EIfEL qualification framework
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 eLearning and the transformation of the teacher/trainer profession
- 3 The competencies
- 4 Components of the Framework
- 5 Implementation guides
- 6 The Competency Framework
- 7 Key Area A - Prepare a learning event
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Unit A.1. Provide guidance to learners and staff for the effective use of KILT
- 7.3 Unit A.2. Prepare participants for the learning event
- 7.4 Unit A.3. Design learning programmes
- 7.5 Unit A.4. Develop KILT- based learning resources
- 7.5.1 Knowledge required
- 7.5.2 Element A.4.1. Agree specifications for learning resources
- 7.5.3 Element A.4.2. Develop learning resources according to specifications
- 7.5.4 Element A.4.3. Use authoring tools to develop learning resources according to specifications
- 7.5.5 Element A.4.4. Use authoring tools to adapt learning resources
- 7.6 Unit A.5. Select and implement learning resources
- 8 Key Area B - Run a learning event
- 9 Key Area C - Support learners
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Unit C.1. Help learners manage their own learning
- 9.2.1 Knowledge required
- 9.2.2 Element C.1.1. Help learners identify their learning needs
- 9.2.3 Element C.1.2. Help learners identify their preferred learning styles
- 9.2.4 Element C.1.3. Help learners select learning opportunities
- 9.2.5 Element C.1.4. Help learners develop and review their personal learning plans
- 9.3 Unit C.2. Support individual learners, using KILT
- 9.4 Unit C.3. Support groups of learners, learning communities and networks using KILT
- 9.4.1 Knowledge required
- 9.4.2 Element C.3.1. Support group learning with KILT
- 9.4.3 Element C.3.2. Support active learner interaction and collaborative learning using KILT
- 9.4.4 Element C.3.3. Support the development of online learning communities
- 9.4.5 Element C.3.4. Provide support for knowledge construction and sharing
- 9.5 Unit C.4. Promote the development of learner autonomy, confidence and effectiveness in a supportive learning environment.
- 9.5.1 Knowledge required
- 9.5.2 Element C.4.1. Actively support learners in developing independence, confidence and ethical behaviour
- 9.5.3 Element C.4.2. Provide support for learner collaboration and socialisation to enhance learning experiences
- 9.5.4 Element C.4.3. Construct learning experiences in which learners assess and plan their personal development
- 9.6 Unit C.5. Support application of learning
- 9.7 Unit C.6. Manage non-formal and informal learning
- 10 Key Area D - Assess learner progress
- 10.1 Introduction
- 10.2 Unit D.1. Plan assessment of learner progress
- 10.3 Unit D.2. Monitor, assess and report on learners’ progress
- 10.3.1 Knowledge required
- 10.3.2 Element D.2.1. Assess what individuals have learned and achieved
- 10.3.3 Element D.2.2. Provide feedback to learners
- 10.3.4 Element D.2.3. Maintain records on learners’ achievements
- 10.3.5 Element D.2.4. Use assessment results to guide programme planning, delivery and assessment
- 11 Key Area E - Promote accessibility for learners
- 12 Key Area F - Evaluating learning programmes
Introduction
This competency framework concerns those teachers and trainers (as well as those responsible for their training and development, and policy makers) who are directly involved in the management and delivery of learning programmes and events to individuals and groups. It will also be relevant to other people who are involved in supporting learners, such as coaches, mentors, librarians etc, who constitute an important part of the community of learning professionals.
The emphasis in this framework is on the facilitation of a broad range of learning opportunities through the use of Knowledge, Information and Learning Technologies (KILT). The knowledge, skills and attitudes required are presented under the heading of eLearning competencies, but it is clear that these competencies are in the process of becoming mainstream competencies. The use of these technologies is becoming increasingly widespread for learning purposes, as their potential is recognised and as new demands are made on those who support learners and on the learners themselves.
The Key Role or ‘mission’ for the competency framework is:
Employ knowledge, information and learning technologies to provide high-quality teaching and training, to create effective opportunities for learning and to enable all learners to achieve to the best of their ability
eLearning and the transformation of the teacher/trainer profession
As is made clear in the description of the methodology sections accompanying the framework, the definition of eLearning is broad. In this framework, eLearning is not taken to be ‘distance learning’ or ‘online learning’, so the rather simplistic distinction between ‘distance learning’ and ‘face to face delivery’ that has resulted in the widespread use of the term ‘blended learning’ will not be found here. eLearning may take place at a distance or in the presence of a teacher, trainer or tutor. What qualifies the experience as eLearning is the use of one of a range of KILT to enable and enhance the learning experience.
There is clearly an important interface between what may be understood as generic teacher/trainer (TT) competencies and the new competencies required in a knowledge society, and the framework reflects this. Therefore, the necessary skills of planning, communicating, analysing learning and development needs, providing meaningful learning activities, assessment of learners and evaluation of programmes, will be recognisable to all those involved in education and training. What is new is not only the need to acquire technical competencies but also to be ready for a transformation of ‘traditional competencies’ and for the acquisition and development of those competencies that result from radical changes in roles and practice. These changes are being simultaneously driven by the evolution of society and by the previously unimagined opportunities offered by technology. Societal demands for improved accessibility, inclusion and learner-centred pedagogy are being facilitated by innovative techniques and tools for teachers and trainers.
Some of the principal trends are summarised here:
- An increased emphasis on learner-centred and personalised learning – from ‘push’ to ‘pull’
- An accompanying responsibility on the part of learners for their own personal development and lifelong learning
- Flexibility on the part of trainers– being ready to respond to evolving situations rather than arrive with a ready-made solution.
- A change of role from ‘expert’ to facilitator, guide, coach – and, where appropriate, manager of the learning environment
- A recognition that the learner may play the role of teacher: content comes from the interaction of the participants as well as the educators
- Collegiality and collaboration: the onus is on teachers and trainers as well as learners to create communities of practice among peers and with those who have very different skills and backgrounds
- Responsibility of teachers/trainers for knowledge management and contribution to organisational learning
- Knowledge and learning seen as organic and connected to work and to other activities
- An explicit responsibility on the part of teachers/trainers to promote equal opportunities, inclusiveness and the valuing of diversity
- An Increasing demand to encourage, recognise and validate non formal learning
- Access to learning resources and expertise throughout the world: a global ‘marketplace’.
Who is the competency framework for?
According to several TTnet studies[1] a professional educator can have different job classifications: trainer, group leader, tutor, teacher, instructor, trainer of trainers. Perhaps the only two definitions that would be universally accepted are the following:
- The term teacher is generally used in European Union countries to designate personnel in primary schools, secondary schools and initial vocational training colleges in education systems, regardless of the level of education.
- A trainer refers to professionals involved in apprenticeship systems, on-the-job and off-the-job training activities and, more generally, in private sector training markets.
Other terms are used in many different ways depending on countries and professional sectors. What these titles have in common, however, is that the holders have been officially recognised as playing a formal role in teaching and training. It is clear that this is the most easily identifiable section of our target population.
If we now take into account the startling estimation that as much as 80% of what we learn is acquired through non-formal and informal means, we start to think about other potential users who would not be classed as ‘professional educators’ but are involved in helping others to learn on an occasional or part-time basis. Librarians, work-based coaches and mentors etc may well find a competency framework useful, both as to help them carry out these activities, and also perhaps to enable them to gain recognition for their achievements.
The competencies
The competencies contained within the framework require the identification of the learning goals, needs and styles of individuals and the design, management and evaluation of programmes to meet those individuals’ requirements. They involve a sound knowledge of the contribution of KILT to successful learning events, and appropriate levels of expertise in using KILT to enhance the learning experiences of individuals and groups.
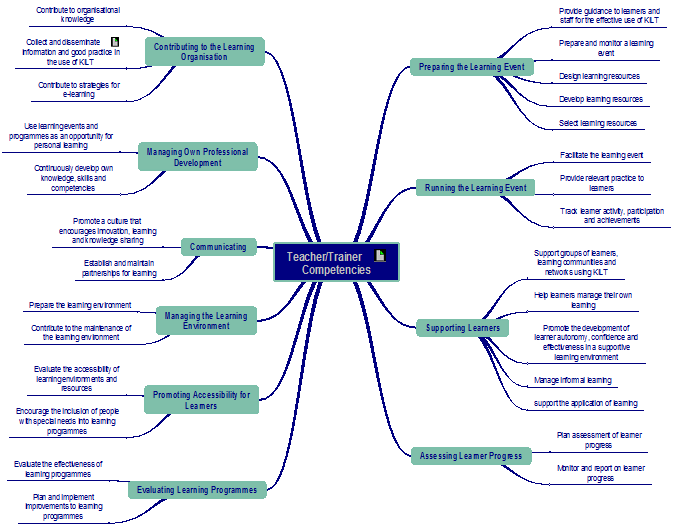
The framework will be presented in two versions. The full framework, as indicated in the graphical representation of the competencies above, contains 10 areas of competence:
- Preparing the learning event
- Running the learning event
- Supporting learners
- Assessing learner progress
- Promoting accessibility for learners
- Evaluating learning programmes
- Managing the learning environment
- Contributing to the learning organisation
- Managing own professional development
- Communicating
The scope of the framework ranges from the preparation of the learning environment through to application of learning to workplace activities. It encompasses both formal and informal learning experiences. The framework also covers the contribution of these learning activities to organisational knowledge and performance, as well as the opportunities afforded for the personal learning and development of learning personnel. The areas contain eLearning competencies that concern the broad population of teacher/trainers. On the other hand, the competencies presented here will not all be demanded of the same person. Teachers/trainers will have a greater or lesser responsibility for technology or for management aspects, for example. It will be up to individuals to identify and use those parts of the framework that are of immediate or potential relevance. The order of presentation does not indicate any chronological or functional order, or any order of importance. Nor are any levels of competence indicated.
The shorter version of the competency framework that is presented here focuses uniquely on the interaction between teachers/trainers and learners and so contains these six competencies:
- Preparing the learning event
- Running the learning event
- Supporting learners
- Assessing learner progress
- Promoting accessibility for learners
- Evaluating learning programmes
Components of the Framework
We have seen that the Key Role or Purpose of the competency framework is:
Employ knowledge, information and learning technologies to provide high-quality teaching and training, to create effective opportunities for learning and to enable all learners to achieve to the best of their ability
The Key Role is then divided into Key Areas, which begin to detail the activities that answer the question, “what has to be done to achieve this?’” These are in turn further subdivided into units of competence and thence into two or more elements of competence. It is at the unit level that we can start to talk about discrete competencies, the performance of which can be evaluated and assessed.
The elements of competence as presented in this framework have two essential components:
- Knowledge requirements
- Performance criteria
Knowledge requirements
A competent performance is based on sound knowledge and understanding of the activities being performed – this is what enables us to repeat the performance and to transfer the competency to other situations and contexts.
The competency framework begins with a statement of the core or generic competencies that all learning professionals should possess. Each unit of competence then indicates the knowledge requirements specific to that unit.
Performance criteria
The performance criteria specify the results expected in carrying out the activity indicated in the element title. They thus provide a detailed description of the performance required that enables evaluation – either by individuals themselves, or by external evaluators.
Implementation guides
Accompanying the competency framework are two guides to help you use the framework most effectively in your particular context.
The User Guide gives information about how the framework may be used for a variety of training and development activities, including training needs analysis, design of learning programmes and assessment of competencies. It indicates the variety of contexts in which the framework may be used. It also suggests the evidence that you may present in order to demonstrate competency if you wish to use the framework for a professional development programme.
The Skills Check diagnostic tool will help you to position yourself in relation to the activities detailed in the guide. It summarises these activities and enables you to determine what you do now.
The Competency Framework
Core knowledge requirements
The following list indicates the knowledge requirements that are central to the first six core competency areas. Additional knowledge requirements are also indicated for individual units of competence.
To perform competently in the competency framework you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- the organisation’s requirements regarding learners’ participation, progress and achievements
- the organisation’s resource constraints
Health and safety
- occupational health and safety regulations pertinent to your responsibilities
- the organisation’s occupational health and safety policies
- your own responsibility for ensuring a healthy and safe learning environment
- how to deal with breaches in health and safety requirements promptly and in line with organisational and legal requirements.
- how to obtain help where necessary for the maintenance of health and safety
Legal requirements
- relevant data protection legislation: and how to ensure that this is rigorously applied
- relevant legislation with regard to individual rights and equality of opportunity
- the law of copyright and how this may restrict the use of certain resources
Learning technologies
- the range of ways KILT (hardware, software and systems) may be used to facilitate the learning of others
- the ways in which KILT can help match learning opportunities to learners’ abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles
- how to adapt KILT resources to the requirements and constraints of the learning environment
- how to provide learners with the KILT resources and facilities required to put into practice the learning objectives of the event, e.g.
electronic white board
email,
forum and discussion group
virtual media or resources centre
tools (java applets, simulation, etc.)
Learning and development
- how to establish learning objectives
- how to evaluate the extent to which learning objectives have been achieved.
- the characteristics of formal, non-formal and informal learning
- ways of learning, learning styles and appropriate learning strategies in relation to the required outcomes of learning programmes
- the importance of helping learners to identify their learning needs and select learning opportunities autonomously, and how to do so
- how to analyse the suitability of different learning opportunities with regard to the range of abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles learners may have
- methods of assessing learners
- how to provide constructive feedback to learners, both formative and summative
- methods of assessing learning programmes
- how to plan and promote application of learning
Providing support
- methods of giving information, advice and support in a manner that promotes individual autonomy and encourages self-development
- general and specific sources of guidance
- the range of resources and tools for providing support to individual learners and groups of learners, e.g.
email, computer mediated communication, telephone
journals, mailing lists
learning communities, communities of practice
colleagues, management, family
professional bodies and communities
- own limits in terms of giving advice and guidance
- sources of referral
- how to communicate and interact with learners in a manner that fosters learners’ confidence, self-esteem and self-image
Monitoring and evaluation
- how to evaluate whether the outcomes of learning indicate that learning opportunities are suitable to learners’ particular abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles
- the importance of evaluating the effectiveness of activities, and how to make valid evaluations
- the importance of maintaining complete, accurate and up-to-date records and how to do so using KILT.
- how to analyse information to identify trends and common and emerging problems
- the importance of involving users in evaluating the quality of the support they receive, and how to do so
Managing resources
- how to provide individual learners and groups of learners with the resources required to achieve their learning objectives
- how to adapt resources to the requirements of the learning environmentCommunication
- how to ensure that all those involved in the learning event recognise their responsibility for ensuring an optimal learning environment
Continual improvement
- how to use information and experience to improve systems and personal performanceAccessibility
- the importance of providing access to learning to all, regardless of physical or intellectual disabilities or environmental disadvantages
- basic principles of ensuring accessibility in the learning environment
- the range of KILT tools available for identifying preferred learning styles and needs of learners with a diverse range of abilities
- how to exploit the possibilities offered by KILT to ensure accessibility
Professional ethics
-
- the attitudes and behaviour expected of professional teachers/trainers
N.B. the term organisation is used here to describe the entity responsible for providing the learning services. This may be your own organisation (of any size including freelance training services) or an external organisation that has commissioned your services.
Key Area A - Prepare a learning event
Introduction
This Key Area is for teachers/trainers who are involved in the preparation of learning events - either autonomously, or for example, under the supervision of a training manager or head of department. They may have a responsibility for ensuring that the participants in the event are fully briefed and prepared to get the most out of the experience, with the aid of KILT. The basic principles of designing learning programmes that include challenging and meaningful learning activities are the responsibility of all learning professionals. If your responsibilities involve the design, development and selection of learning resources you will find that these competencies are also covered here.
Staff involved in this area need to use KILT to record information about learners’ participation, starting with their induction into the organisation and its facilities. They need to record information about learners’ attendance and participation in activities associated with learning, and use this information to identify any need for intervention. They also need to monitor what learners have achieved against their personal learning plans. Furnished with this information, staff need to plan to provide feedback to learners and to report to colleagues on progress, participation and achievement.
In an extended learning environment it is particularly important to consider how learners will continue to access the resources used and/or produced in the course of the programme.
The Area comprises 5 Units:
- Unit 1.1 Provide Guidance to learners and staff for the effective use of KILT
- Unit 1.2 Prepare a learning event
- Unit 1.3 Design Learning Resources
- Unit 1.4 Develop Learning Resources
- Unit 1.5 Select Learning Resources
Unit A.1. Provide guidance to learners and staff for the effective use of KILT
Specialists in the use of KILT need to support other staff in developing the knowledge, skills and competencies they require to use KILT hardware, software and systems efficiently and effectively in order to facilitate the learning of others. They also need to provide advice, guidance and support to users on a continuous basis to allow them to increase their autonomy and effectiveness in using KILT.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning and development
- the range of tools and techniques that can be used to identify the emerging needs of staff and learners
- how to assess staff levels of knowledge, skills and competence in terms of the level required
- how to assess learners’ levels of knowledge, skills and competence in terms of the level required
Learning technologies
- the resources and support staff need to enhance their competence in using KILT to facilitate the learning of others, and how to develop these
- the importance of establishing service standards and how to do so
Providing guidance and support
- the range of appropriate strategies and techniques to help learners and staff develop the knowledge and skills they need to use KILT
- the different types of support required: technical (hotline) pedagogical (tutoring) and how to implement them
- how to ensure that personnel receive appropriate induction and ongoing support
Accessibility
- how to ensure accessibility to guidance and support, especially to learners and staff with special needs.
Communication
- how to make known the availability of guidance and support to learners and staff
Element A.1.1. Support staff in acquiring and developing the knowledge and skills needed for using KILT to facilitate the learning of others
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish the range of ways in which KILT may be used to facilitate the learning of others, currently and in the future.
- identify the knowledge and skills staff need to apply KILT effectively to facilitate the learning of others.
- accurately identify the current levels of knowledge and skills of staff, and what they need to learn in order to use KILT effectively.
- provide appropriate advice and guidance to help staff develop the knowledge and skills they need to use current and future hardware, software and systems to facilitate others’ learning, taking into account the learning styles of individual members of staff.
- encourage staff to take a systematic and proactive approach to continuously enhancing their competence in using KILT to facilitate the learning of others.
- evaluate the extent to which staff have developed the required knowledge and skills
- develop and promote appropriate resources and support for staff continuously to enhance their competence in using KILT to facilitate the learning of others.
Element A.1.2. Help learners to acquire and continuously develop their use of KILT
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish the knowledge and skills learners require to use KILT for effective learning
- accurately identify learners’ current levels of knowledge and skills and what they need to learn in order to use KILT effectively.
- use appropriate, effective and efficient strategies and techniques to help learners develop the knowledge and skills they need to use KILT, taking into account learners’ abilities and learning styles.
- provide learners with practical opportunities to apply their knowledge and skills in using KILT.
- evaluate the extent to which learners have developed the required knowledge and skills.
- use alternative strategies and techniques, if learners have not fully developed the required knowledge and skills.
- encourage learners to take a systematic approach to their continuing personal and professional development through KILT.
Unit A.2. Prepare participants for the learning event
This competency entails putting in place measures to ensure an optimal learning experience for both learners and those who are facilitating the learning event. It involves ensuring that the event is suitable for learners and that they are fully briefed with essential information regarding the learning programme. It also entails agreeing with learners the criteria for success and how this will be measured. Providing access to learners with special needs is a further important component of this competency. Staff also have a responsibility for ensuring that those who are facilitating the learning experience are also fully briefed regarding the needs and objectives of learners, that agreement is reached on methods of monitoring and evaluation of learner progress, and that measures are in place to ensure collaboration and teamwork on the part of contributors.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning and development
- identification of learner prerequisites
Learning technologies
- the ways in which KILT can be used to record, process and provide information about learner participation, e.g.
- electronic portfolio or ‘digital binder’
- firewall, software compatibility, computer configuration, network bandwidth
- interoperability
- nature of technical problems and the procedures for getting them solved
Providing support
- how to prepare learners by providing essential information
- the support learners may require to record and update information, and how to provide this support
- how to provide information and ongoing support to all staff contributing to the learning event
Accessibility
- how to welcome, and provide access to learning for, learners with special needs
- the importance of encouraging learners with a diverse range of abilities to record and update details about themselves and their participation, and how to do so
Monitoring and evaluation
- the data required about learners and their use of the organisation’s services.
- the range of appropriate KILT tools available for recording learners’ participation, progress and achievements
- how to use information about learner participation to identify trends and evaluate the need for intervention to improve participation
- how to evaluate any need for intervention to improve learners’ participation, and report this to appropriate colleagues
Communication
- how to put in place systems that optimise the production and exploitation of relevant information
- how to make known the facilities and support available to learners and staff
Element A.2.1. Prepare learners for the learning event
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- check learners’ prerequisites to attend the learning event
- send the necessary information to learners for participation in the learning event and obtain acknowledgement when possible
- state clearly the opening and the closing time/conditions of the event
- put in place a facility for learners to check in well in advance of their access to the event, and to contact the technical support service if problems arise
- establish in negotiation with learners the criteria for success for the learning session
- welcome and encourage learners’ feed-back through a variety of channels
- make arrangements for learners with special needs
Element A.2.2. Prepare contributors to the learning event
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
provide contributors with clear and accurate information about the planned outcomes, inputs and processes of the learning event and the requirements of learners
provide contributors with clear, accurate and relevant information about learners’ current knowledge and skill levels
brief contributors on the input and activities of other contributors to the learning event
provide contributors with adequate opportunities and facilities to enable them to collaborate effectively in the facilitation of the learning event
provide contributors with adequate guidance to enable them to observe required procedures and protocols
agree tracking, reporting and evaluation methods with contributors, using KILT where appropriate.
Unit A.3. Design learning programmes
This Unit is for those teacher/trainers who have some responsibility for designing learning programmes. Depending on the context in which you operate, this may involve the design of curricula, courses or events. Necessary skills include ensuring that the proposed programme meets learners’ needs and objectives; building in methods of assessing learners, and evaluating the programme or event. The competency also involves designing challenging learning experiences, the outcomes of which are relevant to the context of learners. Designing different types of feedback is a further essential feature of this competency.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning and development
-
- how to identify and analyse training needs related to the situation and learning needs of the individual
- the range of formal and informal methods that can be incorporated into learning programmes, what each can contribute, and how to integrate different methods into programme design
- how to integrate different learning opportunities and create a coherent learning programme
- the range of resources available to ensure authentic learning
- how to design relevant practice, employing, for example
- simulation
- work experience
- models
- case studies
- different types of feedback, e.g.
- intrinsic / extrinsic
- self-assessment
- exercise
- tests
- comparison with a reference model
- others
- sources of feedback, e.g.
- the learner
- the learning resource
- the learning management system
- a teacher; a tutor
- other learners
-
- methods of monitoring and reviewing learners’ progress
Communicating
-
- how to gain commitment to training proposals and plans for individuals and groups
- how to achieve shared and realistic views among stakeholders about the design, content, learning strategy and methods
Accessibility
-
- how to ensure that learning programmes are designed to promote accessibility and take into account the special needs of learners
Element A.3.1. Design a learning programme
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify clearly and accurately the learning requirements that have to be addressed
- select options for meeting learner requirements to ensure that learners will have the opportunity of achieving learning objectives
- select options for meeting learner requirements that promote equality of opportunity and access to learning and achievements
- ensure that learning programmes specify how learning requirements will be met and the opportunities available to do so
- specify clearly methods of evaluating the effectiveness of the learning programme
- specify methods of monitoring and reviewing learners’ progress and assessing their achievements
- specify provision for the support of learners
- specify clearly the roles and responsibilities of all those involved in delivering the learning programme and obtain their agreement
- identify additional resources required to deliver the programme
Element A.3.2. Design challenging and relevant learning
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- base activities on an accurate identification of learners’ needs.
- define the conditions and the resources you have to supply so that practice can take place
- plan to provide learners with a wide variety of learning experiences and media to increase the potential for acquiring knowledge, making effective use of KILT
- ensure that the planned learning situations are authentic so that the activities learners perform is based on the roles they play as students, workers and citizens
- plan learner access to the kinds of information sources that people use in their careers and lives.
- design learning programmes to enable all learners to apply what they learn to settings beyond the school/university/training centre door.
Element A.3.3. Design feedback
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- define the different types and levels of feedback that will be provided to the learner during the learning programme
- define the level of interaction between the learner, other learners and the learning support staff from self-study to group learning that will produce feedback.
- define when different types of feedback will be provided
- define how the different types of feedback will be provided
- define any external sources of diagnosis and correction needed.
- define interaction with the organisation’s information system and reporting data to determine how the results of the feedback will be tracked and reported to the management system and provide collectable evidence
Unit A.4. Develop KILT- based learning resources
This competency is for those teachers/trainers who are responsible for the development of KILT-based learning resources. It covers agreeing the specifications with those commissioning the resources (where appropriate) and then developing them on this basis. One element deals generally with the development of resources, while two others are specifically concerned with the use of authoring tools to develop and adapt resources.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Legal requirements
-
- legal and contractual implications of using media and software
Learning technologies
-
- how to access reliable sources of information on developments in KILT
- Criteria for developing resources, e.g.
- The value of different media (text, image, sound, simulation) and how to select and combine them in an optimum way to provide relevant learning experiences the hardware requirements
- the software platforms to be used
- programming and authoring tools and methodologies to be used
- documentation standards and requirements
- Criteria for evaluating learning resources, e.g.
- ability to deliver the specified learning objectives
- learning style and modalities (self-study, trainer led, group learning, blended, distance)
- learning environment (asynchronous or synchronous, competence based or not)
- access and integration to the workplace (though a portal, within an application)
- The nature of specifications, e.g.
- storyboards
- sketches
- algorithms, scripts
- working drawings
- finished visuals
Learning and development
-
- the ways in which the characteristics of the learning environment may impact on the design of KILT resources, and how to minimise any negative impact
Software and hardware
-
- the range of software platforms that may be used, and how to select appropriate ones
- how to establish the hardware requirements for learning resources
- the range of programming and authoring tools and methodologies that may be used, and how to select appropriate ones
- likely documentation requirements and how to establish these
- the importance of checking that the specifications are capable of delivering the agreed learning objectives, and how to do so.
standards
-
- sources of current standards
- how to identify and assess current standards for their relevance to the product's requirements
- how to estimate the costs, specify and select distribution formats
- select and apply suitable conventions, methods and media to produce drawings and associated graphical information
- how to select methods, media and systems for producing drawings
Element A.4.1. Agree specifications for learning resources
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish with those commissioning the learning resources the nature of the learning objectives, content and the format of the learning resources in line with learner requirements
- establish the characteristics of the learning environment in which the resources will be used.
- when specialist skills are required, collaborate with subject, learning and design specialists to develop specifications for KILT
- draft specifications that are complete, accurate, comply with design information and relevant documentation and meet the recognised technical conventions required
- base specifications on identified, applicable, current source information, including any relevant supplier and cost information
- produce specifications and supporting information within agreed deadlines and check them for accuracy before release
- check with those commissioning the resources that the specifications fully meet their requirements
Element A.4.2. Develop learning resources according to specifications
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- define and agree on the method of development which is most relevant to the objectives and to the experience and abilities of the development team
- design, develop and test user interface with learning activities to ensure they meet client and users requirements
- draft resources according to technical specifications
- develop the complete learning resource
- import the resource to the delivery platform(s) and test that it functions correctly
- test the usability and capability of the resources to meet the agreed learning objectives and its manageability with a representative sample of typical users
- deliver finished KILT-based learning resources to those commissioning them and obtain their acceptance.
- review the design and development process and identify ways in which the process could be improved in the future.
Element A.4.3. Use authoring tools to develop learning resources according to specifications
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and assess authoring tools for their capability to support the author in creating the expected learning experience from combining existing components
- select authoring tools that offer the greatest potential for meeting requirements based on the author(s) abilities, complexity of the learning resource and its operation
- when existing tools are inadequate for the task, assess alternatives such as acquiring another tool
- in the course of using authoring tools, identify and remedy and bugs and difficulties in achieving the performance required by the specification promptly
- identify accurately and exploit opportunities to improve the efficiency of operations within the constraints of the production
- produce resource within agreed deadlines, assess them thoroughly and confirm them as meeting specifications
- store finished resources and associated documents securely and make them available to those who require them
Element A.4.4. Use authoring tools to adapt learning resources
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and assess authoring tools for their capacity to modify existing learning resources in order to create the expected learning experience from combining existing components
- select authoring tools that offer the greatest potential for adapting existing learning resources cost-effectively
- operate authoring tools efficiently, and identify and remedy promptly any bugs or difficulties in achieving the performance required by the specification
- produce completed resource within agreed deadlines, assess them thoroughly and confirm that they meet specifications
- store finished products and associated documents securely and made them available to those who require them
Unit A.5. Select and implement learning resources
Teachers/trainers responsible for the selecting and implementing learning resources need to identify sources of relevant KILT-based learning materials and assess the quality and appropriateness of these materials to meet user requirements. They need to acquire relevant KILT-based learning materials, format them and make them available for use within the organisation’s physical and virtual environments. They also need to encourage people to use the materials by publicising how they can be used and the benefits they may provide.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Legal requirements
-
- legal and contractual implications of using media and software
- the law of copyright and how this may restrict the use of certain resources
Learning technologies
-
- how to evaluate sources of KILT-based learning materials in respect of the range and quality of materials, quality and speed of service and value for money
- the range of networks and learning communities involved in developing and using KILT-based learning materials
- sources of free and priced KILT-based learning materials
- sources of information about the product, and about intended end users
- storage and security facilities and requirements for agreed proposals
- criteria for selecting resources:
- The value of different media (text, image, sound, simulation) and how to select and combine them in an optimum way to provide relevant learning experiences the hardware requirements
- hardware or software
- accessibility or mobility facilities
- delivery modes
- adaptability, customisation
- Criteria for evaluating learning resources:
- ability to deliver the specified learning objectives
- learning style and modalities (self-study, trainer led, group learning, etc.)
- learning environment (asynchronous or synchronous, competence based or not)
- licence requirements for the use of KILT-based learning materials
Learning and development
-
- the ways in which the characteristics of the learning environment may impact on the selection of KILT resources, and how to minimise any negative impact
Software and hardware
-
- the range of software platforms that may be used, and how to select appropriate ones
- how to establish the hardware requirements for KILT resources
- likely documentation requirements and how to establish these
Standards
-
- sources of current standards
- how to identify and assess current standards for their relevance to the product's requirements
- how to estimate the costs, specify and select distribution formats
Element A.5.1. Identify sources of KILT-based learning materials
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify sources of learning resources and keep updated about current and future development
- participate actively in networks and learning communities involved in developing and using KILT-based learning materials
- identify a sufficient range of sources of both free and priced KILT-based learning materials to meet the organisation’s current and anticipated future needs
- evaluate sources of KILT-based learning materials in respect of the range and quality of materials, quality and speed of service and value for money
- publicise recommended sources of KILT-based learning materials in formats that are easily accessible to staff who may use the materials
Element A.5.2. Select KILT-based learning and support resources
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish the criteria for the selection of learning and support resources in terms of learner requirements and objectives and available resources with appropriate personnel
- establish criteria, based on the requirements of, clients, colleagues and learners, for assessing the quality and appropriateness of current learning resources provision.
- assess current provision for learning resources and tools,
- assess the quality and appropriateness of available KILT resources against established criteria and present your assessment resources in ways that allow clients, colleagues or learners to decide whether and how to use them.
- where necessary, commission and manage the production of new resources and tools to meet identified needs – taking into account possible constraints and legal requirements in using or commissioning learning resources.
- assess the ability of the organisation’s KILT infrastructure to support learning delivery
- carry out feasible, timely and cost-effective evaluation of learning resources and make any necessary changes to provision and practice
Element A.5.3. Integrate learning resources in the learning environment
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- test the compatibility of the learning resource with existing resources
- test, with a representative sample of learners, the usability and capability of the learning resources to meet the agreed learning objectives
- establish systems for gathering information on the use of the resources and evaluating their effectiveness
- involve learners and colleagues in evaluating the effectiveness of the resources
- gather complete, valid and up-to-date information about the use of the resources
- evaluate the effectiveness of the designed materials in meeting learning objectives for learners with a diverse range of abilities
- provide information about the effectiveness of the designed materials to those authorised to have it
Key Area B - Run a learning event
Introduction
This Key Area is for those people who are directly responsible for the delivery or facilitation of a learning event. They will be responsible for the whole learning event from opening to close. This involves managing the learning event, ensuring that learners are provided with relevant practice activities to enable them to achieve the desired objectives, and providing them with supplementary resources where necessary, as well as contributing to the assessment of learner progress and of the learning event itself. Those carrying out these activities will demonstrate competence in using the opportunities afforded by KILT to enhance the learning experience.
The Area comprises 2 Units:
Unit B.1 Provide Guidance to learners and staff for the effective use of KILT
Unit B.2 Prepare a learning event
Unit B.1. Facilitate a learning event
This unit concerns the key activities associated with responsibility for facilitating a learning event. It covers opening the event and ensuring that learners are welcomed and fully briefed in order to perform effectively. The focus of the second element is on the facilitation skills required for a successful learning event. Closing an event entails debriefing learners and carrying out a preliminary evaluation of the programme. An important ongoing activity is the tracking of learner activity, participation and achievements.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning and development
- different training roles, styles and tasks, and their practical implications for the teacher/trainer's work
Learning technologies
- the importance of using a mix of appropriate tools and techniques to identify, record and review learners’ preferred learning styles, and how to use KILT to best effect within this mix
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously – for example by using electronic portfolios
Providing support
- how to establish and maintain effective learning, coaching and counselling relationships with a wide variety of learners in a range of different training situations.
- difficulties experienced by learners in different types of learning situations, and how to recognise and tackle them
Group dynamics
- key theoretical models of group roles and work
- how to adapt facilitation techniques to group size
- how to address individual needs in a group setting
Monitoring and evaluation
- how to involve stakeholders in the evaluation results
- how to debrief learners
Accessibility
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice in relation to group work.
Knowledge management
- how to collect the information produced during the learning event for the future – e.g.
recording activities and outcomes – manually or electronically, e.g. by using conferencing software functions to record the performance
using a forum to record contributions asynchronously
Element B.1.1. Open the learning programme
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- introduce learners to the learning environment (physical and digital) in a way that builds their confidence and encourages them to experiment
- introduce learners to the content, schedule and activities of the proposed learning programme
- inform learners about access to technical and learning support
- provide a ‘test’ space for practising working with the environment.
- establish the rules and procedures for communication with others
- help learners to identify their preferred learning styles
- establish with learners how they will learn in the learning environment, according to their learning style, ability and the facilities available
- encourage learners to develop and continuously review their personal learning plans autonomously
- encourage learners with different abilities to benefit from available learning opportunities
Element B.1.2. Facilitate a learning event
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- manage event times and scheduling
- present clear and accurate information in a tone, manner, pace and style that is appropriate to the needs and capabilities of the learners
- employ delivery and facilitation methods appropriate to learners’ levels and needs, taking into account the size and composition of the group
- make adjustments to delivery and facilitation methods in response to learners’ needs
- employ learning resources to optimise the learning experience
- assess the effectiveness of the learning environment and suggest necessary improvements
Element B.1.3. Close a learning event
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- collect assessment results (formative and summative) and other information in line with the success criteria defined and make an assessment based on these criteria
- debrief learners using appropriate and agreed methods
- prepare a post-course summary and evaluation and disseminate it to the relevant people, observing the required level of confidentiality
- when required, send a report to learners’ managers
- review the end of course process and suggest possible improvements
- agree action plan with learners, and their line managers where appropriate, for application of learning and evaluation of results
Element B.1.4. Track learner activity, participation and achievements
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify the data required about learners’ use of learning services
- use appropriate KILT systems to capture and process data about learner participation and ensure the confidentiality of this data
- encourage learners with a diverse range of abilities to use KILT to record and update information about themselves and their participation autonomously
- provide the support learners need to record and update data about themselves
- maintain complete, accurate and up-to-date information on learner participation using KILT
- use KILT to evaluate learners’ participation and identify trends
- evaluate any need for intervention to improve learners’ participation, and report this to appropriate colleagues
- use information obtained to improve the tracking system
Unit B.2. Facilitate authentic learning and relevant practice
This unit focuses on the nature and quality of the learning experience. It is the responsibility of the teacher/trainer to create a learning environment that allows a variety of leaning approaches and activities that stimulate learners and that have a clear relationship to their own situation. The provision of relevant practice reinforces the pertinence of the learning activity to the learners’ context. The teacher/trainer should make use of the opportunities offered by KILT to enhance the learning experience in line with organisational resources and constraints.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently in this unit, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning and development
- different facilitation roles, styles and tasks, and their practical implications for the teacher/trainer's work
- a range of methods for encouraging authentic and challenging learning, for example:
- problem-solving
- case-studies
- simulations
- communities of practice
Learning technologies
- the contribution of KILT to the provision of authentic and challenging learning
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously
Providing support
- how to establish and maintain effective learning, coaching and counselling relationships with a wide variety of learners in a range of different learning situations.
- difficulties experienced by learners in different types of learning situations, and how to recognise and tackle them
Group dynamics
- key theoretical models of group roles and work
- how to adapt facilitation techniques to group size
- how to address individual needs in a group setting
Monitoring and evaluation
- how to involve stakeholders in the evaluation results
- how to debrief learners
Accessibility
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice in relation to group work
Element B.2.1. Facilitate authentic and challenging learning
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- provide learners with a wide variety of learning experiences and media to increase the potential for acquiring knowledge
- raise and encourage essential questions to guide enquiry
- include research and evidence-gathering opportunities in learning activities.
- provide learners with opportunities to use creative thinking to generate solutions in the context of real situations.
- provide opportunities for learners to speak, record and reflect on their own learning.
- provide a social context for learning, with effective use of cooperative learning and learner interaction.
- encourage learners to apply what they learn during the learning event to their own situation
Element B.2.2. Provide relevant practice to learners
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- make explicit the relation between learning objectives and practice
- provide clear information about the aims and expected outcomes of the activity
- give learners clear and sufficient instructions in order to enable them to perform the activity
- provide learners with the resources required to put into practice the learning objectives of the event
- make sure that activities are appropriately structured in order to maximise learning
- make sure that all participants have the opportunity to practise
- provide feed-back on learners’ performance and, when needed, the means to improve their performance later
- encourage self and peer assessment
Key Area C - Support learners
Introduction
Teachers/trainers carrying out this function need to make effective use of KILT to help learners take control of their own learning and development. This involves helping learners to identify their needs and learning styles, and select the learning opportunities that best match their abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles. In particular, staff need to exploit the potential of KILT to widen access to learners who lack confidence. Staff need continuously to support learners in using KILT to develop and review their personal learning plans to meet their learning objectives. This key area covers support needed for learners in general, but also focuses on the specific needs of individual learners and of groups of learners. A further important feature of the Area is the support to be given to learners to ensure application of learning and the management of formal and informal learning.
The Area comprises 6 Units:
Unit C.1 Help learners manage their own learning
Unit C.2 Support individual learners
Unit C.3 Support groups of learners, learning communities and networks using KILT
Unit C.4 Promote the development of learner autonomy, confidence and effectiveness in a supportive learning environment
Unit C.5 Support application of learning
Unit C.6 Manage formal and non-formal learning
Unit C.1. Help learners manage their own learning
This unit focuses on the skills needed by teachers/trainers to help learners to manage their own learning. The unit covers ways in which KILT can be used to help learners to identify their learning needs and preferred learning styles. Encouraging learner autonomy to enable learners to select learning opportunities is included, as is the support that learners need to develop and review their personal learning plans.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning Technologies
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously, for example through digital learning logs or electronic portfolios
Learning and development
- the importance of learners’ developing and continuously reviewing their personal learning plans autonomously, and how to encourage them to do so
Providing support
- how to establish and maintain effective learning, coaching and counselling relationships with a wide variety of learners in a range of different training situations
- difficulties experienced by learners in different types of learning situations, and how to recognise and tackle them
Accessibility
- the contribution KILT can make to identifying the learning needs of learners with a diverse range of abilities
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice in relation to group work.
Element C.1.1. Help learners identify their learning needs
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate the particular contribution KILT can make to identifying the needs of learners with a diverse range of abilities
- provide appropriate tools for identifying learners’ needs, consistent with the resources available.
- use KILT within a mix of appropriate tools and techniques to identify learners’ needs
- encourage learners to identify their learning needs autonomously
- ensure the identified needs are consistent with the learners’ aspirations and abilities
- help learners record their learning needs, plan to meet them, and review them periodically
- ensure the confidentiality of information about learners’ needs, in line with organisation policy and legal requirements
- evaluate the effectiveness of using KILT to help learners identify their needs
Element C.1.2. Help learners identify their preferred learning styles
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate the particular contribution KILT can make to identifying the preferred learning styles of learners with a diverse range of abilities
- provide appropriate KILT tools for identifying learners’ preferred learning styles, consistent with the resources available
- use KILT within a mix of appropriate tools and techniques to identify learners’ preferred learning styles
- use KILT to allow and encourage learners to identify their preferred learning styles autonomously
- ensure learners understand the implications of their preferred learning styles for the selection of learning opportunities
- ensure the confidentiality of information about learners’ preferred learning styles, in line with organisational policy and legal requirements
- evaluate the effectiveness of using KILT to help learners identify their preferred learning styles
Element C.1.3. Help learners select learning opportunities
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- analyse the suitability of learning opportunities for the range of abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles learners may have
- make information about the suitability of learning opportunities available via KILT
- use KILT to signpost those learning opportunities that provide the best match with learners’ abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles
- use KILT to help learners select learning opportunities autonomously
- evaluate the outcomes of learning to identify whether the learning opportunities are suitable for learners’ particular abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles
- use the results of evaluation to improve the accuracy of signposting to learning opportunities
Element C.1.4. Help learners develop and review their personal learning plans
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- encourage learners to use KILT to record their learning objectives and how they plan to meet these by establishing a personal development plan
- encourage learners to establish dates for reviewing their personal learning plans
- use KILT to encourage learners to review their personal learning plans autonomously in line with established schedules
- encourage learners to consult relevant members of staff before making revisions to their personal learning plans
- provide security systems to ensure the confidentiality of personal learning plans, in line with organisation policy and legal requirements
- evaluate the effectiveness of using KILT to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans
Unit C.2. Support individual learners, using KILT
Teachers/trainers responsible for the support of individual learners need to be able to identify and exploit opportunities to use KILT to enhance the learning experience. Individuals may be members of a group or they may be learning alone. There is a particular focus here on the need to work with individuals to help them use KILT autonomously to achieve their learning objectives.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning Technologies
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help individual learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously
- the range of opportunities available for using KILT to encourage learners to learn from each other
- the range of opportunities available for individual learners to develop the knowledge required to use KILT autonomously and effectively for their own learning
- tools and techniques for communicating effectively and promptly with learners online
Learning and development
- how to analyse the suitability of different learning opportunities with regard to the range of abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles individual learners may have
- the importance of ensuring that individual learners understand the implications of their preferred learning styles, and how to do this
- the importance of encouraging individual learners to identify their learning needs and select learning opportunities autonomously, and how to do this
- the importance of learners’ developing and continuously reviewing their personal learning plans autonomously, and how to encourage them to do so
- how to encourage individual learners to participate actively in online learning communities
- how to sequence and pace information and gauge appropriateness of language for individual learners.
- how to put individual learners at ease and elicit their personal views.
- factors which impact on learners’ ability to plan and achieve their own learning objectives, e.g. lack of technical expertise or isolation
- progression routes and further learning opportunities
Providing support
- how to identify guidance most suitable for individual learners.
- methods of giving information, advice and support in a manner that promotes individual autonomy and encourages self development
- the particular needs of isolated learners
- the types of support teachers/trainers can provide online and how to provide this support
Monitoring and evaluation
- How to involve stakeholders in the evaluation results
- How to plan application of learning
Accessibility
- the range of KILT tools available for identifying preferred learning styles of individual learners with a diverse range of abilities
- the contribution KILT can make to identifying the learning needs of individual learners with a diverse range of abilities
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice in relation to individual learners
Managing resources
- how to provide individual learners with the resources required to achieve their learning objectives
- how to acquire appropriate KILT tools for the needs of individual learners
Element C.2.1. Support individual learners
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate opportunities for supporting individual learners, using KILT
- gather relevant information about the learners, their knowledge and skills, their learning needs, styles, objectives and environment in line with organisational policy and legislation
- establish - by means of a formal agreement or learning contract - what the learner and the member of staff supporting the learner can expect from each other
- liaise with appropriate people, when necessary, to provide additional support
- provide learners with support, encouragement and reinforcement, whilst encouraging them to work autonomously using KILT where appropriate
- communicate effectively and promptly with learners, using appropriate media and language
- use alternative ways of supporting and communicating with online learners, as required
- evaluate the effectiveness of KILT in supporting individuals
Element C.2.2. Agree the roles and resources required to support the achievement of individual learning objectives
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- specify and agree the roles, responsibilities and resources needed to support learners in achieving their learning objectives.
- base specifications of roles and resources on an accurate assessment of learners’ needs and context.
- accurately identify likely difficulties in obtaining the necessary people and resources.
- provide additional support for isolated learners where necessary
- develop plans to provide on site and distant support to individual learners, taking account of the learning programme, the technology and the resources available.
- provide learners with information about the types of onsite and distance support they can benefit from
- where difficulties cannot be overcome, seek advice from relevant people.
Unit C.3. Support groups of learners, learning communities and networks using KILT
In this unit, the focus is on using KILT to support groups of learners in fully exploiting the benefits of group working in order to achieve their learning objectives. It involves managing the balance between tasks to be achieved and group dynamics. An important element of this competency is the facilitation of collaborative learning. Beyond this, a further vital competency the ability to capture and exploit the knowledge produced during a learning event.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning Technologies
- the range of opportunities available for using KILT to support group learning and encourage learners to learn from each other
- the range of tools and techniques available for asynchronous and synchronous group work, and how to use them
- the range of online and offline media available for promoting online learning communities.
- tools and techniques for communicating effectively and promptly with learners online
Learning and development
- the importance of learners’ developing and continuously reviewing their personal learning plans autonomously, and how to encourage them to do so
- how to encourage learners to participate actively and autonomously in online learning communities
- how to sequence and pace information and gauge appropriateness of language for groups of learners
- how to put learners at ease and elicit learners’ personal views
- how to encourage learners to participate actively in online learning communities
- how to establish criteria for membership of online learning groups
- the importance of establishing and monitoring the observance of communication etiquette
- the range of relevant online learning communities
- how to initiate and provide on-going support for the development of online learning communities
- how to gather information about learners online
- progression routes and further learning opportunities
Providing support
- providing support to groups of learners
- how to arrange additional support
- the types of support teachers/trainers can provide online and how to provide this support
Group dynamics
- key theoretical models of group roles and work
- facilitation and intervening skills adapted to group size
- how to form, maintain and close groups
- how to establish ‘ground rules’ governing behaviour in a group setting.
- how to recognise and deal with issues of power and authority in groups
- How to monitor learners’ progress in a group setting
Monitoring and evaluation
- the importance of recording, planning and review, and how to use KILT to facilitate this.
- how to evaluate whether the outcomes of learning indicate that learning opportunities are suitable to the learner’s particular abilities, aspirations, needs and learning styles, and how to use the results of evaluation to improve the accuracy of signposting.
- How to involve stakeholders in the evaluation results
- How to plan application of learning
Accessibility
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice in relation to group work.
Managing resources
- resources and media available to provide online support to groups of learners. The resources might include:
email, computer mediated communication, telephone conference call, chats
peer support, online communities
groupware
- appropriate techniques – e.g. delegating by appointing deputy moderators – to alleviate tutor’s workload and maximize learning opportunities
Knowledge management
- how to collect the information produced during the learning event for the future – e.g.
recording activities and outcomes – manually or electronically, e.g. by using conferencing software functions to record the performance
using a forum to record contributions asynchronously
- methods of disseminating knowledge captured
Element C.3.1. Support group learning with KILT
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- agree the purpose, process and intended outcomes of group activity with the group
- identify and evaluate opportunities for using KILT to support learning in groups
- establish the specific learning objectives and criteria for membership of each learning group
- establish, and monitor observance of, communication etiquette for each learning group
- use appropriate tools and techniques to initiate, manage and close asynchronous and synchronous group discussions
- evaluate the effectiveness of KILT in supporting groups of learners
- challenge excluding and discriminatory behaviour or language appropriately
- use power, authority and influence in the group constructively to enhance learning
- deal with conflict within the group in a way that maintains the ability of group members to continue learning
- provide effective support to learners with special needs and keep them motivated.
Element C.3.2. Support active learner interaction and collaborative learning using KILT
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- make sure that learners understand the benefits of using KILT for communication and take the necessary steps to bring them to the right level of proficiency
- communicate effectively using active listening and appropriate questioning techniques
- establish indicators to track communication and encourage participants to communicate actively
- identify learners’ preferred style to interact with the group and act accordingly in order to maximize individual and group gain
- encourage learners’ autonomous and/or group activities
- identify and evaluate opportunities for using KILT to encourage learners to learn from each other
- provide opportunities for learners to develop the Knowledge required to use KILT effectively to learn from each other
- evaluate the effectiveness of KILT in helping learners learn from each other
Element C.3.3. Support the development of online learning communities
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify existing online learning communities that may be relevant to learners and initiate the development of online learning communities, where no relevant learning communities exist
- develop plans to provide online support to groups of learners, taking account of the resources and media available
- encourage all group members to contribute appropriately to online group discussions within an agreed timeframe
- provide support for the continuous development of online learning communities
- promote relevant learning communities, using both online and offline media
- evaluate the effectiveness of online learning communities in helping learners meet their learning objectives
Element C.3.4. Provide support for knowledge construction and sharing
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify technology available for knowledge construction and sharing.
- make sure that learners understand the benefits of using KILT for building knowledge and take the necessary steps to bring them to the right level of proficiency.
- adapt the learning environment, using the tools provided by the environment
- plan how the knowledge built during the learning process should be made available, once the event or the learning programme is completed.
- make explicit what is expected from learners and value their contributions.
- encourage group production for knowledge sharing and construction and, when necessary, create new opportunities.
- summarise contributions regularly (or ask a group member to do it), and edit regularly to ensure readability and navigation.
- identify the boundaries for dissemination.
Unit C.4. Promote the development of learner autonomy, confidence and effectiveness in a supportive learning environment.
This unit involves helping learners to operate effectively in the learning environment. It concerns enabling learners to become increasingly autonomous in assuming responsibility for their own learning and its outcomes, while remaining aware of the needs of others and working in a way that encourages fruitful and ethical collaboration.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Learning Technologies
- the range of opportunities available for learners to develop the knowledge required to use KILT autonomously and effectively for their own learning
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously, e.g. by using electronic portfolios
- the range of opportunities available for using KILT to encourage learners to learn from each other
Learning and development
- the importance of learners’ developing and continuously reviewing their personal learning plans autonomously, and how to encourage them to do so
- how to encourage learners to participate actively and autonomously in online learning communities
- how to sequence and pace information and gauge appropriateness of language for individual learners.
- how to put learners at ease and elicit their personal views.
Providing support
- how to provide support for learner collaboration and socialization
- how to arrange additional support
- methods of giving information, advice and support in a manner that promotes individual autonomy and encourages self-development.
- how to support learners who may be at risk
- how to communicate and interact with learners in a manner that fosters learners’ confidence, self-esteem and self-image
Group dynamics
- facilitation and intervention skills adapted to group size
- how to establish ‘ground rules’ governing behaviour in a group setting.
- how to recognise and deal with issues of power and authority in groups
Accessibility
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice
Element C.4.1. Actively support learners in developing independence, confidence and ethical behaviour
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish and maintain a learning environment in which relationships between learners and other actors are based on trust and mutual respect and where learners interact respectfully with others, including those with whom they have differences
- plan, implement and evaluate learning experiences that enable learners to identify, clarify, and reflect on their ideas, values and opinions
- plan, implement and evaluate learning experiences that involve learners in analysing their roles and responsibilities in their organisation and community
- plan, implement and evaluate learning experiences that include group activities so learners can use collaborative processes to set and achieve goals, conduct investigations, create solutions and solve problems
- communicate and interact with learners in a manner that fosters learners’ confidence, self-esteem and self-image
Element C.4.2. Provide support for learner collaboration and socialisation to enhance learning experiences
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- encourage, and where appropriate, create socialisation opportunities for learners
- use relevant technology to create public and private spaces for socialisation and collaboration
- establish and agree ground rules for learner collaboration and socialisation
- support socialisation in an unobtrusive way and encourage the participation and autonomy of all learners
- ensure that all learners have access to collaboration and socialisation opportunities
- identify inappropriate behaviour and deal effectively with it
Element C.4.3. Construct learning experiences in which learners assess and plan their personal development
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- construct learning experiences that foster learner decision making in accordance with their learning needs and objectives
- encourage learners to develop a vision of the future, set personal goals and establish plans for achieving those goals
- provide opportunities for learners to develop skills in personal decision making, evaluating life choices, and locating and using information and professional services that take into account lifestyle, health and human relations issues
- identify how technology can support learners in personal development planning
- where appropriate, develop strategies for assisting, and obtain support for, learners who are at risk
Unit C.5. Support application of learning
Staff carrying out this function need to be able to identify and exploit opportunities to apply knowledge and skills gained during learning programmes and to adapt learning programmes in order to facilitate transfer to the workplace and produce competence. This involves taking into account activities. Application of learning includes exploiting the outcomes of both formal and non-formal learning activities.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- Identification of stakeholders in the application of learning in the workplace
- Procedures for providing opportunities for application of learning
Learning and development
- relevant workplace activities for application of learning in the workplace
- how to provide opportunities for application of learning
- how to collect evidence of application
- theories of competence development
Learning technologies
- the range of KILT that can be used for carrying out, reviewing and evaluating application of learning
- how KILT may be used to support relevant practice, e.g.
- problem-solving
- case-studies
- simulations
- communities of practice
- problem-solving
Accessibility
- how to ensure that learners have equal access to opportunities for application of learning
Communication
- liaison with stakeholders to promote the results and benefits of learning experiences
Monitoring and evaluation
- reporting and recording procedures
- scheduling workplace activities
- methods of collecting evidence of application of learning
- evaluation of application of learning
- how to review learning strategies to improve learning programmes and experiences
Knowledge management
- how to capture the results of the application of learning
- how to promote the exploitation of the results of application
Element C.5.1. Agree on workplace learning activities
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- agree with learners and other stakeholders on the outcomes of the application of learning
- identify work activities during which the outcomes of learning can be produced and observed
- if all outcomes cannot be achieved in the work environment, create alternative situations to practice competencies acquired, using KILT where appropriate
- plan a schedule for carrying out and reviewing work activities
- agree methods and timetable for the collection and presentation of evidence of application of learning
- encourage learners to carry out an ongoing review of the results of application of learning
- consult with all relevant persons involved in the application of learning in the workplace
Element C.5.2. Review, assess and record results of application of learning
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- review with learners activities and outcomes of the application of learning in the workplace
- assist learners in organising proof of application of learning using the opportunities afforded by KILT
- assess evidence against criteria agreed with learners and appropriate people in the organisation
- encourage learners to carry out their own assessment of the process and outcomes of the application of learning
- provide learners with relevant and encouraging feed-back on their application of learning
- review learning strategies in order to improve learning programmes and experiences
- communicate results to stakeholders
- record outcomes of the application of learning to contribute to organisational knowledge using KILT
Unit C.6. Manage non-formal and informal learning
This unit of competence concerns the management of learning experiences and opportunities that do not fall naturally within the scope of formal training and development interventions. We need to bear in mind that informal learning accounts for the vast majority of learning, whether this be by observation, experimentation, informal instruction and coaching etc. The learning professional has a responsibility both to value this learning and to help the learner to manage his/her informal learning in order to exploit and apply the results as effectively as possible. KILT can play a major role in enabling learners to record, reflect on and gain recognition for the non-formal and informal learning activities and outcomes.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- the opportunities available for non-formal/informal learning in the organisation
- organisational arrangement for the recognition of non-formal/informal learning
Learning and development
- the nature and importance of informal learning
- how to exploit opportunities for informal learning
- naturally occurring informal learning opportunities:in diverse activities at work
in activities beyond immediate work responsibilities: clubs, associations, unions etc.
libraries, journals
Internet, mailing lists
professional communities, colleagues- sources of support for learning:
colleagues
family
friends
experts - techniques of reflection, analysis and synthesis
- how to encourage learner interaction and mutual learning
- feedback techniques
- coaching techniques
- sources of support for learning:
Learning technologies
- the range of opportunities available for individual learners to develop the knowledge required to use KILT effectively for their own learning
- the ways in which KILT may contribute to the identification and exploitation of informal learning opportunities
- the ways in which KILT may be used to reflect on and record the experience and outcomes of non-formal and informal learning, e.g.electronic portfolios
personal website
weblogs- the range of opportunities available for using KILT to encourage learners to learn from each other’s non-formal/informal learning experiences
- the ways in which KILT can be used to help learners develop and review their personal learning plans autonomously
- the importance of encouraging learners to work autonomously through KILT, and how to do so
Providing support
- the types of support learners may need to identify opportunities for identifying and exploiting opportunities for non-formal/informal learning, and how to provide this support.
- how to identify opportunities for learner collaboration
Accessibility
- the contribution KILT can make to identifying the learning needs of learners with a diverse range of abilities
- issues of equality of opportunity and non-discriminatory practice
Communication
- how to communicate the importance of non-formal/informal learning opportunities
- how to communicate the outcomes of non-formal/informal learning opportunities
- how to recognise and value the outcomes of non-formal/informal learning, providing positive and encouraging feedback:
annual review
meetings
during ‘formal’ learning activities
Knowledge management
- how to exploit the results of informal learning, e.g. through knowledge management systems and the organisation’s internet
Element C.6.1. Help learners identify and exploit the opportunities for non-formal/informal learning
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- help learners understand the nature and importance of non-formal/informal learning
- help learners to identify a variety of sources for learning
- encourage learners to take responsibility for organising non-formal/informal learning opportunities, using KILT where appropriate
- encourage learners to identify and exploit naturally occurring learning opportunities involving non-formal/informal learning, using KILT where appropriate
- help learners to identify sources of support for identifying and exploiting the opportunities for non-formal/informal learning
- encourage learners to learn from each other and to support others’ non-formal/informal learning, using KILT where appropriate
Element C.6.2. Encourage learners to build on and recognise the outcomes of non-formal/informal learning
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- encourage learners to reflect on, and formalise what they have learned, using KILT where appropriate
- encourage learners to communicate what they have learned to others and get feedback from others
- integrate the outcomes of the learning activities into the learning programme
- publicise the value of informal learning and demonstrates how it can make a difference
- identify opportunities to recognise and value the outcomes of informal learning
- provide positive and encouraging feed-back using appropriate incentive and rewards
- support application of the outcomes of non-formal/informal learning
Key Area D - Assess learner progress
Introduction
This key area focuses on the competencies associated with the assessment of learner progress. The first unit concerns planning the assessment using a variety of methods and making use of KILT to enhance the assessment process. The competency covers all aspects of the assessment process from planning to using the results of assessment to improve future learning programmes.
The Area comprises 2 Units:
Unit D.1 Plan assessment of learner progress
Unit D.2 Monitor, assess and report on learners’ progress
Unit D.1. Plan assessment of learner progress
This Unit concerns planning how to assess the progress made by learners in the course of a learning experience – non-formal and informal as well as formal, and involves identifying the contribution that KILT can make to the assessment process. The emphasis is on using a range of assessment methods and encouraging self and peer assessment to complement that of the teacher/trainer.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- the organisation’s policy and procedures for recording information about learners
Learning and development
- methods of assessing learners, e.g.competence based
knowledge based
standards based- relevant information for planning assessment, e.g.
programme/curriculum objectives,
standards of competence - evidence required for assessment of results
- relevant information for planning assessment, e.g.
Learning technologies
- role of KILT in the assessment process, e.g.:collection of data and evidence
presentation of data and evidence
tools to assess skills, knowledge and understanding- KILT assessment tools and methods, e.g.
digital portfolio
simulation
distant assessment
automated tests
- KILT assessment tools and methods, e.g.
Accessibility
- how to ensure that learners have equal access to assessment opportunities
- how to involve learners in planning assessment
Monitoring and evaluation
- methods of evaluating KILT assessment tools
- how to use KILT to monitor and assess learner progress
Element D.1.1. Identify the value of KILT in the assessment process
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate from a diversity of sources the particular contribution KILT can make to assessing what individuals have learned (both formally and non-formally)
- identify and evaluate KILT assessment tools, methods and strategy in regard to specific learning objectives and in line with organisational policy
- review and assess KILT assessment tools, methods and strategy, based on your experience, that of your organisation and best practice
- make recommendations on the use of KILT for improvement of the assessment process and communicate your recommendations to the relevant people
Element D.1.2. Plan assessment
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- obtain and interpret relevant information to identify learning goals and assessment criteria
- establish evidence required to make judgments about learner achievement in consultation with colleagues
- select a range of assessment methods, including peer assessment and self-assessment to take account of the characteristics of the learner group, learning styles, the type and amount of evidence required and resource requirements
- plan assessment activities, including formative, diagnostic and summative assessment methods, in order to ensure that a variety and balance of assessment approaches are used to gather evidence throughout the program
- select or develop assessment materials in order to gather valid, reliable and sufficient evidence
- organise and arrange resources required to support assessment activities within a safe and accessible learning environment
- take into account the special assessment needs of the person being assessed in respect of organisational policy
- communicate and explain learning goals and assessment criteria to learners and other stakeholders
- involve learners in planning assessment
Unit D.2. Monitor, assess and report on learners’ progress
Teachers/trainers involved in this activity need to use KILT to record and analyse information about learner achievement. They need to assess what individuals have learned and achieved and monitor their progress against their personal learning plans. Furnished with this information, they need to give learners feedback to support their future learning and report on learners’ achievement as required by the organisation or by external agencies.
Knowledge required
To perform competently, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- the organisation’s policy and procedures for recording information about learners
Assessment of learning
- the organisation’s policy regarding learner assessment and verification
- the range of opportunities available for providing feedback to learners using KILT
- how to give constructive feedback, both formative and summative
- how to collect informed testimonies
- methods of self assessment, e.g.skill-check lists
competence database
simulations
tests
feed-back from other learners, colleagues, clients- evidence to support assessment:
exercises, problems solved
work outcomes
testimonies
peer reviews - providing feedback to learners on outcomes of assessment
- evidence to support assessment:
Learning technologies
- how KILT can automate reporting on learners’ achievements.
- how to identify and evaluate the particular contribution KILT can make to assessing what individuals have learned
- the range of appropriate KILT tools available to assess what individuals have learned and achieved
- how to integrate KILT within an appropriate mix of assessment tools and techniques.
- the range of tools available for supporting the collection and presentation of evidence
Accessibility
- how to ensure that learners have equal access to assessment opportunities
- how to involve learners in planning assessment
Communication
- how to prepare and communicate reports on learner progress and performance to the relevant people (manager, administrator, etc) and authorities in accordance with organisational policy and procedures.
Monitoring and evaluation
- keeping records on learner progress and results of assessments, e.g. scores, statistics, assessment records of learners’ portfolio or any other relevant information.
- methods of evaluating assessment methods and results
- how to use the results of monitoring and evaluation to improve future assessment activities
Element D.2.1. Assess what individuals have learned and achieved
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- implement assessments using a range of appropriate methods
- review the outcomes of assessment
- use outcomes of assessment processes to identify strengths and weaknesses in individual learner performance in relation to the learning outcomes of the programme
- encourage learners to carry out self-assessment
- encourage learners to collect a variety of evidence to support assessment
- when required, provide alternative assessment methods
- reach a decision regarding learners’ achievements based on relevant evidence and in line with organisational policy.
Element D.2.2. Provide feedback to learners
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate opportunities for providing feedback on progress and achievements to learners
- provide clear, accurate and concise feedback on progress and achievements to learners effectively and promptly, using language appropriate to the learners
- provide learners with opportunities to reflect on their assessment results, undertake self-assessment and identify their own learning needs
- prepare and communicate reports on learner progress and performance to the relevant people and authorities in accordance with organisational policy and procedures
- conduct assessment activities and reporting of assessment results in an ethical manner, with due regard for confidentiality and the privacy of learners
- evaluate the effectiveness of KILT in providing feedback to learners
Element D.2.3. Maintain records on learners’ achievements
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify and evaluate the particular contribution KILT can make to recording learners’ progress and achievements, taking into account the organisation’s policies and resources
- define the format of reports on learners’ achievements, taking into account the organisation’s policies, resources and learning management system where relevant
- inform learners of the existence of learning records and provide them with an opportunity to check or update their contents
- provide complete, accurate and up-to-date reports on learners’ achievements to those entitled to this information, in the required formats and at the required times
- ensure the confidentiality of information about learners, in line with organisational policy and legal requirements
Element D.2.4. Use assessment results to guide programme planning, delivery and assessment
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- analyse learner performance on assessment activities to identify learning needs as well as strengths and weaknesses in programme planning, delivery and assessment
- review programme content, learning strategies and assessment arrangements during the programme to take into account the outcomes of assessment processes
- incorporate assessment data in reviews of assessment methods, materials and procedures.
- incorporate assessment data in program review and planning processes
- communicate results to stakeholders
Key Area E - Promote accessibility for learners
Introduction
This Key Area concerns all those involved in providing learning services. It entails assuming personal responsibility for ensuring that learning is accessible to all those who wish to benefit, especially those with special needs. This will require keeping abreast of current organisational and legal requirements regarding accessibility to learning; gaining the commitment of all relevant actors; making the best use of available resources, and constantly monitoring progress and recommending improvements.
The Area comprises 1 Unit:
Unit E.1 Promote accessibility to learning
Unit E.1. Promote accessibility to learning
This unit focuses on the ways in which teachers/trainers can use KILT to ensure that learning opportunities are available to a diverse range of potential learners. It entails evaluating the accessibility of learning environments and resources and being proactive in encouraging the inclusion of people with special needs into learning programmes.
Knowledge required
In addition to the core knowledge requirements, to perform competently you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Health and safety
- how to ensure that the learning environment within your control conforms to organisational and legal requirements regarding accessibility to learning.
- your own responsibility for ensuring a healthy and safe learning environment for all learners and especially those with special needs
Legal requirements
- legal requirements concerning making learning opportunities accessible to all
- data protection requirements concerning recording information on those with special needs
Accessibility
- how to access information on current legislation, recommendations and guidelines on accessibility, e.g. Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
- how to access best practice in accessibility provision
- how to apply legislation on accessibility
- how to apply recommendations and guidelines on accessibility
Learning and development
- how to make a learning experience accessible to people with different abilities
- how to provide alternatives when critical resources are not accessible to learners with special needs
- how to involve potential learners in ensuring that learning opportunities are accessible – particularly those with special needs
Learning technologies
- the range of ways in which KILT (hardware, software and systems) may be used to facilitate the learning of those with special needs, currently and in the future
- the basic principles of technological standards and their impact on interoperability with regard to assistive technologies
- the importance of establishing service standards and how to do so
Providing support
- how to provide support for learners with particular accessibility needs
- how to provide support for staff working with those with particular accessibility needs
Communication
- how to make known to all potential learners the learning opportunities available
- how to communicate the importance of extending learning opportunities to those with particular accessibility needs
Element E.1.1. Evaluate the accessibility of learning environments and resources
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- establish and exploit the range of resources available to access current information on accessibility regulations relating to learning opportunities
- identify the contribution of KILT to providing and extending accessibility to learning
- identify best practice and conformant solutions in ensuring accessibility to learning opportunities in the physical and digital world
- carry out an evaluation of facilities and resources in the light of conformant practice
- involve potential users in your evaluation of learning environments
- identify potential physical and digital barriers and provide alternatives, when possible
- report to the appropriate authority any discrepancy with laws, regulations or the organisation’s policy regarding accessibility
Element E.1.2. Encourage the inclusion of people with special needs into learning programmes and value diversity
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- ensure that the area under your responsibility reflects best practice in accessibility.
- provide recommendations to improve accessibility in your area of responsibility.
- take the advice of those with special needs to ensure that their needs and expectations are met.
- encourage the inclusion of people with special needs into learning programmes by providing appropriate guidance and support.
- provide information and training to staff on working with those with particular accessibility needs.
- provide opportunities for learners to use a rich variety of learning strategies to maximize learner acquisition of required learning.
- provide a variety of assessments to ensure that all learners have an equal opportunity to demonstrate what they have learned.
- communicate the importance of inclusion at an organisation-wide level.
- make known the learning opportunities and resources available as widely as possible.
Key Area F - Evaluating learning programmes
Introduction
Evaluating the effectiveness of learning programmes is the responsibility of all those responsible for learning events. Assessing the service or programme against clearly defined criteria allows teachers/trainers and their managers and clients to reach an informed decision about the success of the learning experience and to put in place necessary improvement measures for future interventions. KILT can play an important role in this process.
The Area comprises 1 Unit:
Unit F.1 Assess the effectiveness of learning services and programmes
Unit F.1. Assess the effectiveness of learning services and programmes
This unit focuses on two vital aspects of the evaluation of learning services and programmes; the ongoing monitoring and review of programmes and a summative assessment that will allow corrective measures to be taken where necessary and improvements made to improve the quality of future events.
Knowledge required
To perform competently, you need to know, understand and be able to apply:
Organisational context
- the organisation’s policy and procedures for recording information about learning events
Learning technologies
- how KILT can automate reporting on the performance of learning services and programmes
- the range of appropriate KILT tools available to assess what individuals have learned and achieved
- how to integrate KILT within an appropriate mix of assessment tools and techniques.
Monitoring and evaluation
- the range of evaluation criteria available, e.g.
-
- performance indicators
- national standards
- organisational standards
- methods of evaluating learning services and programmes
- how to collect information for evaluating learning services and programmes, e.g.
- questionnaires
- individual interviews
- group interviews
- tracking
- records of event: documents, electronic records etc
- how to keep records on the ongoing progress of the learning event
- how to use the results of monitoring and evaluation to improve future assessment activities
-
Accessibility
- how to involve learners in evaluating learning services and programmes
Communication
- how to prepare and communicate reports on the progress and outcomes of the learning event to the relevant people (manager, administrator, etc) and authorities in accordance with organisational policy and procedures
- methods of promoting and facilitating commitment to change
Continual improvement
-
- the importance of reviewing processes to identify ways in which they can be improved
- how to judge the strengths and weaknesses of systems
- how to prepare plans that are capable of implementation
Element F.1.1. Monitor and review the effectiveness of learning services and programmes
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- identify clearly the specific objectives and desired outcomes of the learning services and programmes to be monitored
- schedule monitoring and review activities in consultation with stakeholders
- put in place methods of monitoring and review that are capable of being implemented within the resources allocated
- specify clearly the information required to monitor learning services and programmes
- collect information using suitable methods and procedures, using KILT where appropriate
- ensure that information collected is sufficient and representative enough to produce reliable results on which to base future decisions
- evaluate information, and report the results at required intervals, using agreed methods and against specified performance measures.
- apply monitoring and review procedures correctly and consistently, and record the results according to agreed procedures and following rules of confidentiality
Element F.1.2. Evaluate and improve learning services and programmes
To perform competently in this element, you must ensure that you
- provide opportunities for those involved in using or operating the learning services and programmes to contribute to their improvement
- define and agree on the criteria against which services and programmes should be assessed
- analyse the information collected using the agreed criteria and identify potential improvements
- carry out an accurate assessment of the feasibility of potential improvements with regards to their costs and benefits
- present suggested improvements to relevant people at a time and place and in a format appropriate to their needs, and confirm their understanding
- agree on changes, obtain the support of all stakeholders and resolve any conflicts of interest
- implement changes within an agreed timescale and in accordance with resource constraints
- fully inform those people affected by the proposed improvements
- put in place measures to monitor and review the impact of the improvements implemented.
- ↑ Trends in the development of training and the role of innovations a transferable practice, TTnet Dossier no 1, 2000. The role of the tutor from a Community perspective, TTnet Dossier no 2, 2000. PROFF - Professionalisation of VET teachers for the Future, draft final report, 2003.