Macroeconomics activity and demand/Aggregate demand
From WikiEducator
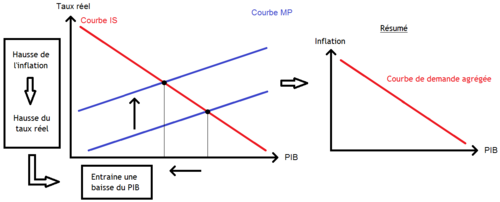
The aggregate demand is the sum of consumption, investment, government expenses, and net exports. Aggregate supply is the total output an economy produces at a given price level. Firms achieve equilibrium when they produce the quantity of goods and services consumers want to buy - that is, when aggregate supply equals aggregate demand. Here we will examine shifts in aggregate supply and aggregate demand and their short-term and long-term effects for the whole economy.