Matter and Energy
|
Contents
Matter
Everything in the world can be divided into two things:
- Matter
- Energy
- Matter
- anything that has mass and takes up space
Conservation of Mass
Conservation of Mass
All mass is conserved - it is neither created nor destroyed.
It may however, change forms
Chemical Reactions
- Chemical reaction
- chemicals recombining to form other chemicals is called a chemical reaction
Reactions which release heat are called exothermic.
Reactions which absorb heat are called endothermic.
All of life processes are actually chemical reactions. The two most important of these are photosynthesis and respiration
Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis
- The process which plants use to create glucose from carbon dioxide and water
Glucose is the simplest sugar and the building block for all higher carbohydrates.
This reaction requires light. Such a reaction is called a photochemical reaction.
Respiration
- Respiration
- Use of oxygen to break down complex chemicals and release energy
Respiration is what provides energy for other process to occur.
Energy
- Work
- force acting through a distance
- Energy
- the capacity to do work
- Heat
- energy transferred due to a temperature difference
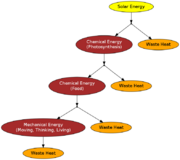
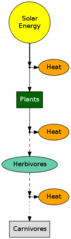
All of nature is driven by energy. How this energy flows through the environment is important. The ultimate source of this energy is the SUN.
The flow of energy is governed by the two laws of thermodynamics.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy is never destroyed or created
or
There is no free lunch
Examples:
- you need fuel to keep your car running
- you need food to keep yourself running
Second Law
Questions:
- How do we uncook rice?
- How do we unpeel an orange?
First law says cooking and uncooking are exactly the same.
These questions lead to the second law of thermodynamics.
Second law of thermodynamics
No system can completely convert heat to work
or
All systems tend toward disorder
or
You cannot break even
The measure of disorder is called the Entropy
The second law therefore says that the total entropy will always increase.
Since heat cannot be entirely converted to work, we say heat is lower quality than work. Whenever energy is converted from one form to another, some is lost as heat.
As we said before energy flows through the environment starting with energy from the sun. However, by the second law this energy gradually loses its quality.
The percentage of energy transferred as useful work is called the efficiency.
Examples
- Electrical Power Plant 30%
- Fuel Cell 60%
- Human Body 25%
- Fluorescent Light 15%
- Car Engine 10%
- Incandescent Light 5%
In food chains the efficiency of each level is about 5 - 20%. Carnivores have about 1% of the energy that plants capture.
|
Thermodynamics - A wikieducator project on this topic |