Antarctica/Exploration ICEBLOCK/Benthic Life
BENTHOS
This Benthos Power Point will help NE to Year 8 children gain an understanding of what the Benthic Organisms are.
BENTHOS
A more detailed description:
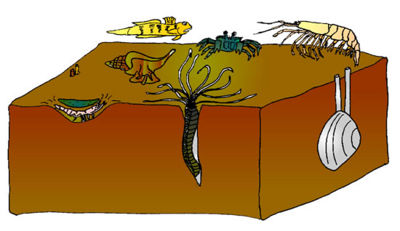
Plants and animals living on or in the bottom of the sea (or lake) floor are called the benthos. Nearly 16% of all living animal species are benthic.
Organisms that live on the ocean bottom or on rocks, shells, seaweeds, pilings, etc., are called epiflora (plants) and epifauna (animals).- The Epifauna don’t necessarily have to be attached to the sea floor, they may just move over it.
- Sea anemones, sponges, corals, snails and crabs are all epifauna.
- The epifauna include about 4/5 of all benthic animals.
Attached marine plants (epiflora) are found only in the intertidal and subtidal zones, the only benthic zones reached by light.
- * (WHY do you think the plants don’t grow any deeper down?)
The great majority of benthic animals also live in these zones (depths of less than 600 feet) because of the availability of food there.
- * (So, what do you think benthic animals eat?)
Most benthic environment is in perpetual darkness, and animals that live there must feed on each other or on food that falls down from the photic zone.
- * (What do you think ‘photic’ means?)
Animals that live buried in the bottom, such as clams and worms, are known as the infauna. There are about 30 000 species of infauna compared with more than 125,000 species of epifauna.
- * Does this fit with the statement above that epifauna make up 4/5 of all benthic animals?