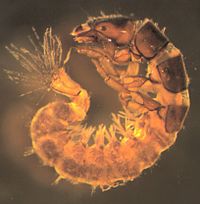
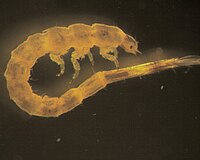
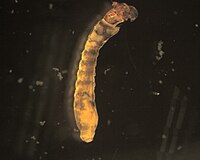
Mettawee River (USF&W)
From WikiEducator
(Redirected from Mettawee River (Upstream))
| [▲] | |
|---|---|
| Stream code: | LCC_MetRv_742 |
| Basin: | Lake Champlain Canal |
| State or Province: | Vermont |
| Country: | USA |
| Latitude: | 43.264770 |
| Longitude: | -73.099565 |
| School: | Long Trail School |
The following are the most common invertebrates collected from this stream site.
Contents
[hide]Drunella
The mayfly Drunella is distinguished by its large femoral “biceps;” these femora have tubercles on the leading margins. Gills are present on segments 3-7.
Dubiraphia
The larvae of this genus are distinguished by the last abdominal segment, which is very elongated. Adults of this genus usually have prominent longitudinal markings on their elytra and, like adult Optioservus, have a fringe of tomentum on their anterior tibia.
Image of the fringe of tomentum.
Chironomidae
Midge larvae tend to be the most common macroinvertebrate at our sites. As with other Diptera, there are no true jointed legs. Chironomidae do have a pair of prolegs at each end and preserved individuals tend to curl into a 'C'. Identification past family requires slide-mounted heads. We have seen philopotamid caddisflies misidentified with the chironomids and we suspect that that happens when samples are being sorted from trays. Under a microscope, six prominent legs can be seen on members of the caddisfly family Philopotamidae.
More information on Philopotamidae.
Baetis
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Baetidae
- Genus
- Baetis
- Common name
- The Little Olive
- Tied fly
- Sawyer Pheasant Tail Nymph
This mayfly has three "tails" and a unique head shape. Its gills are oval shaped and insert dorsally. More mature nymphs have long, dark wing pads.
Image of the long, dark wing pads.
Simuliidae
Simuliidae appear rather like bowling pins with heads. Relatively speaking, we collect few members of this family and have we have not identified them past family at this point.
Click here for a close up image of the heads.
Stenelmis
The larvae of Stenelmis, as in Ordobrevia, have a sternum on the ventral side of the pronotum. The main difference between the two genera is in the antennae the second segment is less than twice as long as the first in Stenelmis.
The adult Stenelmis has a clear separation between the thorax and abdomen as well as a more distinctly separate head as compared to other genera.
Acerpenna
This genus is can be identified by the costal process, or projection, distal to the hind wing pad. Gill 7 is slender and may be pointed at the end. The antennal scape and pedicel have a few scattered setae (hairs).
Image of the antennal scape. A ventral view can be seen here.
Baetidae
This mayfly has either two or three cerci ("tails") and a unique head shape. Its gills are oval shaped and insert dorsally. Commonly encountered genera include Acerpenna, Baetis and Pseudocloeon.
More information on the genera:
Epeorus
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Heptageniidae
- Genus
- Epeorus
- Common name
- The Quill Gordon
- Tied fly
- Quill Gordon
This is the only Heptageniidae genus present in this area with two tails!
Leuctra
This family of stonefly is fairly slender by stonefly standards. The divergent wing pads are a helpful characteristic. Leuctridae are similar in overall shape to the Capniidae; however, Leuctridae often do not have pleural folds. If they are present, they only extend from abdominal segments 1-7. Leuctra are recognized by abdominal terga with posterior fringes of short hairs and last few segments with longer hairs.
Image of the divergent wing pads.
Brachycentrus
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Brachycentridae
- Genus
- Brachycentrus
- Common name
- The Olive Dun Caddis
- Tied fly
- Deer Hair Caddis
These larvae are typically found with their legs extended out of their case for feeding. The cases are square in cross section and made of plant materials. Brachycentrus has 2 large sclerites on the metanotum. In fresh samples (preserved for less than one week) these organisms often have a pale green tint; live specimens are a more vivid green.
Glossosomatidae
Larvae in this family build domed cases made of small rocks, and are often wider at segment 5. The pronotum is covered in dark, sclerotized plates, but there are either no sclerites on the mesonotum, or the mesonotum is unsclerotized with the exception of a few patches. The anal proleg is broadly joined to segment 9; the anal claw has one or more accessory hooks. The pronotal excision is small (approximately 1/3 anterolaterally) to accommodate the coxae.
Commonly encountered genera include Glossosoma and Agapetus.