Complementary medicine/CMT101/Products and its Practitioners
Whether we are looking to maintain or improve our health, or to overcome a particular health problem, there are a number of approaches that we can take
There is no definition that is internationally accepted, but these are some of the standard definitions suggested by the National Institute for Complementary Medicine which is a complementary medicine research centre based at the University of Western Sydney.
Have a look around these pages and use the information you find there to answer the questions below.
Contents
H5P Object Parameters
The H5P parameters below will be replaced by the actual H5P object when it's rendered on the WordPress site to which it's been snapshotted.
Are vitamins, supplements and herbal medicines new additions to our ideas about healthcare? Perhaps the most honest answer is 'yes and no'. The growth of the CAM industry is a recent phenomenon - as you may have seen on the NICM website that you just visited, in Australia it is now worth $3.5b a year.
However traditional understandings that underpin many of these products very often go back much further, and indeed some systems of traditional medicine, including Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ayurveda have been used for millennia.
Let's look at some history of the most common complementary medicine products found in our pharmacies, supermarkets and health food shops.
Vitamins
The discovery of vitamins can be traced to the early years of the 20th century, where Casimir Funk suggested that there was a class of 'amines' (organic compounds formed from the breakdown of proteins) which were necessary for good health - 'vital amines'. Later it was found that not all of these substances were amines, but the word was shortened to 'vitamin' - which stuck.
However long before this discovery, a disease caused by (what we now know to be) a vitamin deficiency was diagnosed - and the cure, well established by 1800, was foods that contained that vitamin.
If you are interested in finding out more about the history of the discovery of vitamins, this is a good article
Vitamin C and scurvy
At the time of European settlement of Australia, sea voyages were long and arduous. You may recall that the First Fleet set sail from England in May 1787 and arrived at Botany Bay in January 1788 - more than 8 months after they had set sail. Clearly the continued availability of fresh food and freshwater was one of the major concerns on these long voyages.
One of the major health problems for those who spent extended periods at sea, in particular sailors, was scurvy. This was a horrible disease characterised by loose teeth and bleeding gums, and scaly, bleeding skin. It could lead t a painful death. Its cause was unknown, but between the 16th and 18th centuries, it is estimated that a million sailors died of the disease.
While it had been accepted that the disease could be affected through diet, and for example, Captain James Cook had some success with reducing the problem on his ships, through insisting on his sailors have a diet that included, among other things, greens, sauerkraut and citrus extracts, the problem continued. However, in 1795 the British Admiralty, building on work that had been done by a Scottish doctor, James Lind, made it compulsory for all sailors to have a daily ration of lemons (and later limes) which effectively eliminated the problem.
Thus while today we know scurvy is a problem which occurs when Vitamin C is absent from the diet, it was known that including citrus in the diet was beneficial for scurvy long before Vitamin C was isolated and named.
Supplements
As you will have seen in the list provided in the presentation above, this covers an enormous range of substances, including vitamins and medicinal plants. It is beyond the scope of this course to go into each of the categories in detail. However, if you were to join us at UTAS for the complete unit, you may be exposed to supplements in greater detail.
Herbal medicines
Herbal medicines have been used throughout history and across cultures to treat disease.
Learning by observing nature
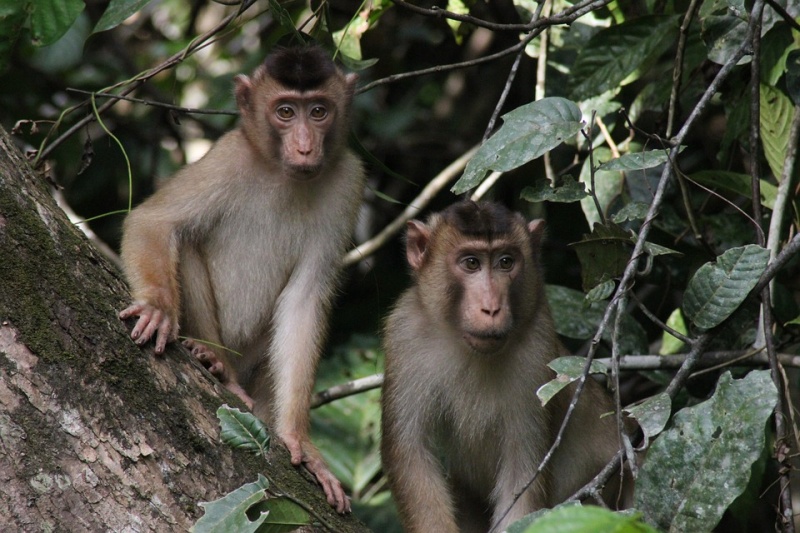
It is not only humans who use plants to self-medicate - animals and birds appear to do so as well. The science of animal self-medication is called zoopharmacology, and it is likely that over the ages humans have learned from animals about plants that are useful in this way.
<center>
Most of the research that has been done on zoopharmacology has involved the study of monkeys.
There are numerous examples of animals that self medicate. Read about some of them here.
In this blog, Cool Green Science, the author suggests that birds make very intelligent decisions about their use of medicinal plants.
In particular, they use medicinal plants to reduce parasites in their nests and to improve the health of their young. While it is clearly difficult to determine intention by birds, the choice of materials they put in their nests does seem to be related to positive benefits. The author suggests that this because of natural selection.
Practitioners
Complementary medicine - often called natural medicine - is used both for the control of symptoms and disease and for health maintenance. In chronic disease, there is an overlap between these two uses. Individuals may consult a practitioner for individualised treatments, or they may self-prescribe complementary medicine products, usually vitamins, herbal remedies and food supplements, and access them over-the-counter (OTC) in pharmacies, supermarkets, health food shops and over the internet.
How do complementary medicine practitioners fit into healthcare in Australia? We will be going into the regulation that surrounds their practice - and the use of complementary medicines in Australia more generally, later in the unit.
The first of these videos is a short introduction to give you some background. You can find the notes to this presentation here and you can download and/or print them out if you require.
Disciplines
This presentation outlines the history and ideas that underpin some of the major CAM disciplines popular in Australia - Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Western herbal medicine (WHM) and naturopathy.
Traditional Chinese Medicine, Western herbal medicine and naturopathy