Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the science of co-ordination the physical and psychological aspects of human beings with their working environment. Although computers present us with great opportunities for making our work easier, they do present some health and safety risks if used incorrectly. The science of ergonomics tells us how to use computers correctly.
Monitors
If you work with a monitor, tired, sore or blood-shot eyes indicate eye strain. The following points indicate some aspects of monitors to be aware of.
- Refresh rate: The refresh rate of a monitor is the rate at which it updates the images on the screen. When the refresh rate is too low, the screen appears to flicker. Apart from the annoyance factor, this causes eye strain. The refresh rate should be at least 72 Hz (72 times a second) and preferably higher.
- Monitor filter (Anti-glare screen): Reflections on the screen can cause eye strain. This can be overcome by using a monitor filter with an anti-glare screen or by placing a special anti-glare cover in front of the screen.
- Focus: The image on the screen should be sharp. Poor quality monitors have a slightly blurred effect. This causes the eyes to continually attempt to reduce the blur.
- Low radiation: The beam of electrons that strikes the screen to display the image also sends out electromagnetic radiation. There is some fear that this can be a health hazard, particularly to pregnant women. Use a monitor with low electromagnetic radiation.
- Position: Place the monitor in a position where you can look into the distance at regular intervals. To the side of a window is an ideal position. You need to change the focus of your eyes on a regular basis to prevent eye strain.
- Angle: The monitor should be slightly below eye level. Looking up at a monitor can cause strain in the neck.
- Rest: Take regular rest periods where you do not look at the monitor.
Keyboards and mouse
Repeated use of the same muscles and joints can result in a type of injury called RSI or Repetitive Strain Injury. This type of injury can range from inflammation of joints, to damaged ligaments and muscles or even hairline fractures in bones. RSI is usually caused by the incorrect use of the keyboard and mouse.
- Ergonomic keyboards: Ergonomic keyboards are designed in such a way that the strain on the hands and finger are reduced.
- Touch typing: Learning to touch type can help reduce strain as it distributes the work evenly between the fingers. Users who can touch type also tend to use far less force when striking the keyboard.
- Mouse mats (pads): Mouse mats or pads are available with a cushion for the wrist to rest on. Repeated clicking of the mouse buttons can lead to inflamed finger joints. Resting the wrist on the cushion reduces this effect.
- Rest: Take regular breaks to rest the muscles and joints.
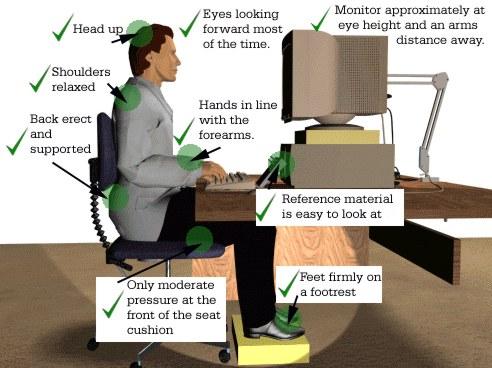
Desks and chairs
- Height and position of chairs: The height and position of the chair is an important factor in reducing strain. These should be adjusted so that:
- the feet can rest flat on the floor. This maintains blood circulation.
- the thigh is horizontal to the floor.
- the head can be kept upright in line with the spinal column. If the chair is too high, the head will be bent. This will in turn cause backache.
- A chair with adjustable height will allow you to find the most appropriate and comfortable height for your build.
- Posture: The back should be slightly bent forward. Sitting rigidly upright for long periods can cause stress in the back and shoulders.
- Support: There should be support for the lower back to avoid sitting in a hunched position.
- Rest: It is important to get up and move around on a regular basis. Ideally should do some stretching exercises to help relax tense muscles.
- Height of the desk: A common problem is having a desk which is too high. This is largely a matter of trial and error. A good test is whether the elbows are able to rest comfortable on the work surface.