LESSON ONE - INTRODUCING THE COMPUTER
Computers have been called ‘mind tools’ because they enhance our ability to perform tasks that require mental activity. Computers are adept at performing activities such as making calculations quickly, sorting large lists, and searching through vast information libraries.
Human can do all these activities, but a computer can often accomplish them faster and more accurately. Our ability to use the computer complements our mental capabilities and makes us more productive. The key to making effective use of the computer as a tool is to know what a computer does, how it works, and how you can use it. This course focuses briefly on these.
1.1 - What is a computer?' A computer is a device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces output.
A Computer Accepts input
Computer input is whatever that is put into a computer system. Inputs means to feed information into a computer, through input devices. A person can supply input, by the environment, or by another computer. Some examples of the kinds of input a computer can process are the words and symbols in a document, numbers for a calculation, instructions for completing a process, pictures, audio signals from a microphone, and temperatures from a thermostat.
A Computer process Data
Data refers to the symbols that describe people, events, things, and ideas. Computers manipulate data in many ways, and we call this manipulation “processing’’. In the context of computers, then, we can define a process as a systematic series of actions a computer uses to manipulate data. Some of the ways a computer can process data include performing calculations, sorting lists of words or numbers, modifying documents and pictures according to the user instructions, and drawing graphs. A computer processes data in a device called the central processing unit or CPU.
A Computer Stores Data
A computer must store data so it is available for processing. The places a computer puts data are referred to as storage. Most computers have more than one location for storing data. The place where the computer store data depends on how the data is being used. The computer puts data in one place while it is waiting to be processed and another place when it is not needed for immediate processing. Memory is an area that holds data that is waiting to be processed. Secondary Storage is the area where data can be left on a permanent basis while it is not needed for processing.
A Computer Produces Output
Computer output is the results produced by a computer. “Output’’ means the process of producing output. Some examples of computer output include reports, documents, music, graphs, and pictures. An output device displays, prints, or transfers the results of processing from the computer to memory.
1.2 - Computer System Basics
A computer system includes a computer peripheral devices and software. The electric, electronic, and mechanical devices used for processing data are referred to as hardware. In addition to the computer itself, the term “hardware’’ refers to components called peripheral devices that expand the computer’s input, output, and storage capabilities. Computer hardware in and of itself does not provide a particularly useful mind tool. To be useful, a computer requires a set of instructions, called software or a computer program, which tells the computer how to perform a particular task.
1.3 - Computer Hardware
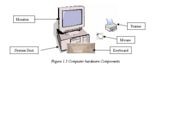
Computer hardware consists of the parts that are tangible, visible and takes up space. Figure 1.3 shows basic components of computer hardware. Computer hardware falls into the following categories: the system unit, input devices, output devices and Secondary storages.
The system unit- the system unit is housed within the computer cabinet. The system unit consists of electronic circuitry that has two parts.
The central processing unit (CPU) controls and manipulates data to produce information. A computer’s CPU is contained on a single integrated circuit or microprocessor chip. These chips are called microprocessors.
Memory, also known as primary storage, holds data and program instructions for processing the data. It also holds the processed information before it is output. Memory is sometimes referred to as temporary storage because it will be lost if the electrical power to the computer is cut off. Data and instructions are held in memory only as long as the electrical power to the computer is on. Memory is located in the system unit on tiny memory chips.
Output devices- output devices are pieces of equipment that translate the processed information from the CPU into a form that humans can understand. One of the most important output devices is the monitor, or computer screen, which may resemble a TV screen. Another important output device is the printer.
Input devices- Input devices are equipment that translates data and programs that human can understand into a form that the computer can process. The most common input devices are the keyboard, and the mouse. The keyboard on a computer looks like a typewriter keyboard, but it has additional specialized keys. A mouse is a device that typically rolls on the desktop. It directs the cursor, or pointer, on the display screen. A mouse usually has two buttons for entering commands. It is also used to draw figures.
Secondary storage- Secondary storage also holds data and programs. However, it stores permanently. That is, the data and programs remain even after the electrical power is turned off. Secondary storage devices are located outside of the central processing unit, although they may still be built into the system unit cabinet. The most important kinds of secondary storage media are as follows:
Floppy Disks/CD-ROMs-hold data or programs in the form of magnetized spots on plastic platters. The storage mediums are inserted into disk drives. The mechanism reads data from the disk. That is, the magnetized spots on the disk are converted to electronic signals and transmitted to primary storage inside the computer Floppy disk capacity is 1.44 Megabytes (MB) and CD – Rom is 650 – 700 Megabytes (MB).
USB Flash Drive – a small light weight removable data storage device. Its capacity ranges from 64MB, 126MB, 512MB, 1GB and 2GB. However as technology continues to grow, such storage devices are improved as well.
A hard disk (or hard drive) contains one or more metallic disks encased within a disk drive. Like floppy disks, hard disks hold data or programs in the form of magnetized spots. They also read and write data in much the same way, as do other storage disks mentioned above. However, the storage capacity of a hard –disk unit is many times that of a floppy disk (10 gigabytes – 40 gigabytes).
1.4 - Computer Software
Software is another name for programs. Programs are instructions that tell the computer how to process data into the form you want. In most cases, the words software and programs are interchangeable.
There are two kinds of software- application software and system software. You can think of applications software as the kind you use. Think of system software as the kind the computer uses.
APPLICATION SOFTWARE- Application software might be described as “end-user’’ software. Application software performs useful work on general- purpose tasks. Examples of common general- purpose programs are:
- Microsoft Word - used to prepare written documents
- Microsoft Excel - used to analyze and summarize data
- Microsoft Access - used to organize and manage data and information
- Communications programs, used to transmit and receive e.g. Internet Explorer, Fire fox – Mozila.
SYSTEM SOFTWARE- System software enables the application software to interact with the computer. The most important system software program is the operating system, which interacts between the application software and the computer hardware. Examples of common operating system are:
- DOS (Disk Operating System)
- Microsoft Windows
- Windows 2000
- Windows ME
- Windows NT
- Windows XP Professional
- Vista