Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project; A Teacher Collaboration on WikiEducator
Openly shared content, practices, and developing resources from Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project. Join this collaboration and make a difference!
 Brown’s River |
|---|
|
| Basin: | Lamoile |
| State or Province: | Vermont |
| Country: | USA |
| Latitude: | 44.50656 |
| Longitude: | -72.99767 |
| School: | Saint Michael's College |
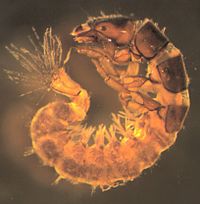
This site is for Brown's River in Jericho Vermont. The following are the most common invertebrates collected from this stream site.
Chironomidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Chironomidae
- Common name
- Nonbiting midge
- Tied fly
- Griffith's Gnat
Midge larvae tend to be the most common macroinvertebrate at our sites. As with other Diptera, there are no true jointed legs. Chironomidae do have a pair of prolegs at each end and preserved individuals tend to curl into a 'C'. Identification past family requires slide-mounted heads. We have seen philopotamid caddisflies misidentified with the chironomids and we suspect that that happens when samples are being sorted from trays. Under a microscope, six prominent legs can be seen on members of the caddisfly family Philopotamidae.
More information on Philopotamidae.
Hexatoma
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Tipulidae
- Genus
- Hexatoma
This Tipulidae can be identified by the swollen 7th abdominal segment. The swelling is bulbous and frequently as much as 2X abdominal diameter in preserved specimens.
Philopotamidae
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Philopotamidae
- Common name
- fingernet caddisflies
Philopotomidae are net-spinning filtering collectors. A casual observer might sort them with Chironomidae, but a close look reveals six jointed legs. The faint white 'T' shaped labrum extending from the front of the head past the mandibles is diagnostic for the family (it is sometimes withdrawn and hard to see).
Image of the faint white 'T' shaped labrum. Common genera include Dolophilodes, Wormaldia, and Chimarra.
Corydalidae
- Order
- Megaloptera
- Family
- Corydalidae
- Common name
- Dobsonfly; Hellgrammite
Members of the family
Corydalidae share some superficial commonalities with Trichoptera, but on careful inspection one can see the
two pairs of anal claws that help place it in the order Megaloptera. The size of mature larvae is impressive; specimens from some genera exceed 8 cm in length. The abdominal segments have ribbon-like gills on the lateral portions. The mouth has mandibles that are serrated and used for biting prey. They can be confused with the more slender
whirligig beetle larvae; whirligig larvae also have
simpler jaws.
Nigronia is the genus we most frequently encounter.
Hydropsychidae
- Order
- Trichoptera (caddisfly)
- Family
- Hydropsychidae
- Common name
- net spinning caddisfly
- Tied fly
- Emergent Sparkle Pupa, Vermont Hare's Ear
This family of net-spinning caddisflies is very abundant at several sites. They are important filtering collectors and are quite common at urban and agricultural sites where particles of organic material can be important food resources. Genus-level identification is possible for mature specimens and we will include the genera we found at your site if possible.
When using the key, some features that are challenging to see are the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites in the folds between segments. Other, more easily seen key features include filamentous gills on the abdominal segments and the sclerotization of the dorsal surfaces of all three thoracic segments. Keep in mind that with smaller or more immature specimens, genus-level ID may not be possible.
Commonly found genera include Cheumatopsyche, Ceratopsyche, and Hydropsyche. Less commonly, we have found Arctopsyche and Potamyia.
Images of the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites.
Optioservus
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Elmidae
- Genus
- Optioservus
The larvae of
Optioservus have open coxae, as determined by the straight definition between segments on the ventral side of the pronotum.
The adult Optioservus have a compact appearance, especially the head and thorax. There are also dorsal ridges and a characteristic diamond-shaped sutellum observable in the dorsal view.
Images of the straight definition between segments, the dorsal ridgesand the diamond-shaped scutellum.
Stenelmis
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Elmidae
- Genus
- Stenelmis
The larvae of
Stenelmis, as in
Ordobrevia, have a sternum on the ventral side of the pronotum. The main difference between the two genera is in the antennae the second segment is less than twice as long as the first in
Stenelmis.
The adult Stenelmis has a clear separation between the thorax and abdomen as well as a more distinctly separate head as compared to other genera.
Click here to see pictures of the sternum and
antennae-
Psephenus
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Psephenidae
- Genus
- Psephenus
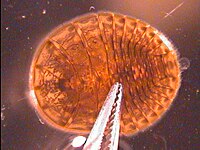
The true "water penny" is commonly found in the waters sampled.
Psephenus has a rounded shape with relatively smooth edge. The
false water penny, whose edges are serrated, has a more oval appearance. The
gills on the ventral surface are found only in the true water pennies.
Another genus encountered in this family is Ectopria.
Gomphidae
- Order
- Odonata
- Family
- Gomphidae
- Common name
- clubtail dragonflies
Like other Odonata, members of this family have four wingpads. Like members of the sub-order Anisoptera, the abdomen terminates in five points. What distinguishes Gomphidae from Aeshnidae is the fact that Gomphidae has clubbed antennae.
Image of the four wingpads and the abdomen.
More information on Aeshnidae.
Serratella
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Ephemerellidae
- Genus
- Serratella
Serratella's distinguishing feature is the set of paired tubercles on the dorsum of its abdomen.
Click her to view the paired tubercles.
Tipula
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Tipulidae
- Genus
- Tipula
This genus of Tipula is rather large as compared with other genera. Tipula larvae are generally dark brown and have creeping welts.
Rhyacophila
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Rhyacophilidae
- Genus
- Rhyacophila
- Common name
- Green Caddis
- Tied fly
- Henryville Special or Glass Bead Caddis
In our lab,
Rhyacophila is known as the "Michelin Man" due to its large banded body. It has a very obviously checker-patterned head. It also has terrifying anal claws with large accessory hooks.
Links to images that may be useful if you have a magnifying glass or microscope:
Checker-patterned head.
Anal claws with large accessory hooks.
Glossosomatidae
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Glossosomatidae
- Common name
- saddlecase caddisfly
Larvae in this family build domed cases made of small rocks, and are often wider at segment 5. The pronotum is covered in dark, sclerotized plates, but there are either
no sclerites on the mesonotum, or the mesonotum is unsclerotized with the exception of a few patches. The anal proleg is broadly joined to segment 9; the anal claw has one or more accessory hooks. The
pronotal excision is small (approximately 1/3 anterolaterally) to accommodate the coxae.
Commonly encountered genera include Glossosoma and Agapetus.
Perlidae
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Perlidae
- Common name
- The Golden Stonefly Creeper
- Tied fly
- Connecticut Curler
This stonefly is characterized by the three pairs of filamentous gills located on the sides of all three thoracic segments. It is distinguished from the family Pteronarcyidae by the absence of gills on the abdominal segments. Often, the thoracic terga are brightly patterned as pictured, though this is not always the case. Another important feature is that the paraglossae and glossae extend different lengths.
Images of filamentous gills and the family Pteronarcyidae.
Genera commonly encountered in this family include Acroneuria, Agnetina, and Paragnetina. Less commonly, we have found Perlesta.
Very rarely encountered genera include Neoperla and Hansonoperla. If you believe you have found either of these, please send a specimen our way!
Heptagenia
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Heptageniidae
- Genus
- Heptagenia
- Tied fly
- Little Graywinged Olive
Heptagenia are easily characterized by their flat head. The claws have just one basal tooth and no denticles (serrated edges). The gill on abdominal segment 7 has multiple fibrils at is base (thread-like structures) and has a single tooth on its claws but is smooth otherwise. Gills on segment 7 are similar to those on all other segments, but may be smaller in size.
Pteronarcyidae
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Pteronarcyidae
Pteronarcyidae have branching gills from the bases of their legs as does
Perlidae. What distinguishes Pteronarcyidae from Perlidae is the presence of gills on the first two abdominal segments. There are only two genera in this family, but the other,
Pteronarcella, is only found in the west/southwest.
Click to see an example of Perlidae or the gills on the first two abdominal segments.
Isonychia
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Isonychiidae
- Genus
- Isonychia
- Common name
- The Dun Variant
- Tied fly
- Flick's Dun Variant
This mayfly has unique long hairs on its forelegs as the main distinguishing characteristic (allowing anyone keying to move through quickly). Carefully observe the limbs because such hair can be matted down and therefore hidden in preserved wet specimens. The body of
Isonychia is slim and "minnow-like" when observed dorsally. In specimens we collected, they were commonly brown and substantial in length and width as compared to the very common Baetidae.
Even when individuals are immature, closer inspection can reveal the setae on the forelegs.
Image of the long hair on its forelegs.
Ancylidae
- Order
- Basommatophora
- Family
- Ancylidae
Members of the family Ancylidae belong in the class of Gastropoda. As Pulmonate snails, these members breathe using lung-like structures but can also use a gill-like structure called a pseudobranch to extract oxygen from water. Their shallow conical shells look like those of miniature limpets.
More information on the class of Gastropoda.
Polycentropus
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Polycentropodidae
- Genus
- Polycentropus
The most common genus we encounter is
Polycentropus. These caseless caddisflies frequently have speckled or freckled heads. The anal proleg typically has a prominent black X, although it can in some specimens appear to be a little faded. They are common at Oakledge Park in Lake Champlain, where we also find an additional genus in the same family:
Nyctiophylax.
Click to see the speckled or freckled heads or the prominent black X.
Veliidae
- Order
- Hemiptera
- Family
- Veliidae
This family of Hempitera actually lives on the surface of the water, but can sometimes float into the net while taking benthic samples. Members of the family Veliidae are characterized by the claw of the foreleg; it is inserted before the apex. Also, its hind leg has a beautiful fan of hydrofuge hairs.
Click here to see the claw inserted before the apex and the fan of hydrofuge hairs.