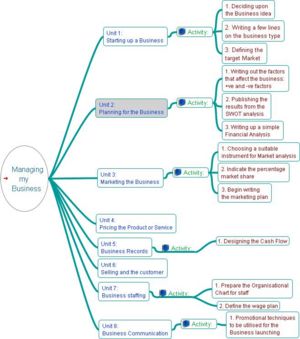
Life Skills Development/Unit Four/Business Plan
Contents
This plan contains the written description of the enterprise, its objectives and the steps necessary to achieve them. It is necessary for new and established ventures.
Why is it important?
- It is the road map;
- It shows the ultimate destination and how to get there;
- It allows for unexpected detours and unforeseen problems;
- It shows how to change the route and still drive ahead safely.
Elements of a Business Plan:
- A thorough explanation of the product or service that the business will provide;
- Why this product/service will satisfy customer needs;
- Why this business will be successful;
- The potential revenue, expenses and profits;
- The possible expansion of the business in the future.
Parts of the Business Plan:
1. Introduction:
- Type of business you intend to conduct;
- The legal form of business: sole proprietorship, a partnership and a corporation;
- Business hours;
- Season ability of the business;
- Management.
2. Strategy Formulation: gap analysis
- What are you doing;
- Where would you want to be;
- How you would be getting there.
Strategy: the managerial game plan for directing and running the business.
3. Accounting:
Systematic recording of the enterprise's income and expenditures, assets, liabilities and owner's equity; in order to determine it's financial performance and financial position.
- Balance Sheet: It shows at a point in time the firm's position with regards to assets, liabilities and net worth, or owners equities;
- Income Statement (Statement of Financial Performance): It shows over a specific time period all the revenues and expenses which result in the profit or loss from those transactions and cash flow statements;
- Cash Flow Statements: Show the inflow of dollar from receipts into the business, and the outflow in the form of expenditures made by the business;
- Capital Equipment list: A statement that includes the details of operating equipment of an enterprise and its corresponding dollar value.
4. Marketing:
Involves those business activities, which relate directly to determining the target market (to whom you will sell) and delivering goods or services to those markets.
- Target Market: the percentage of the total market to whom the enterprise plans to sell its product or services.
- Success will depend upon how, for example the product will be priced and how the business deals with the competition.
- Price and product differentiation from the competition play and important role in the firm's profitability.
5. Location/Layout:
The location of the business may be the key to its success.
- Location: the physical site and the geographic area of the enterprise's facilities.
- Layout: the arrangement of fixtures, equipment and machinery in the business. It varies according to the type of business the enterprise is operating.
6. Production/Operation functions:
- The system from transforming inputs into outputs, and also
- Concern with producing or making the output in the most efficient manner at the lowest cost.
7. Personnel:
- Involves the Recruiting, Selection, Evaluation and Training of the individuals who are employed by and necessary for the functioning of the enterprise.
Human Resource Management: the modern term used to refer to all functions pertaining to personnel.
8. Financing:
- The process of obtaining the necessary money to operate the business. Money is the lifeblood of the enterprise.
9. Controls:
- Those methods used to ensure that the business achieves its objectives;
- The following statements should be included:
- Sources of applications of cash: This statement shows the sources as well as the applications of cash within the enterprise;
- Application and expected effect of loan or investment: If the new or existing business has applied for a loan or has sought outside investment, there should be a complete disclosure in the business plan of how that capital will be utilized.
- Breakeven analysis: Is the volume of sales sufficient to cover all fixed and variable costs. It is the point where revenues equal costs.
- Internal Controls: There are certain controls required in the systems - inventories, accounts receivable, risk management and crime.
- Financial ratios: Or those percentage relationships in the firm such as current ratio, quick ratios, working capital ratio and the firm's performance to industry averages.
10. Executive Summary:
- A brief synopsis of all the elements in the business plan and can only be written last, once all the plan's elements are known. It is however, presented as the first part of the plan.
| Free Business Plans: http://www.bplans.com |
8. Funding for your small business
Money is essential so ask yourself a few questions about funding; what is the amount of money required to start your business:
Study the list below and try to determine which of these will best help in providing the funds you need to start.
Traditional sources of Venture capital:
===Seed Financing:=== Refers to a small amount of personal funds - this include money saved from other forms of income. This is often referred to as ownership capital/owners equity.
===Relatives and Friends:=== Relatives and friends may agree to give or lend you money to start your businesses venture. Many small business start this way, with no need for borrowing. This is great as these relatives seldom want interest and may gift you the money. However, this form of funding may generate problems if these relatives or friends recall their funds at times when the business is least able to return those funds or they may demand a greater or additional involvement in the venture which was not a part of your plan.
===Partnerships:=== There should be a written Agreement between the partners listing duties, responsibilities, amount of capital one has to contribute and also the proportion of profit sharing. This will help if differences should arise regarding who should do what and who should get what out of the business.
===Commercial Banks and Other Financial Institutions:=== A main source of finances, not only to business entrepreneur, but also to the community at large for what ever purpose intended. Loans are offered at different rates of interest. You must ascertain your interest rate and repayment schedule. Here, a comfortable payment schedule must be worked out. The entrepreneur must decide the repayment intervals and how much he/she will be able to pay at each interval. That is how often will you be able to make a payment on your loan and how much. Example: will you pay weekly, monthly, quarterly?
===Sale of Capital Stock:=== Stocks, or ownership shares, issued in exchange for funds needed to operate the business. An entrepreneur may opt to sell shares on the open market. These shares will then be purchased by interested parties/persons. In this way, the entrepreneur gets the needed capital. The parties/persons buying the shares become shareholders and must be assured of some returns on the money they have been put into that business venture.
===Venture Capital=== Refers to funds that are invested in new or higher risk enterprises, by outside investors. Venture Capital investments usually are high risk investments; however, they offer the potential of very high returns. The new entrepreneur seeking venture capital investors have the option of seeking the support of others who have had the experience of using venture capital. This person does not only have the experience in acquiring/finding venture capital; but, can also provide the new entrepreneur with support and direction concerning starting up.
===Corporate Partnership:=== A form of venture businesses, larger companies can keep up with fast-passed developments, a technique referred to as windowing in on recent entrepreneurial developments.
Pros:
- Heightened credibility with customers and bankers;
- Expert managerial assistance;
- Continuing source of financing;
- Small burden of risk.
Cons:
- Loss of substantial equity;
- Investors make most of the decisions;
- Risk of takeover.
Government Sponsored Agencies:
- Small business Administration loans;
- Special Government Programmes;
- Small Business Investment Company loans;
- State and Regional Development Companies.
===Trade Credit:=== Credit extended by Suppliers.
===Equipment Loans and Leases:=== Equipment can be bought on an installment basis. A 25% to 35% down payment is required with a loan period of 3 to 5 years.
Advantages of leasing equipment are:
- Flexibility with equipment needs and payment schedules;
- Smaller capital requirements;
- The leasing company offers maintenance service for equipment;
- Leasing offers a way to beat the obsolence problem.
Disadvantages:
- Absence of depreciation as a non-cash outlay;
- Higher total cost compared to purchasing the equipment.
Characteristics of a Marketing Plan
The characteristics of a Marketing Plan should be to:
- Provide a strategy to accomplish the mission statement of the enterprise;
- Be based on facts and valid assumptions;
- Provide for the use of existing resources;
- Describe how an organization is going to implement the plan;
- Provide for continuity;
- Be simple and short;
- Be flexible;
- Specify a performance criterion that can be monitored and controlled.
The Marketing Plan
First you must set your marketing objectives. These must be SMART:
- be specific;
- be measurable;
- be achievable:
- be relevant:
- have a stated time frame for achievement.
Examples of marketing objectives could be:
- To generate sales of $800.00 during the first year.
- To encourage 100 new persons to try the product in the first six months.
Your marketing strategy section of your plan outlines your game plan to achieve your marketing objectives. It is, essentially, the heart of the marketing plan. The marketing strategy section should include information about the four p's:
- Product - your product(s)and services
- Price - what you'll charge customers for products and services
- Promotion - how you will promote or create awareness of your product in the marketplace
- Place (distribution) - how you will bring your product(s) together with your customers.
- Plan
- Work your Plan
- Succeed
- If you don't succeed at first, do a SWOT analysis on yourself and on your business and start /continue afresh
- Plan
- Work your Plan
- Succeed
|
ENTREPRENEUR SELF-TEST This assessment is designed to help an individual identify and understand his/her entrepreneurial potential. This test can be used at the community level with residents engaged in or considering involvement with a business. The Entrepreneur Self-Test consists of three sections: motivation, capacity, and support. Motivation Evaluate your overall motivation to start and operate your own business. Score on a 1 to 10 scale, where 10 indicate strong agreement with the statement and 1 indicates little or no agreement with the statement.
Flexible - I am flexible and I am able to adapt to changes and surprises quickly and successfully.
Capacity Evaluate your capacity related to the following business skills. Consider not only your own capacities, but also the capacities of the other members of your management team. Rate yourself on a scale of 1 to 10 with 1 being no capacity and 10 being high capacity.
Capacity for Networking Evaluate your ability to network and partner with other organizations and individuals. Score on a 1 to 10 scale where 10 indicates strong agreement with the statement and 1 indicates little or no agreement with the statement.
Support Evaluate the level of support you feel from your family and community as you pursue your business opportunities. Score it on a 1 to 10 scale, where 10 indicate strong agreement with the statement and I indicate little or no agreement with the statement.
SCORING OF TEST Not all questions carry the same value and weight. The following scoring approach is used:
|
Entrepreneurship Diagram to help you revise
1. Name of your business - create a name or re-evaluate the name of your business. Does it integrate well with what you are selling? Is it easy to spell and remember? Is it a name that can be well branded over time?
2. Develop your business idea: Vision - what will your business look like 5 years from now? Think of how you may want to expand it to include other branches or extra employees.
3. Develop your business idea: Mission statement - this defines what your business really does, what activities it performs and what is unique about it that stands out from your competitors.
4. Goals and objectives - clearly define what you want to achieve with your business. Make sure they are SMART - quantifiable and set to specific time lines. Set specific goals for each of your products or services.
5. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats (SWOT ANALYSIS) – by analyzing these characteristics in your business, you will get a clearer idea of what it will take for you to not only to survive but also prosper.
6. Business Plan - set your ideas down in writing.
7. Funding your business
8. Marketing your products or services
9. Measuring and evaluation - you wrote your business plan and set the goals with the intent of achieving them. So now break them down into measurable pieces and monitor the results regularly. A plan that cannot be measured is almost always destined for failure. Celebrate your wins and recharge yourself to accomplish your next goal.
Decide beforehand what constitutes a real serious loss and what loss will be acceptable.
If you find your goals are unrealistic and unattainable, adjust them, but realize that it takes hard work to achieve them, so don't give up easily.
Conclusion: Now that you have a business plan, make it a part of you by knowing and understanding it clearly. Build upon it continuously and refer to it often, so you remain on track to building a profitable business.
Open the following attachments with Open Office:
More information on Business Plans
Please click on the link above to get more information on How to write a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Microsoft Word, thus, you will require this software or one similar to it that would enable document to be opened properly.
An example of a Business Plan for an Internet Cafe
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be opened properly.
An example of a Business Plan for a Events Planner
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be opened properly.
An example of a Business Plan for a Hair Studio
Please click on the link above to view a sample of a Business Plan. Please note that the document is formatted in Acrobat Reader, thus, you will require this software to enable the document to be opened properly
Unit summary
In this unit you learned what it takes to be an entrepreneur that it takes hard work and research to start a business. You know that to start a business in a new or existing trade requires high risk and heavy investing to be able to gain sustainable profits. You have learned that there are entrepreneurships that exist from small ventures to large businesses.
Checklists of Performance Task
| # | RUBRIC of performance criteria | v.well done | well done | ok | not ok | will redo by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I wrote my reflections on being an entrepreneur including
a)the idea of working for someone else all my life
b)visualize myself as an entrepreneur
c)what is involved in starting a business
|
|||||
| 2 | I discussed my new business idea with a friend and wrote my reflection on using
a)my talent and my passion
b)my skills and my hobbies
c)need of the community
d)possible name for my business
|
|||||
| 3 | I reflected on my characteristics that I have that would make me a good entrepreneur
a)wrote three in my portfolio
b)named two entrepreneur in my districts of characteristics of entrepreneur
|
|||||
| 4 | With a friend I discussed how new business venture arise and named a business that started in this way
a) changes in industries stimulated by technology
b) new knowledge encouraging new product and services
c) accidental discovery
d) changing perception in society
e) economic changes, IT revolution
|
|||||
| 5 | I reflected on the risk versus the opportunity in my business idea and noted these in my portfolio | |||||
| 6 | I applied a SWOT analysis to my business idea
a)its strength
b)weakness
c)opportunities
d)its treat
|
|||||
| 7 | I did a complete SWOT analysis on one competitor | |||||
| 8 | I completed my business plan and included
a) type of business hours and season
b) management
c) plan for directing and running the business
d) a gap analysis to get to the point of realizing this plan
e) systematic recording of account of projected income/expenditure
f) assets and liabilities
g) determining market and distribution
h) determining price, product differentiate and competitiveness
i) location and layout
j) projection and process
k) recruitment and training plan
l) financing the business with working capital
m) including inventory and risk management
|
|||||
| 9 | I reflected on the type of capital funding I need for my business and where I can get these funds | |||||
| 10 | I wrote my plan to market my product/service and included
a) way to accomplish mission of my business
b) using existing resources
c) be smart
d) information about the four Ps
Produce
Price
Promotion
Place and distribution
|
|||||
| 11 | I completed self test regarding potential entrepreneur and recorded my level. |