulates the development of the corpus luteum. |
| ................................ | 9. Stimulates the development of female sexual characteristics. |
| ................................. | 10. Stimulates the development of the male sexual characteristics. |
| ................................. | 11. Affect glucose, protein and fat metabolism. |
| ................................. | 12. Prepares the lining of the uterus for pregnancy. |
| ................................. | 13. Prepares the body for emergency situations. |
7. Circle the odd one out.
- 1. melatonin; oxytocin; growth hormone; antidiuretic hormone; follicle stimulating hormone.
- 2. progesterone; oestrogen; luteinising hormone; cortisone; follicle stimulating.
- 3. adrenaline; cortisone; aldosterone, oestrogen, insulin.