Accounting basics
Contents
Introduction
Library of Resources Accounting Basics
Purpose
Accounting is used to record transactions for tax purposes, to compare business performance from year to year, and to provide information to Directors and Shareholders.
Transactions can be recorded manually or using a computer.
Manual Accounting
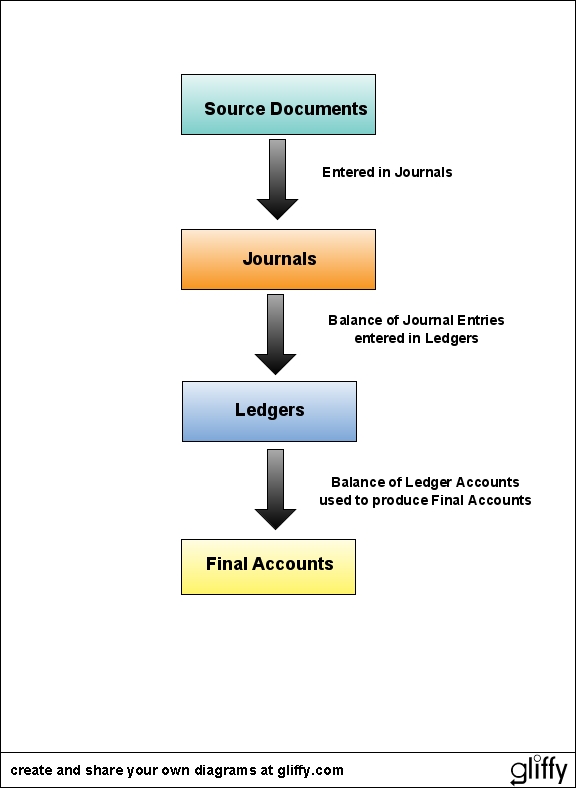
When transactions are recorded manually each source document is recorded in a journal and then posted to a ledger.
Source documents
These are invoices, cheques, credit notes, receipts, purchase orders, statements, bank statements etc which are entered into a Journal.
Journals
There are seven journals: -
Cash Receipts Journal – Cash dockets, receipts issued, direct credits, cheques.
Sales Journal – Invoices issued
Sales Returns Journal – Credit notes issued
General Journal – Memos, contracts
Purchases Journal – Invoices received
Purchases Returns Journal – Credit notes received
Cash Payments Journal – Cheque summary, receipts received, direct debits
Ledgers
General: Are the main accounting record of a business which uses double-entry bookkeeping. It will usually include accounts for such items as current assets, fixed assets, liabilities, revenue and expense items, gains and losses. Each General Ledger is divided in two sections. The left hand side lists debit transactions and the right hand side lists credit transactions. This gives a 'T' shape to each individual general ledger account. By Hugo Davidson
Accounts Receivable
Accounts Payable
Final Accounts
Trial Balance
Profit and Loss Statement
Balance Sheet
Others