EXTAFR100/EXTAFR106/Design Thinking/Technologist Activity 1
From WikiEducator
Jump to: navigation, search
| “ | Our job is not to prepare students for something. Our job is to help students prepare themselves for anything. | ” |
| —A. J. Juliani | ||
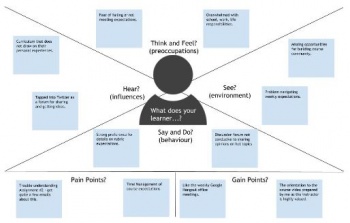
Creating an empathy map
The first exercise in this module asks you to empathise with your 'users' — your learners — to identify a challenge that could be solved through the purposeful use of technology in your professional practice. You are going to create an empathy map! What does an empathy map look like? Here is an example that you can download as a template.
Technologist Activity 1
Create an empathy map following these steps:
- Gather information from and about your learners.
- Try and utilise information that you have already acquired or know to be true through feedback from course evaluations, emails, and other communications. Ideally, you will create a specific method of gathering feedback for this exercise. You might also do this through conversations or other forms of formal or informal information gathering.
- Ask/gather information about what your learners think, feel, say, do, see, and hear. What do they have difficulty understanding or doing in your learning context?
- Think about the various experiences of your learners. What notions around access, ability, inclusion, and diversity can help better design your teaching practices so that it is useful to all?
- Reflect on the feedback you have collected from your learners and begin sketching your empathy map. Use the Empathy Map Template with fields to respond to the above guiding questions.
- To use the template, go into the File menu on the Google document and make a copy of the file. Rename the file for yourself and complete the template.
As evidence of completion, please add a link or a copy of your response to your Extend NZ blog or portfolio.
After your empathy map is complete, try to get additional feedback in one of the following ways:
- Seek out a colleague within your department/discipline area and discuss your empathy map with them. See if there are shared concerns, or perhaps strategies they might suggest that you have not yet considered.
- Circle back to your learners to make sure what you have captured accurately reflects their experience. This could involve an informal conversation with one or more of the learners you gathered the information from.