Keyboard
Keyboard
The most familiar input device is the keyboard. Users type the text directly into the computer.
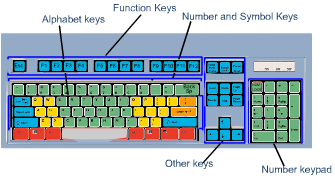
There are a number of layouts of the keyboard. In a QWERTY layout the keys are arranged in the same order as that of a type writer. This is called QWERTY because the keys Q-W-E-R-T-Y occur on the left top row of the keyboard. The keys in this type of keyboard can be grouped into following five types:
1. Function keys – F1 to F12 are programmable keys used as short cut keys to perform certain functions
2. QWERTY keys – alphanumeric keys arranged in same order as that of type writers.
3. Special purpose keys – Tab, Caps lock, Shift, Ctrl, Alt, Esc, Backspace, Enter, Print Scrn, Scroll Lock and Pause/Break are special purpose keys.
4. Numeric pad keys – separate section in the keyboard used for entering numeric data.
5. Cursor control keys- these are used to navigate the cursor on the monitor.
Dvorak keyboards were introduced to improve typing efficiency with simpler layout. However it has yet to overcome the popularity of QWERTY keyboards.
Concept keyboard layout has flat board containing a grid of switches. An overlay image is placed on top of the grid to indicate what will be done on pressing different areas of the keyboard. Such keyboards are useful for children who may find QWERTY keyboard quite complicated to use. Other variation in the keyboards is based on the language variations. For example, the US and UK keyboards are quite similar but are very different from the French keyboard.